This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Le Thi Phuong - Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology - Vinmec Ha Long International Hospital. Dr. Le Thi Phuong has 29 years of experience in the field of obstetrics and gynecology.A cesarean section is the surgical removal of the fetus, placenta, and amniotic membrane through an incision in the abdominal wall into the intact uterus. Compared with vaginal birth, cesarean section is applied in urgent cases, it is necessary to remove the fetus in order to reduce the risks to the fetus and mother.
1. Reasons for having a cesarean section
The reasons for cesarean section are:Abnormal mother's pelvis: If it is not the cephalothorax, the cesarean section must be performed. distorted pelvis; perform the cephalic maneuver to challenge the lower birth canal if the pelvis is limited (the fetus is not large), if it fails, there is an indication for cesarean section.
The way out of the fetus is obstructed such as: Tumor of the prostate, most commonly fibroids in the isthmus of the uterus or cervix, ovarian cysts, other tumors located on the way out of the pregnancy; Central placenta previa or placenta previa causes heavy bleeding, requiring emergency surgery to stop the bleeding to save the mother.
The mother's uterus has surgical scars in the following cases: The surgical scars on the uterine body have fibroid removal scars, the scars of the hysterectomy, the scars of the ruptured stitches, the uterine perforation, the scars of the mutilation surgery. uterine angle, uterine horn; scars from two or more transverse cesarean sections of the uterus or previous cesarean sections less than 24 months ago.
Pregnant women with dangerous medical conditions: Indications for caesarean section surgery because the mother has chronic or acute systemic diseases, if the lower birth canal can pose a risk to the mother's life (severe heart disease, high blood pressure, etc.) pressure, severe preeclampsia and eclampsia); abnormalities in the lower genital tract of the mother such as vaginal strictures (congenital or acquired), history of fistula, caesarean section; malformations of the uterus such as a double uterus (a non-pregnant uterus often becomes a tumor in the prostate), a bicornuate uterus....
Fetal problems : Indicated by caesarean section when the fetus is malnourished. /severe intrauterine growth retardation, or a large fetus > 4,000g not due to an abnormality; If the fetus has a blood type incompatibility with the mother, if the fetus is not removed, there is a risk of stillbirth in the uterus
History of pregnancy: The pregnant woman is 35 years old or older. May or may not include reasons for infertility: history of infertility treatment, rare children.

Multiple pregnancy : if the first pregnancy is not the first one.
Abnormalities in labor: Indication for cesarean section because of abnormalities in labor such as abnormal uterine contractions after using drugs to increase or decrease tocolysis to correct without success; The cervix is not dilated or dilated although the uterine contractions are synchronous, consistent with the cervical dilation; Premature/premature rupture of membranes causes labor to stop progressing and induce labor to fail.
Other complications: Indication for cesarean section for complications in labor such as bleeding because of placenta previa, placental abruption; threatened rupture and rupture of the uterus; umbilical cord prolapse while the fetus is still alive; prolapse after the fetus tried to push up but failed.
