This is an automatically translated article.
After giving birth, the mother's body will begin to recover from the pregnancy, resting and living in a scientific way is very important and necessary for the mother to have a good health.
1. Postpartum physiology
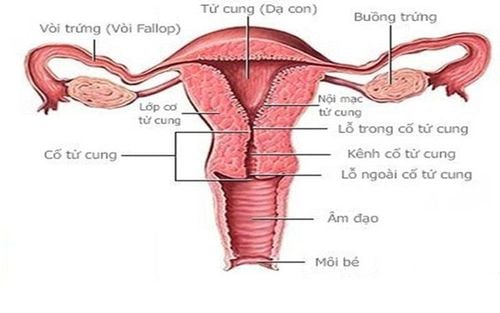
1.1 The first day after giving birth After giving birth, mothers will have physiological changes according to each period. In the first day after giving birth, women will feel tired, have abdominal and perineal pain, and have difficulty in taking care of themselves. In particular, in the first 2 hours after giving birth, a safe sphere will appear. In the next hours, there will be manifestations such as:
Contraction of the uterus Physiological occlusion in the area of placenta accumulating Vaginal blood profuse secretion of colostrum Chills after giving birth. 1.2 The first week after giving birth The first week after giving birth, a woman may feel fatigued for a long time, having difficulty in taking care of herself and her baby. In addition, there will be physiological changes such as:
Uterine contractions
Sự co hồi tử cung khiến sản phụ cảm thấy mệt mỏi trong những tuần đầu sau đẻ
Uterine contractions Secrecy Real milking and secretion The stitches at the perineum (if any) will be painful, possibly swollen, making it difficult for the mother to walk, clean and take care of her baby, ... Change in body weight Diarrhea. 1.3 Six weeks postpartum After 6 weeks, women may worry because of premature menstruation, or difficulties in lactation and breastfeeding. There are physiological changes in the mother's body including:
Uterine contractions in the first few days Vaginal discharge and secretions in the following days Heavy and regular milk production Begins to appear scars in the perineum ( if present) Changes in body mass Urinary tract and bowel movements may be disturbed.
2. Maternal health care in the postpartum period
Maternal health care in the postpartum period is a necessary issue so that the mother can quickly recover. At the same time, child care will be better. Postpartum health care is also divided by period, each stage in accordance with the physiological changes of the mother.

Chăm sóc sức khỏe bà mẹ sau khi sinh cũng chia theo nhiều giai đoạn
2.1 The first day after giving birth The mother needs to rest in the delivery room for the first 6 hours after giving birth. Then take the pregnant woman to her room. Monitor the whole condition, vital signs such as: blood pressure, pulse, uterine contractions, vaginal bleeding every 15-30 minutes within the first 2 hours, and every hour after that. Have the child lie next to the mother. Guide and help mothers with breastfeeding, breast care. Instruct and help mothers change tampons. Guidelines for safe self-monitoring of glomerulonephritis and uterine contractions after delivery. If you find that the uterus is soft, you need to gently rub yourself on the abdominal wall to stimulate the uterus to contract. Instruct the mother how to take care of the baby and monitor the umbilical cord bleeding, other abnormal signs in the baby such as: No breathing, no crying, no sucking, cyanosis,... Instructions on how to recognize the signs of abnormality usually such as: Abdominal pain, heavy bleeding, headache, dizziness, dizziness, fatigue, straining, urinary retention,... 2.2 The first week after giving birth Let the mother rest in the postpartum room. Monitor the whole condition, vital signs: Pulse, temperature, blood pressure, uterine contractions, fluid 2 times/day Put the baby to lie next to the mother. Instruct and help mothers in breastfeeding, how to take care of the breasts, wash the nipples before and after feeding, suck on each side, express all the excess milk, etc. How to wear: Wear loose, clean clothes , cool in summer, warm enough in winter. Instructing and helping mothers to eat well, eat full, drink enough water, avoid unreasonable abstinence.

Sau đẻ sản phụ cần có chế độ dinh dưỡng hợp lý để mau hồi phục sức khỏe
Make sure the mother gets enough sleep. Instruct and help mothers change tampons. Sanitize the genitals 3 times a day with cooled boiled water. Instruct and help mothers take care of the perineal stitches. Clean the perineum after each bowel movement, pat dry, remove the sutures and on the fifth day postpartum. If there is an infection, the sutures should be removed soon. Instructions on how to self-monitor postpartum uterine contractions. If you feel the uterus is soft, you need to gently rub it on the abdominal wall to stimulate the uterus to contract. Instruct the mother how to take care of the baby, monitor the umbilical cord bleeding and other abnormal signs in the baby: No breathing, no feeding, no crying, cyanosis,... Instructions on how to self-identify the abnormal signs in mothers such as: Abdominal pain, heavy bleeding, headache, dizziness, lightheadedness, fatigue, urinary retention, straining,... 2.3 Six weeks postpartum Instruct mothers on self-care such as monitoring vital signs: pulse, temperature, blood pressure, uterine contractions, daily discharge. Guide the mode of rest, work, exercise and intercourse such as: Get enough sleep, gentle exercise, gentle exercise. After 6 weeks postpartum, intercourse is possible and appropriate contraception should be used. Guidance and counseling on family planning measures. Postpartum health care needs to ensure a positive way for the mother to take care of herself and the baby. Create a comfortable environment and atmosphere for mothers after providing care, monitoring and counseling. In addition, for women giving birth by cesarean section, the health care after cesarean section is similar to that of a normal birth. However, it is necessary to pay attention to cleaning the incision to prevent infection and family planning, not to get pregnant early
3. Possible complications after giving birth
Some complications may be encountered after giving birth such as:
3.1 Immediately after childbirth Shock: Due to pain, blood loss, exertion during childbirth, or pre-existing diseases,... Postpartum bleeding : Due to uterine atony, residual placenta, genital tract trauma at birth,... Genital tract trauma at birth: Perineal, vaginal, cervical, genital hematoma,... 3.2 Days after childbirth Anemia: Due to blood loss, poor diet or infection,... Infection: In the perineum, vagina, stitches of cuts or tears of the genitals, infection in the uterus , appendages,... Veggies: Causes bleeding, infections,... Breast diseases In summary, postpartum health care helps the mother's health to recover quickly, stabilize, and improve the health of the mother. The uterus contracts more firmly, reduces blood loss and postpartum complications such as: urinary retention, chills, infection, bleeding,... When seeing abnormal signs, it is necessary to immediately notify the medical staff. to be dealt with in a timely manner.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.