This is an automatically translated article.
The birth of a baby is a great joy for the whole family. However, to give birth to a baby, the mother suffers quite a lot of physical influences. One of the common diseases is postpartum postpartum.1. What is postpartum?
According to modern medicine, postpartum is the period of 6 weeks from the day the baby is born. The 6-week period is defined because: During pregnancy, a woman's sex organs develop to accommodate pregnancy. After giving birth for 6 weeks, except for the breasts that are still developing to support the baby, the sex organs will gradually return to normal like before birth.
Thus, any woman after giving birth will enter the postpartum period. However, if a woman does not receive special care during childbirth, she is prone to some diseases. This group of diseases is called postpartum postpartum disease.
The causes leading to postpartum disease include:
Pregnant women are not well taken care of during pregnancy, so the body is deficient in nutrients, weak in body; Before giving birth, pregnant women suffer from fatigue, prolonged stress, the body cannot absorb nutrients, leading to exhaustion, increasing the risk of postpartum diseases; When taking care of children, it is difficult for mothers to avoid pressures that affect their psychology and health in general; Not abstaining after giving birth, getting close to your husband too soon can also cause damage to the genital organs, making the body susceptible to diseases.

Hậu sản sau sinh gây ra nhiều biến chứng nguy hiểm
2. Some notes when treating postpartum postpartum So how to treat postpartum disease like? Here are some common postpartum complications and effective treatment:
2.1. Postpartum infections Postpartum infections Postpartum infections occur in women in the first 6 weeks after birth, including infections originating from the vagina, cervix, uterus,... Common forms of postpartum infection are:
Infection of the perineum, vagina, vulva; Metritis; Inflammation of the uterine lining ; Inflammation around the uterus; Pelvic peritonitis; Sepsis ; Generalized peritonitis; Thrombophlebitis,... These are obstetric complications that occur due to many causes, which can affect the health, even the life of the mother.
Symptoms of postpartum infection include: The discharge has a bad smell, there may be fever, the uterus is slow and painful,...
Notes when treating postpartum infections include:
Do not have sex This couple after giving birth if their health has not recovered. Caused by sex too soon, it is easy to damage the vagina and reproductive organs, leading to infection and infection; Keep the vaginal area dry and clean. Should clean the intimate area with boiling water to warm, do not douche deep in the vagina to avoid injury; Avoid walking a lot, not exercising early within 1 month after giving birth; Regularly wash and change new blankets, sheets, pillows, cushions; Change underwear constantly to keep the genitals dry and avoid postpartum infections; If you see a discharge that changes color, has a bad smell, is swollen and painful, you should report it to your doctor right away. At the same time, 2 weeks after giving birth, pregnant women should actively re-examine to prevent postpartum infections, detect health problems early and have a timely treatment plan. 2.2. Postpartum fluid retention is a condition in which fluid is stagnate in the uterus and cannot be drained out. If intervened late, this postpartum disease can lead to blood clotting disorders, bleeding that is difficult to stop, which is life-threatening.
Precautions to prevent postpartum fluid retention:
Postpartum women are required to have their cervix checked to detect if there are any abnormal signs; The doctor performs cervical dilation to push the fluid inside out. This is a safe and simple method, but it should be done at reputable medical facilities with clean hygiene conditions to avoid infections and sequelae; When lying down to sleep, pregnant women should not lie cross-legged because this easily causes the fluid to stagnate in the uterine cavity, unable to flow out; Pregnant women should rest reasonably, exercise gently to help the uterus contract better, expel all the secretions. For women who have had a caesarean section, they should abstain reasonably, rest for the first day, then get up and practice walking and gentle exercise to help the uterus contract quickly and push all the fluid out.

Bế sản dịch là một trong những nguyên nhân của hậu sản sau sinh
2.3. Postpartum haemorrhage A woman is defined as having postpartum haemorrhage if the bleeding continues to be more than 500ml after vaginal delivery or more than 1,000ml after cesarean section. Postpartum haemorrhage is common in women who give birth many times, have multiple abortions, large fetuses, have incisions in the uterus,... This is the leading cause of maternal death, usually occurring within first 24 hours after birth.
Warning signs of risk of postpartum hemorrhage: The patient shows signs of shock (fatigue, pale skin, pale, thirst, small rapid pulse, low blood pressure); Massive bleeding from the uterus to the vagina, bleeding with many different levels and forms, there are cases where the blood stagnates in the uterine cavity or forms a hematoma,...
