This is an automatically translated article.
One of the treatment methods for most of those diseases is medical treatment or medication. Medicines have many benefits in curing diseases, but besides that, if used improperly and inappropriately, they can cause harm to the patient's body. In particular, for intravenous antibiotics, it is necessary to pay attention to the position of intravenous injection, injection technique, drug dose... to limit unwanted consequences.
1. Intravenous antibiotics
Any drug when put into the body can cause adverse reactions to human health, and among them, antibiotics have the highest level of danger when transmitted through the body. venous line. In fact, many patients who receive intravenous antibiotics may die soon after, possibly due to medical staff not following the rules when administering intravenous antibiotics, or because the patient is allergic to that drug.
One of the most dangerous conditions when patients receive intravenous antibiotics is anaphylaxis. This is a situation that can occur even when the patient is only given intravenous antibiotics in a very small dose when testing the drug and it is difficult to recognize the signs for timely treatment, so the patient death in a very short period of time. Some manifestations of anaphylaxis that occur in patients after intravenous antibiotics are shock, urticaria, low blood pressure, cyanosis, sweating, signs of shortness of breath, loss of consciousness. awake...
Kháng sinh được pha chế đưới dạng hỗn dịch tiêm
In addition, when giving intravenous antibiotics to patients, there may also be conditions that react to the drug on the skin, causing itching, localized or systemic red spots. Some syndromes may occur more slowly after intravenous antibiotic administration in patients such as Steven Johnson syndrome or Lyell syndrome with peeling skin and mucous membranes throughout the body. Although not as severe as anaphylaxis, these conditions, if handled slowly, can cause skin infections, blood infections, and death. Therefore, when you have any of the above symptoms, you should notify your doctor as soon as possible so that you can diagnose and have the most effective treatment plan. Absolutely do not arbitrarily buy antibiotics without the prescription of a doctor.
2. Instructions for injection/infusion of some antibiotics
Because intravenous antibiotics are absorbed by the body directly into the bloodstream, they travel throughout the body in a short time, understood immediately after use. Intravenous antibiotics do not pass through the intestines, stomach and digestive system of humans, so they will not be involved in their metabolism by digestive juices and liver. In order for intravenous antibiotics to promote their full effects and minimize harmful reactions to the body, it is necessary to strictly follow the principles of drug injection.
Some general rules of intravenous antibiotics are:
Infusion and injection equipment, ensuring 100% sterility Medical staff must perform injections according to the correct procedure, ensuring sterility during the procedure. inject. Do not allow air bubbles to enter the line, the needle... to the vein. Always keep the infusion pressure above venous blood pressure. The speed of intravenous injection must be exactly as ordered by the treating doctor. Monitor the patient closely during the infusion to detect abnormalities and promptly handle them. Do not leave the needle in place for more than 1 day and repeat the same intravenous injection site on the patient's body for 1 day.
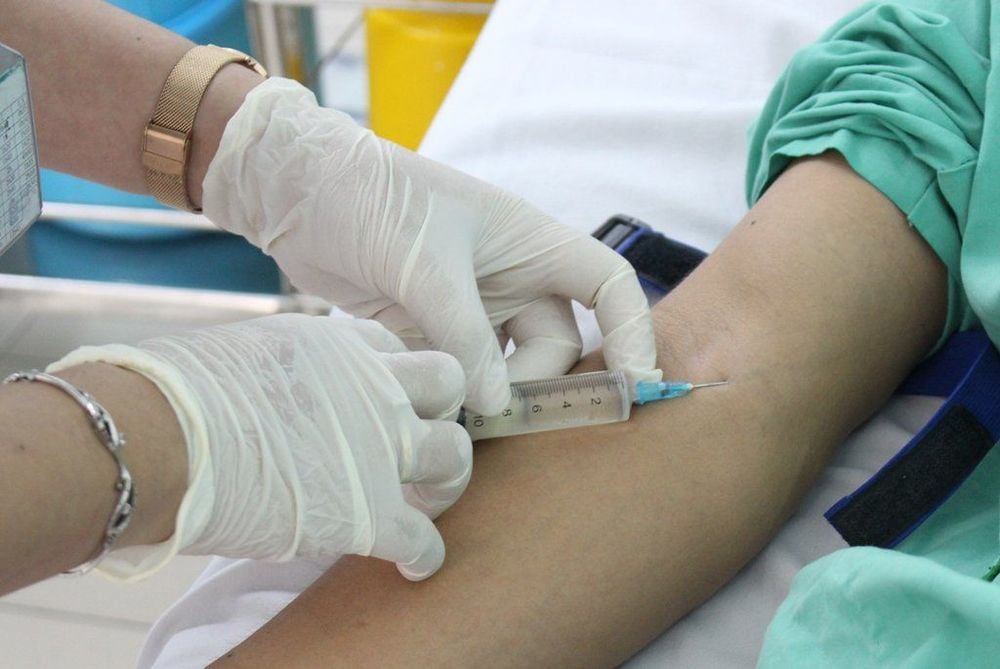
Vị trí thường được lựa chọn tiêm tĩnh mạch
Some contraindications to intravenous antibiotics are as follows:
Patients with severe heart failure or at risk of acute pulmonary edema. Patients with hypertension Some notes on intravenous injection sites are as follows:
For children, the intravenous injection site is usually a vein in the head, back of the hand, forearm, and ankle in the forearm. foot. For adults, the elbow and forearm should be flexed for intravenous injection. May be injected into the ankle vein in the foot. When using intravenous antibiotics on a patient, it is necessary to follow the following steps and ensure all steps during the injection process:
Prepare the injection site for the patient so that it is clean and well-ventilated. , have enough light and ensure 100% sterile environment. patient, dosage, drug quality, preparation date and shelf life of the drug are eligible or not. Prepare tools such as sterile trays, syringes, needles, gauze, infusion lines, Kocher needles to ensure sterility, needles can be butterfly needles or threaded needles, alcohol-soaked cotton, adhesive tape, machine blood pressure monitor, shockproof box, bean tray...
