This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor II Lai Thi Nguyet Hang - Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology - Vinmec Ha Long International General Hospital.
There are many different methods of contraception today. The following article will discuss the benefits and risks of injectable and oral medications, as well as methods for choosing the right birth control method.
1. Oral contraceptives
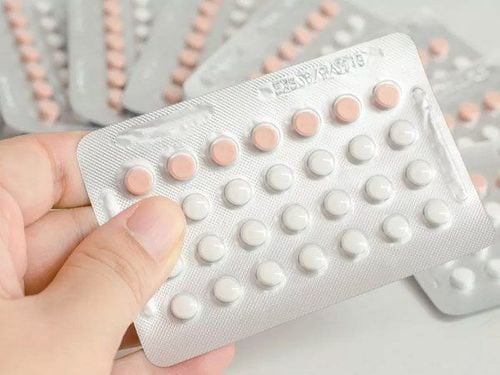
Oral contraceptives are a very commonly used hormonal contraceptive method. It is also indicated to treat menstrual bleeding, treat acne, and relieve symptoms of certain problems related to the reproductive organs.
Oral contraceptives include combined hormonal contraceptives and progestin-only pills. Combination hormonal birth control pills contain the hormones progestin and estrogen. Combination hormonal birth control pills consist of 3 weeks of hormonal pills and 1 week of placebo. During the placebo pill week, you'll get your period. Progestin-only pills are usually packed with 28 hormone pills, and even though they don't contain a placebo, you'll still get your period in the 4th week of taking the pill.
Oral contraceptives work in two ways.
First, the hormone in the pill prevents the ovaries from releasing an egg (ovulation). Without an egg, sperm cannot fertilize it. Second, the hormone increases mucus secretion around the cervix. When these substances are thick enough, sperm is prevented from reaching the egg. The hormone also thins the lining of the uterus. Once an egg is somehow fertilized, the lining is thin, making it impossible for the egg to attach to the lining and make a nest. According to Planned Parenthood, when taken as directed, the pill is more than 99 percent effective. However, most women often use the wrong pill, such as forgetting a dose or two, being late for a new pack of pills, or problems preventing her from taking the pill at the right time of day. With this improper use of the pill, the birth control pill is only 91 percent effective.
Trắc nghiệm: Bạn đã biết cách tránh thai an toàn chưa?
Có rất nhiều biện pháp tránh thai an toàn nhưng không phải ai cũng biết được điều đó. Trả lời đúng những câu hỏi trắc nghiệm dưới đây chứng tỏ bạn có kiến thức tốt về các biện pháp ngừa thai an toàn.It's also important that oral contraceptives do not protect you against STIs. Barrier measures such as condoms are recommended.
Once you stop taking the Pill, your period will return almost immediately. You may have your first normal period back up to 2 months after stopping the pill.
2. Injectable contraception
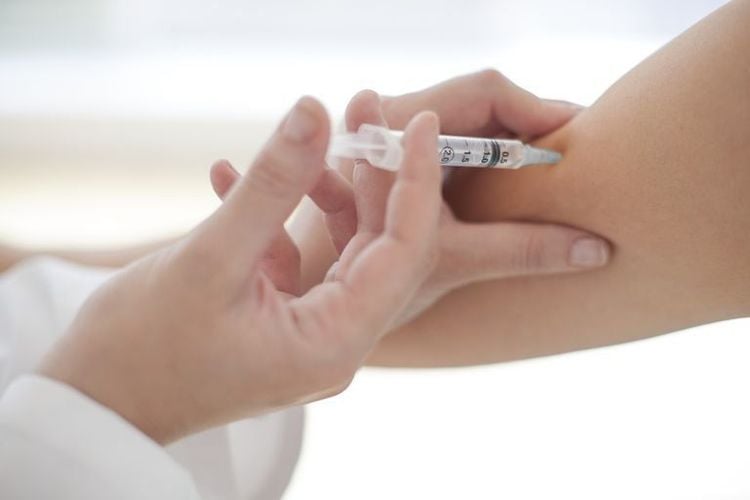
Depo-Provera contraceptive injection is a hormonal injection that prevents unwanted pregnancy for 3 months with a single injection. The hormone used is progestin.
The injectable contraceptive also works on the same mechanism as the oral contraceptive pill. It prevents ovulation and increases mucus at the entrance to the cervix
According to Planned Parenthood, when used correctly, the shot is up to 99 percent effective. To ensure the desired effect, women should inject birth control pills every 3 months as recommended. If a woman gets the injection at the right time, the pregnancy rate is 1 in 100 in a year of taking the pill.
For girls who didn't take their medication exactly as directed – often referred to as improper use – the safety rate slipped to 94 percent. Injections every 12 weeks are extremely important for preventing pregnancy.
Just like the oral contraceptive pill, the injection cannot protect you against sexually transmitted diseases. You should still use barrier measures to prevent disease!
After the last injection, your fertility and pregnancy will not return for the next 10 months. If you just need a temporary contraceptive and are hoping to get pregnant soon, the injectable birth control pill is probably not right for you.
3. Side effects of oral contraceptives and injections
Both oral and injectable birth control pills are safe for women. Like any other drug, these contraceptives will have an effect on the user's body. Both the oral contraceptive pill and the injection put a higher amount of hormone into the body. Any time the body's endocrine system is interfered with, the user is at risk of related side effects.
For oral medications, side effects include:
Vaginal bleeding, or bleeding while taking hormone pills. Chest pain, sensitive breasts, Tight breasts, Nausea, vomiting.

Most of these side effects go away on their own within 2 to 3 months of starting the medication.
For injectables, side effects include:
Irregular periods, usually thickening for 6-12 months after the first injection Increased vaginal bleeding or menorrhagia Changes in appetite Weight gain Changes in sexual habits and preferences Nausea Tension chest pain Headache Mood changes

4. Risk factors
While oral and injectable birth control pills are both very safe for most women, there are times when doctors don't prescribe them for the safety of their patients. You should not take birth control pills if:Have an inherited blood clotting disorder or a history of blood clots Have aura migraine headaches (Aura) Have a history of heart attack or serious heart problems Smoke or more 35 years old Diagnosed with Lupus Have untreated diabetes or have had diabetes for more than 20 years. You should not use the injectable contraceptive if:
Have breast cancer Are taking aminoglutethimide to treat Cushing's syndrome Have osteoporosis or fragile bones When your female friend is ready to make a decision about choosing contraception, you need visit with a specialist. With expert support, you can weigh your options and rule out inappropriate measures. Then you can find the right goal and choose the most suitable measure. If you have unusual symptoms, you should be examined and consulted with a specialist.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References: Acog.org