2. Notes in the cesarean section technique
2.1. Preparation before cesarean section Patient and family:Be fully consulted about the reasons and risk of complications that may occur during cesarean section, sign a written commitment to surgery Prepare from the night before surgery: Drink sedation at 8pm; fast from 10pm; enemas at 5 am on the day of surgery, cleaning the abdomen and TSM Performer:
Midwifery team preparing for surgery Anesthesia resuscitation team Surgical team Newborn care team when needing newborn resuscitation Means and equipment , drugs:
Kits, drugs for spinal/epidural anesthesia, general anesthesia Sterilized cesarean section equipment Newborn care and resuscitation equipment Medicines for resuscitation and drugs used in obstetrics, neonatology 2.2. Steps to perform cesarean section Step 1. Anesthesia:
General anesthesia or epidural or spinal anesthesia
Step 2. Intra-abdominal:
Incision below umbilicus or transverse supraclavicular line depending on the ability of the surgeon, the condition of the mother and the fetus, Incision of the subcutaneous fat, Incision of the white line between the two rectus abdominis muscles (a small incision can be made and then separated with a finger) if the surgery is longitudinal If the technical procedure If the cesarean section is transverse, the fascia is made to both sides according to that incision, separates the fascia from the broad muscle layer upwards, and then opens the line between the rectus abdominis muscles Enter the peritoneum by the surgeon pairing the peritoneum with surgical forceps. teeth, auxiliary dissection of the peritoneum on the opposite side with a toothless hemostatic forceps. The surgeon and the surgical assistant took turns releasing and re-pairing, then using a knife or scissors to open a hole in the peritoneum. Use scissors to widen the peritoneum above and below Insert wet gauze on both sides, leaving the cord out Place the valve on the bladder guard and expose the lower uterine segment Incision of the peritoneum horizontally about 2cm below the “tight line” of the peritoneum" Using curved scissors to separate the peritoneum, peel the lower segment up and down, the nose is curved upwards to avoid injury to the uterine artery Use a knife to make a small incision 1-2 cm across on the lower segment and then Use 2 index fingers to widen the incision to both sides Step 3. Remove the fetus and placenta from the uterus:
The surgeon takes the pregnancy with her left hand while the woman sucks blood and amniotic fluid (if the head is too high, it can cause pregnancy loss). Forceps can be used) After the tip is exposed outside the incision, the assistant presses the fundus of the uterus to help the baby's head come out. In case of transverse position: take the fetus by the foot of the fetus. If it is breech: take the baby by the buttocks (breast breech position) or by the feet (complete breech position) Wipe dry, Clamp the umbilicus slowly, remove the fetus to wipe clean, lay the baby on the mother's chest (if the mother is induced spinal anesthesia or epidural) Put 10 units of oxytocin into a flowing infusion bottle and let it flow rapidly to make the uterus contract well (do not inject oxytocin directly into the vein) Carry out vegetable extraction, clean the uterine cavity with big gauze. If during cesarean section, the woman is not in labor, dilate the cervix with a finger and then change the cast iron
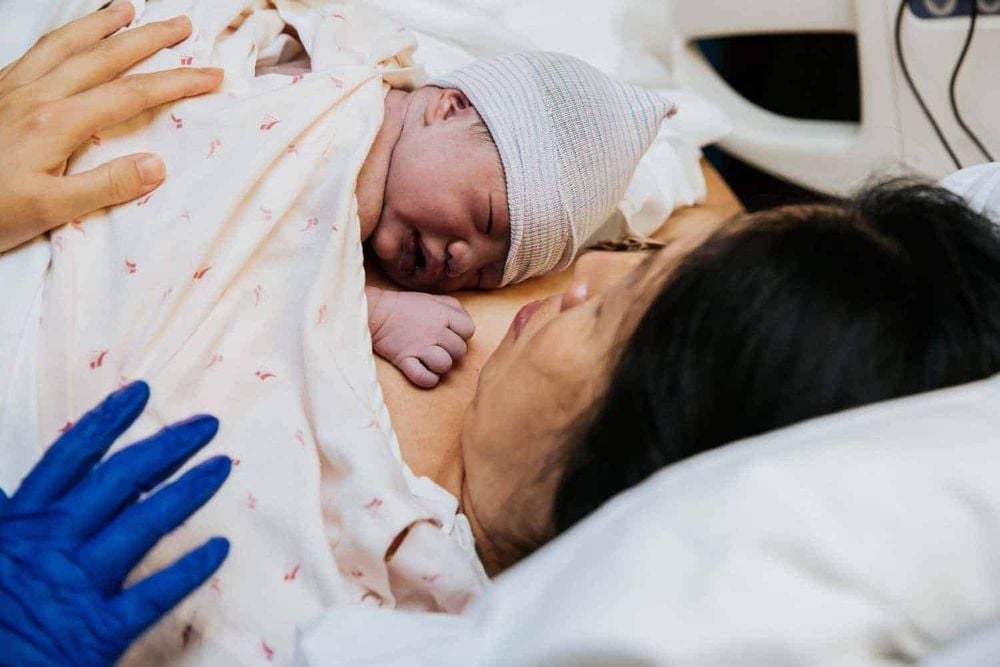

Restoring the lower uterine muscle with Vicryl 0 thread, starting with stitching the 2 corners of the uterus, avoiding missing corners Continue suturing the myometrium with continuous or separate stitches 1cm apart. , can add a 2nd layer to bury the first layer, check hemostasis Cover the peritoneal cavity with Catgut 00 suture with continuous stitches, check hemostasis Remove valve on the guard, take gauze, clean the abdomen, check Examine the 2 ovaries, 2 fallopian tubes, posterior uterine surface and posterior sac with Douglas Step 5. Abdominal closure:
