This is an automatically translated article.
The article was advised by a Radiologist - Radiology Department - Vinmec Central Park International General HospitalDoppler echocardiography is a fairly comprehensive echocardiographic technique, which helps to accurately assess the structure, state of activity, hemodynamics,... thereby helping to orient the effective treatment of many cardiovascular diseases.
1.Overview of Doppler echocardiography
Cardiac Doppler echocardiography is a widely used method in the diagnosis and evaluation of cardiovascular diseases. Doppler echocardiography includes: two-dimensional (2D) echocardiography, venous echocardiography, cardiac tissue Doppler ultrasound, pulse Doppler ultrasound, continuous Doppler and color Doppler. This is a fairly comprehensive echocardiography technique, helping to accurately assess the working state, structure of the heart, the state of blood movement in the circulatory system and the hemodynamic state. Thereby helping to detect signs or abnormalities of the cardiovascular system. From the results of Doppler echocardiography, it is possible to orient the treatment of many cardiovascular diseases such as heart valve disease, cardiomyopathy, pericardial disease, coronary artery disease, ...
2.Treatment of heart disease by Doppler ultrasound
2.1. Aortic regurgitation Aortic valve regurgitation is a condition in which the leaflets of the aortic valve do not close properly, causing a retrograde diastolic flow from the aorta into the ventricles. Aortic regurgitation can be divided into two categories, acute and chronic. Acute aortic regurgitation is usually caused by infective endocarditis, aortic dissection, or trauma. Chronic aortic regurgitation is usually caused by thickening and curling of the leaflet margins, or by dilatation of the aortic root-annulus.
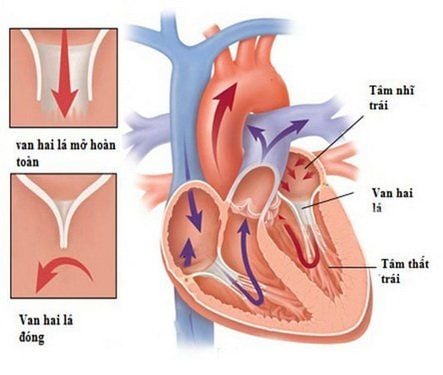
Bệnh lý hở van động mạch chủ
The leaflets are thick but still open: low posterior sigmoid valve prolapse left ventricular: prolapse The ascending aorta is > 2mm in diameter and parallel septal separation >16mm: phenomenon aortic dissection. Increase in aortic diameter >55mm: aortic aneurysm. The results of ultrasound guidance for cardiac treatment are as follows:
Orientation for medical treatment of heart disease:
When there is no left ventricular dysfunction, only diuretics are used in combination with vasodilators. When the left ventricle is large, the EF decreases, requiring more Digoxin. Grade 1-2 aortic regurgitation may not require treatment, grade 3-4 regurgitation consider vasodilators even if there are no symptoms. Nifedipine can slow left ventricular dysfunction. Orientation for surgical treatment of heart disease:
If EF < 55%, left ventricular systolic diameter > 50mm, surgery should be scheduled for the patient within 12 months even though there are no functional symptoms. Aortic valve regurgitation and no functional symptoms, no left ventricular dysfunction: patients need to have regular checkups every 3-6 months for doctors to monitor. Aortic valve regurgitation grade ≥ 3 and NYHA ≥ 3: the patient will be indicated for surgery even though there is no left ventricular dysfunction. 2.2. Aortic valve stenosis
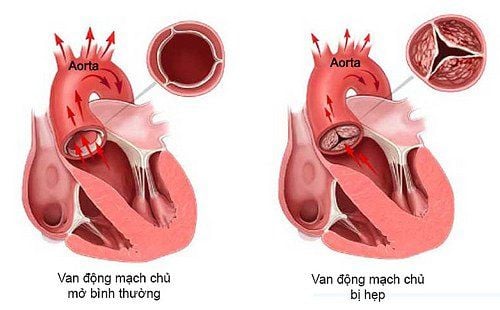
Bệnh hẹp van động mạch chủ
Aortic valve stenosis is the most common cause of left ventricular ejection fraction obstruction. Aortic valve stenosis can be congenital; due to degeneration and calcification; due to rheumatic heart disease,... Normal aortic valve opening area: 3 - 5cm2, severe aortic stenosis when the area is ≤ 30% of normal (≤ 1cm2), very severe when the area ≤ 0.75cm2.
Orientation for treatment of heart disease from ultrasound results:
Medical treatment: patients with no functional symptoms can be treated for rheumatic fever and heart failure monitoring, using low-dose digoxin and diuretics when there is no treatment. surgical event.
Surgical treatment:
Children with aortic stenosis: need surgery when mean transvalvular pressure gradient ≥ 70 mmHg Adults: need surgery before left ventricular dysfunction, when EF is severely reduced. Severe aortic stenosis and functional symptoms, patients need immediate surgery. All patients with aortic stenosis should be monitored every 6 months. When EF decreases but there are no functional symptoms, the patient also needs surgery. 2.3. Mitral valve disease The mitral valve is located between the two left chambers of the heart and helps blood flow through the heart valve when the heart rhythm is normal. Mitral regurgitation is a condition in which the mitral valve does not function properly, does not close tightly, blood cannot move through the heart or to the rest of the body effectively, causing fatigue, shortness of breath, ... Mitral valve has many forms such as acute, chronic, mitral regurgitation alone or in combination. The main cause of mitral regurgitation is rheumatic heart disease.