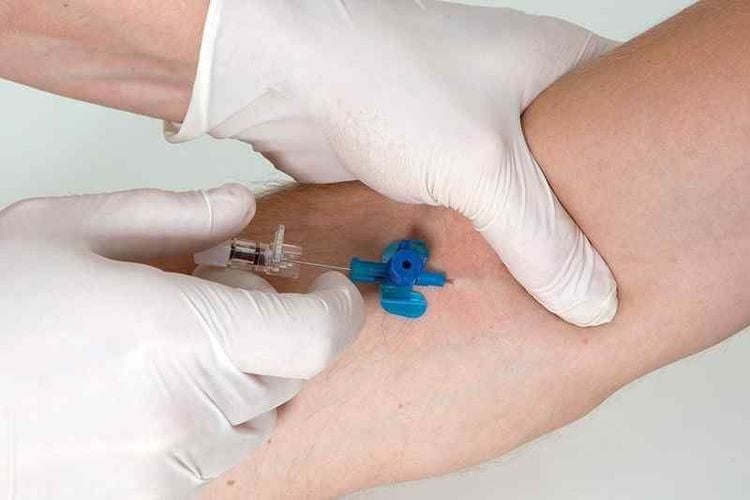
Kim luồn được sử dụng trong tiêm tĩnh mạch
Explain to the patient and family about the technique to be performed. Have the patient go to the toilet before administering the injection. Re-measure vital signs including pulse, temperature, blood pressure, and heart rate for the patient before administering intravenous antibiotics. Place the patient in the most comfortable position for the injection. Medical staff wash hands according to the procedure, disinfect with alcohol and wear gloves Put the bottle of solution on the hanger, insert the needle of the infusion line into the bottle and lock the infusion line, Open the air stopper on the bottle Aim for the fluid to start flowing into the line, discharge the first drops of the bottle to remove the air bubbles in the line, then lock the line. Place a brace and pillow under the area where the IV is intended to be administered. Select a vein for infusion, then tie a gauze cord about 3-5 cm away from that position. Disinfect the injection area from the inside out with alcohol-soaked cotton. Insert the sterile needle into the vein so that the beveled side of the needle must face up and at an angle of 15°-30°. When blood is seen entering the fluid, remove the gauze tie and begin to untie the cord. fluid for the drug to be delivered into the body's veins. Closely monitor the infusion process for timely handling.
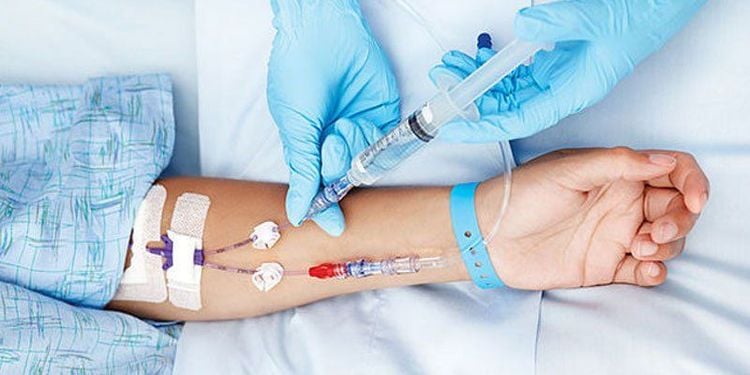
Tiêm tĩnh mạch cần đề phòng một số biến chứng có thể xảy ra
Intravenous antibiotics are a method of treating a number of diseases, but there are still dangers to health that patients and medical staff need to be aware of before, during and after the infusion. It is necessary to strictly adhere to the principles of drugs, drug doses, indications, contraindications, intravenous injection sites ... when using intravenous antibiotics on patients to limit possible risks. .
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.