Notes on treatment Postpartum haemorrhage:
Use intravenous Oxytocin (uterine contractions); If Oxytocin is not available or does not respond to treatment with this drug, use intravenous ergometrin, a combination of Oxytocin + Ergometrin or use of Prostaglandin; Prioritize infusion of isotonic solutions before colloidal solutions during the initial resuscitation of women with postpartum haemorrhage; Use tranexamic acid to treat bleeding if oxytocin and other uterotonics fail to stop bleeding or if traumatic bleeding is suspected; Uterine massage; In case the woman does not respond to treatment with drugs that increase uterine contractions, use a balloon tampon if the bleeding is caused by uterine atony; If other measures fail, uterine artery embolization may be used if the bleeding is due to uterine atony; If measures have been applied using drugs to increase uterine contractions and intervention with uterine massage, uterine balloon tamponade but not effective, surgery can be performed; Two-handed uterine insertion can be used temporarily until other appropriate treatment measures are available in case of haemorrhage due to uterine atony after vaginal delivery; External aortic insertion may be used to treat bleeding from uterine atony after vaginal delivery (as a temporary measure until more appropriate therapy is available); Insertion of uterine gauze to treat bleeding caused by uterine atony after normal delivery; In case the placenta does not fall off spontaneously, using Oxytocin 10Ui intravenously, can be combined with controlled pulling of the umbilical cord. 2.4. Blocked milk ducts Milk duct obstruction is a phenomenon where milk cannot escape or escape in a very small amount when the baby suckles (due to insufficient sucking force, external pressure,...). If not treated in time, this postpartum disease can lead to breast abscess or fibroadenoma formation, causing infection. Blocked milk ducts can occur at any time during breastfeeding, especially in the first few days postpartum.
Symptoms of blocked milk ducts include: Breast fullness, pain; palpation of the chest reveals 1 or more hard lumps; milk is not secreted or secreted very little; pregnant women may have fever,...
Note when treating blocked milk ducts:
Maintain breastfeeding to reduce blocked milk ducts or use a breast pump to clear milk ducts. The baby should suckle on the painful breast first because at this time, the baby will suck with the strongest force, helping to clear the blocked energy rays; Gently massage your breasts while feeding or pumping; Pregnant women should rest more, drink plenty of water and eat foods that strengthen resistance to produce more milk; Warm compresses around the breasts to unclog, help milk flow more evenly; Breastfeed your baby in a lying down position to help drain the milk. 2.5. Breast Abscess One of the postpartum diseases after giving birth is breast abscess. This is a phenomenon in which inflammatory foci appear deep inside the mammary gland, mainly caused by streptococci and staphylococcus.
Symptoms of breast abscess include: High fever, chills; breast area is swollen, hot, red, painful, with soft nodules and fluid reservoirs on examination; painful axillary lymph nodes, milk mixed with yellow pus; apply ultrasound measures, test results for bacteria,...
Notes when treating breast abscess:
Mothers should rest more and do not breastfeed in the affected breast. car to avoid baby infection; The mother should eat soft food, easy to digest but still ensure nutrition to recover health soon; Gently massage the breast, apply heat and express milk to unclog the milk ducts; Use antibiotics, anti-inflammatory, pain relievers as prescribed by your doctor. If oral medications do not help, the breast with abscess can be extracted to remove pus (only for shallow abscesses). After draining the pus, a drainage tube will be placed to pump out the outbreak with an antiseptic solution and use systemic antibiotics.
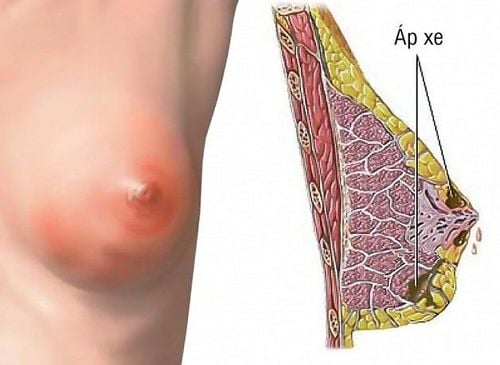
Áp xe vú là một tình trạng phổ biến của hậu sản sau sinh
2.6. Defecation, urinary incontinence Urinary incontinence, defecation incontinence is a common postpartum condition after giving birth. Urinary incontinence, especially when laughing, coughing or straining can be caused by stretching of the bladder base during pregnancy or childbirth. Women with urinary incontinence should use tampons to cope. In addition, you also need to pay attention to pain, burning or discomfort when urinating as these can be signs of a bladder infection.
Incontinence is often caused by weak pelvic muscles, perineal tears, and nerve damage in the muscles around the anus at birth. This condition is common in women who give birth vaginally and have a prolonged labor.
To fix, you just need to wait a little longer to bring the muscles back to normal, combine with appropriate exercises (according to the doctor's opinion). In case of prolonged urination and defecation, the doctor may appoint the patient to take medicine or have surgery.
2.7. Postpartum haemorrhage Postpartum haemorrhage is a condition of high blood pressure after birth. If the blood pressure does not return to normal 12 weeks after giving birth, it is defined as high blood pressure. Most cases of hypertension are idiopathic, with no identifiable cause. If not detected and treated early, postpartum hypertension can lead to many dangerous complications such as: Right ventricular dilatation, left ventricular thickening, coronary artery disease, heart failure, cerebrovascular accident, kidney failure, disease. retinal disease, proteinuria, peripheral vascular disease,...
