This is an automatically translated article.
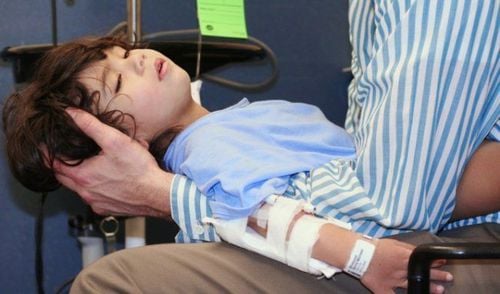
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Phan Ngoc Hai - Department of Pediatrics - Neonatology - Vinmec Danang International General HospitalFebrile convulsions are common in children 6 months - 6 years old. The vast majority of cases are completely cured. However, in some cases, it is necessary to take anticonvulsant drugs to avoid brain damage caused by lack of oxygen to the brain during prolonged convulsions. The use of drugs for children with febrile seizures requires attention to a number of important issues to prevent possible side effects.
1. Overview of febrile convulsions in children
1.1 What is a febrile convulsion? Febrile convulsion is a convulsion that occurs when there is a high fever, usually in children from 6 months to 6 years old (mainly at the age of 12-18 months) when there is a high fever, accounting for about 5%. Febrile seizures are mostly benign and do not affect the child's brain or intelligence. Children with febrile seizures need to be distinguished from epilepsy, encephalitis, and meningitis in children.1.2 Symptoms of a febrile seizure in a child The symptoms of a febrile convulsion depend on two types of fever: simple and complex. Specifically:
Febrile simple convulsion: Common. When a child has a seizure, the child loses consciousness, convulsions all over the body, the seizures usually do not last more than 2 minutes, sometimes can last up to 15 minutes. When a child has a seizure, there may be additional symptoms such as vomiting, foaming at the mouth, white eyes, and incontinence. After the seizure, the child may be drowsy but not have weakness of the limbs, after the seizure, the child is awake, without focal neurological manifestations. Febrile convulsion: Less common. When a child has a seizure, the convulsion may last for more than 15 minutes, has repeated febrile seizures within 24 hours, convulsions on one side of the body, and may have temporary weakness in an arm or a leg after the seizure. jerk.
Trẻ bị sốt cao co giật không phải bị bệnh động kinh vì động kinh có đặc điểm là co giật tái diễn và nguyên nhân gây bệnh không bắt nguồn từ cơn sốt
1.4 What to do when a child has a febrile seizure? Put the child down on the floor or bed, away from hard, sharp objects that can bump and injure the child; Tilt your baby's head to the side to make it easier for vomit or saliva to come out of the mouth; Do not put anything in your child's mouth during a seizure, including medicine to avoid the risk of aspiration; Loosen baby clothes, do not cover blankets; Reduce fever for children by using antipyretic drugs in the form of anal tablets, dosage 10-15mg/kg body weight; Pay attention to the duration of the seizure, if the seizure lasts more than 5 minutes, call 911 immediately. When the seizure ends, parents should take the child to the doctor to find out the cause of the fever. Children may need to be hospitalized for monitoring and testing if they have complex febrile seizures, are less than 12 months old with febrile convulsions, or the child has febrile seizures with unusual symptoms such as lethargy, stiff neck, vomiting,...
2. Use anticonvulsant medicine when the child has a high fever
Dùng thuốc gì dự phòng cơn co giật khi sốt cao?
Can give children paracetamol and Brufen fever reducer alternately with dose appropriate for age. In addition, it is necessary to treat the cause of the fever in the child. However, in reality, strictly controlling body temperature is not easy because the baby's body temperature can rise very quickly. In some cases, if a child has 2 or more seizures with a high fever, anticonvulsants can be given to the child. The medication used is valproate de sodium (depakine) or phenobarbital (gardenal) as prescribed by your doctor.