Echocardiography helps diagnose specific medical conditions such as:
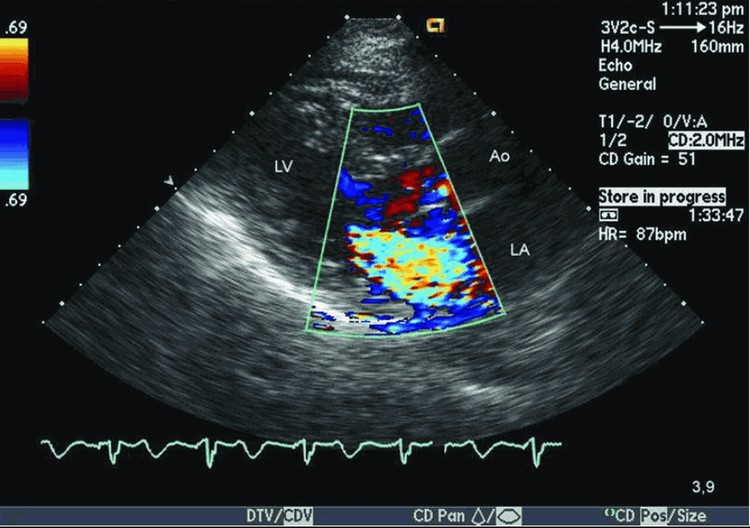
Siêu âm tim hở van hai lá
When you see that the leaflets are thickened, the movement of the posterior leaflet is reduced, the anterior leaflets are prolapsed or shortened, and the ligaments are fused together: there may be a low posterior mitral regurgitation. EF 40 - 50% is severe mitral regurgitation, much myocardial damage, EF < 40%, the risk of surgery is very high, even myocardial valve replacement may not be reversible. High-density annulus with a dorsal shadow appears on echocardiography: annulus calcification. Thick, long, prolapsed valve leaflet: Mucine degeneration. The results of ultrasound guide heart treatment are as follows:
Medical treatment: with ACE inhibitors in atrial fibrillation. Note that medical treatment does not reduce the progression of the disease, the patient needs surgery.
Surgical treatment:
Mitral regurgitation ≥ 3/4 and NYHA ≥ 3: surgery. Mitral regurgitation ≥ 3/4 and NYHA ≥ 2: follow-up, if left atrium, left ventricular enlargement or atrial fibrillation occurs, surgery is required. Elderly patient, NYHA 4, with little remission by medical therapy, combined with coronary artery disease, left ventricular diameter > 25% normal, pulmonary artery pressure > 100 mmHg, EF < 40%: poor prognosis at surgery art. 2.4. Mitral stenosis Mitral stenosis is the most common disease in acquired heart disease, accounting for about 40% of heart valve diseases. The mitral valve consists of two leaflets, the large and the small. The valvular orifice area (S) in normal diastole is 4-6 cm2. Mitral valve is called narrow when S ≤ 2 cm2 (1.2 cm2/m2 skin). Mitral stenosis is tight when S ≤ 1 cm2 (0.6 cm2/m2 skin).
Results of echocardiography to guide mitral stenosis:
Pulmonary artery pressure > 70 mmHg: risk of right ventricular failure and tricuspid regurgitation. Mild mitral regurgitation when S > 2 cm2, moderate mitral regurgitation when S between 1 - 2 cm2, severe mitral regurgitation when < 1 cm2, very severe mitral regurgitation when S < 0, 8 cm2.
Siêu âm tim hẹp van 2 lá
Orientation for treatment of heart disease from ultrasound results:
Medical treatment: Use beta blockers to slow heart rate, diuretics in pulmonary hypertension or right heart failure, anticoagulation when atrial fibrillation or Left atrial blood clot or tight stenosis with left atrium > 50 mm, digoxin when atrial fibrillation is present. However, medical treatment can only reduce the functional symptoms, not prevent the progression of the disease.
Surgical treatment:
Valve dilation surgery - valve repair when the valve damage is small and when: mitral stenosis is tight; Severe mitral stenosis and new complications of atrial fibrillation; Severe mitral stenosis and NYHA ≥ 2; have an embolism; with pulmonary hypertension. Valve replacement: when the valve is damaged a lot and NYHA ≥ 3. Doppler echocardiography is a comprehensive ultrasound technique that can evaluate many medical conditions to have an effective treatment regimen.
Currently, the Cardiovascular Center at Vinmec International General Hospital is equipped with a modern echocardiogram system and equipment comparable to prestigious hospitals in the world to support doctors in treatment. cardiovascular diseases in patients. Along with that is a team of experts including experienced professors and doctors who have successfully performed many surgeries for patients with heart disease.
In addition, in order to improve service quality, Vinmec is now deploying Cardiac Screening Package - Basic Cardiovascular Examination. The examination package helps to detect cardiovascular problems at the earliest through tests and modern imaging methods. The package is for all ages, genders and is especially essential for people with risk factors for cardiovascular disease.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.