Sew the abdominal wall peritoneum with Catgut 00 suture with continuous stitches Sew the 2 rectus abdominis close together. with 2-3 stitches Catgut stitches separate stitches Sew with Vicryl thread balance 0. If the fat layer is thick, sew with Catgut stitches with separate stitches or continuous stitches Sew the skin with linen thread, loose stitches or continuous stitches under the skin with small Vicryl threads Antiseptic Close the incision and a sterile bandage The surgeon keeps his hands clean to take blood from the vagina and see if the uterus is in good contraction, disinfect the vagina Wipe the blood off the patient before switching to recovery. breast
3. Care after cesarean section
3.1. The doctor's side During the first week after cesarean section, the incision is still not dry, so the obstetrician-gynecologist and midwife will take care of the mother and clean the incision.The doctor will prescribe pain relievers, antibiotics or uterotonics to avoid complications such as infection. It is completely normal to take pain medication after cesarean section, because it does not affect the quality of milk, so if the pain has exceeded the tolerance threshold, then the mother should ask the doctor for pain reliever. .
3.2. On the mother's side Nutrition:
The mother is not allowed to eat anything within 6 hours after the cesarean section, because at this time your bowel movements are at a very low level, the intestines are full of gas, the stomach is active. Weak movement, so it will be difficult to digest, making the body more tired and taking longer to recover. Therefore, mothers should only drink filtered water, sugar water, eat diluted porridge until farting. In the following days, mothers eat as usual, increase foods rich in protein and calcium, and drink lots of water to have more milk for lactation and avoid constipation; Do not use foods that are easy to cause diarrhea or allergies, cause keloid scars (chicken, beef, seafood, water spinach...). Eat foods rich in nutrients such as protein, sugar, iron, cooked fresh vegetables and fruits.

During this time, the mother should wipe her body with warm water or take a quick shower, avoiding soaking the body in the bath that makes the incision wet. After bathing, the mother should use a clean cotton ball to dry the incision, so that the open incision does not need to be covered with a bandage, and the incision is always dry and clean. The incision can be cleaned with 10% betadine or povidine solution, which helps the incision heal quickly and avoid infection. Do not apply antibiotics, betel leaves, crushed garlic on the incision. Physical activity:
As soon as the catheter is removed, the woman can get out of bed and practice walking again. Before that, mothers should move their limbs gently or sit up. For women who have experienced a difficult labor before deciding to have a cesarean section or a difficult cesarean section that loses a lot of blood, it is necessary to rest to restore energy before moving. Exercise is great and speeds up the recovery process after giving birth, but if you have a cesarean section, it will still take 4-6 weeks after giving birth to exercise again. At Vinmec International General Hospital, mothers who give birth by caesarean section in Vinmec are relieved of pain on the first day after surgery by using lumbar squamous sphincter, helping the mother to take care of her baby and recover better. This is a regional anesthetic technique performed by Vinmec to help block the pain signal before it is transmitted to the spine and to the brain, causing postoperative pain for pregnant women.
In addition to the technique of anesthesia of the lumbar squamous muscles under ultrasound guidance, in obstetrics, Vinmec also implements the technique of pudendal neuroanaesthesia to relieve epigastric and epigastric pain, helping pregnant women experience birth in a safe way. the most comfortable, whether it's a vaginal birth or a cesarean section. Thanks to these measures, mothers giving birth at Vinmec can enjoy complete pain relief, quick recovery, early return of bowel movements, early exercise and walking, no chronic pain. Evaluation results The most recent pain-relieving effect showed: ''All pregnant women who have a caesarean section do not have to use morphine, and post-partum pain is almost no longer recorded''
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.