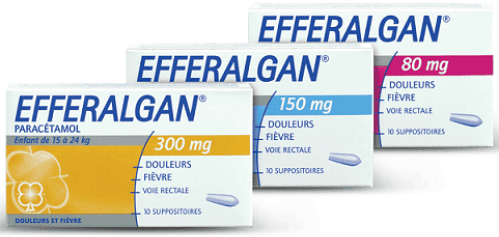
2.2 Notes when using anticonvulsants when high fever for children Paracetamol Indicated for use when symptoms of pain and fever are mild to moderate. Although not toxic with therapeutic doses, if paracetamol is used in high doses and for a long time, it will adversely affect liver function. In particular, if paracetamol is used in combination with some anticonvulsant drugs for high fever such as phenytoin, barbiturates or carbamazepine, it can increase the toxicity of the drug on the liver.
To reduce the risk of drug overdose, the dose must be strictly adhered to according to weight or prescribed by the doctor;

Paracetamol được chỉ định sử dụng khi có các triệu chứng đau và sốt từ nhẹ đến vừa.
Specifically, on the digestive system, the drug causes nausea, indigestion, epigastric discomfort, heartburn and even peptic ulcers.
The effect when combined with paracetamol has a better antipyretic effect, however, it should be used when recommended by the doctor and in the correct dose according to weight and time interval between doses
Valproate de sodium ( depakine) is an antiepileptic drug that acts mainly on the central nervous system. The drug is also indicated in epileptic seizures.
Using the drug may encounter some unwanted side effects such as drowsiness, confusion (rare), gastrointestinal disturbances in the early stages of treatment (controlled by gradually increasing the dose), weight gain due to appetite, mild thrombocytopenia, mild elevation of liver enzymes, skin allergies (rare), very severe hepatocellular destruction (usually appearing in the first 6 months of treatment, common in children) under 6 years of age in combination with many drugs).
Valproate de sodium (depakine) is especially toxic to the liver, so it is contraindicated in cases of acute and chronic hepatitis, family history of chronic hepatitis (especially drug-induced hepatitis). Most cases of liver damage in the first 6 months of treatment.
Therefore, when giving drugs to children, it is necessary to monitor liver function periodically or when there are signs such as fatigue, loss of appetite, vomiting, abdominal pain,... Need to take medicine before meals, take it in certain hours, avoid forgetting or quitting suddenly.
Phenobarbital (gardenal) This is an anticonvulsant, sedative and hypnotic drug belonging to the group of barbiturates. The drug is indicated for the prevention of recurrent febrile convulsions in young children. Side effects of this drug include somnolence, cognitive dysfunction, agitation in children, rickets and osteomalacia (due to vitamin D degradation), skin toxicity. When using the drug, it is important to follow the instructions of the doctor.
It is best when the child has a high fever but has not shown signs of convulsions, parents should give the child fever-reducing medicine. At the same time, it is necessary to pay attention to distinguish febrile convulsions outside the nervous system with high fever convulsions with neurological manifestations such as delirium, loss of consciousness, coma, continuous convulsions,... to take the child to the hospital immediately. .
Children need to go to the doctor if the convulsion is under 6 months or over 6 years old, the first seizure, the convulsion with stiff neck, bulging fontanelle, vomiting a lot, convulsions many times, recurring. All of the above cases need to find and rule out the cause.
As a key area of Vinmec Health System, Pediatrics Department always brings satisfaction to customers and is highly appreciated by industry experts with: Gathering a team of leading pediatricians: including: leading experts, with high professional qualifications (professor, associate professor, doctorate, master), rich experience, have worked at major hospitals such as Bach Mai, 108.. The doctors are all well-trained, professional, conscientious, knowledgeable about young psychology. In addition to domestic pediatric specialists, the Department of Pediatrics also has the participation of foreign experts (Japan, Singapore, Australia, USA) who are always pioneers in applying the latest and most effective treatment regimens. . Comprehensive services: In the field of Pediatrics, Vinmec provides a series of continuous medical examination and treatment services from Newborn to Pediatric and Vaccine,... according to international standards to help parents take care of their baby's health from birth to childhood. from birth to adulthood Specialized techniques: Vinmec has successfully deployed many specialized techniques to make the treatment of difficult diseases in Pediatrics more effective: neurosurgery - skull surgery, stem cell transplantation. blood in cancer treatment. Professional care: In addition to understanding children's psychology, Vinmec also pays special attention to the children's play space, helping them to have fun and get used to the hospital's environment, cooperate in treatment, improve the efficiency of medical treatment. Reference source: webmd.com; mayoclinic.org