2.8. Eclampsia Eclampsia is a complication of hypertensive disorders during the third trimester of pregnancy. Symptoms of eclampsia include: Severe pregnancy toxicity (edema, proteinuria, hypertension,...); preeclampsia syndrome (headache, dizziness, blurred vision, vomiting, epigastric pain,...); appearance of eclampsia (through 4 stages of infiltration, spasm, interval convulsion, coma). Complications of cerebral hemorrhage can occur when having a convulsion, the mother is in a deep coma for a long time, and dies.
Note when treating eclampsia:
Pregnant women who are having a seizure need to be placed on their side to avoid inhaling sputum, ensure blood circulation to the placenta. The doctor will put a piece of soft tongue brace or plastic air tube between the 2 teeth; suck fluid or food out of the glottis, trachea; Seizures can be stopped by IV magnesium sulfate 4g or diazepam 5-10mg over 4 minutes or until seizures stop. If the patient has significant renal impairment, a continuous intravenous infusion of magnesium sulfate is started, then started at 3 g/hour. Then, every 4-6 hours, check the serum magnesium level, adjust the infusion rate to maintain the required magnesium concentration. Deep tendon reflexes, respiratory rate and depth, and hourly urine output should be checked to monitor magnesium toxicity. Can be detoxified by calcium gluconate; Monitor pregnancy, blood group and cross-reactivity. Urinary catheters should be placed to monitor urine excretion, blood tests, platelet counts, liver enzymes, uric acid, creatinine, urea, and electrolytes. If the woman is hypertensive with a diastolic blood pressure above 110 mmHg, antihypertensive drugs should be used to reduce diastolic blood pressure to 90-100 mmHg; Use oxytocin to induce labor. Regional or general anesthesia may be given. Caesarean section is indicated if necessary; Magnesium sulfate infusion continues until eclampsia is resolved to manage postpartum postpartum. The infusion can last 1-7 days. 2.9. Hemorrhoids and constipation postpartum hemorrhoids and constipation are conditions that can appear during the postpartum period or during pregnancy. This condition can be aggravated by an increase in the size of the uterus, which puts pressure on the veins in the lower abdomen. The effective postpartum treatment for hemorrhoids and constipation is: Use ointments, sprays, and a diet high in fiber and fluids. Pregnant women should not use laxatives, suppositories or enemas unless indicated.
Note when treating constipation after giving birth:
Limit the use of drugs for constipation because the drug will pass into breast milk, causing the child to be passively administered drugs, causing many bad effects; Add fresh vegetables and fruits with laxative effects such as bananas, pears, apples, oranges, grapefruits, etc. to the daily menu. Mothers can eat more yogurt to add beneficial bacteria to stimulate digestion; Limit indigestible foods such as fried foods, greasy foods, thick soups, fast foods, stimulants; Eat on time, should divide meals, choose liquid foods, avoid solid foods and indigestion; Drink plenty of water and keep your spirits up as stress can cause constipation; Exercise and exercise appropriately; Go to the toilet on time, don't hold your bowels, don't sit on the toilet for a long time.

Trĩ và táo bón có thể xuất hiện trong thời kỳ hậu sản
Note when treating hemorrhoids in postpartum women:
Prioritize conservative medical treatment, use appropriate and safe drugs for women who are breastfeeding. If the disease is too severe, causing acute bleeding, ineffective with conservative treatment, embolization or necrosis of hemorrhoids, surgical intervention is required; Use of drugs to treat hemorrhoids include: vasoconstrictor drugs and increased vascular resistance, reducing the size of hemorrhoids, reducing bleeding; anti-inflammatory drugs to relieve pain, reduce swelling of hemorrhoids, antispasmodic anal sphincter, soften stools to avoid constipation; Hemorrhoidectomy is indicated for cases of mixed hemorrhoids, internal prolapsed hemorrhoids with strangulation complications, and hemorrhoids with embolism complications; Soak the anus with warm salt water for about 15 minutes/day, wash with clean water after each bowel movement, eat a lot of green vegetables, fresh fruits, drink enough water, limit eating hot spicy foods or stimulants, exercise Exercise regularly, avoid doing heavy work or standing/sitting for too long. 2.10. Postpartum depression Postpartum depression is a common postpartum illness. This is a condition in which a woman suffers from emotional disturbances, always having negative thoughts, boredom, fatigue, worries about many problems,... The disease manifests itself as mild, moderate or severe, self-limiting or does not go away on its own if not promptly intervened.
Symptoms of postpartum depression include: Body weakness, anxiety, severe pain in many places on the body for no reason, panic, stress, feelings of obsession, loss of concentration, confusion sleep disorders, loss of sex drive,...
Notes when treating postpartum depression:
Psychotherapy: Talking about the mother's condition and related mental health issues, provide emotional support and help you understand your feelings, clearly identify problems to find the best solution. Mothers can join many postpartum depression support groups to share experiences and how to deal with negative thoughts; Exercise: After physical recovery after giving birth, women should try to exercise every day (choose exercises suitable for their physical condition) to raise their spirits, increase their sense of happiness and love life; Using psycho-biotic specific probiotics to interact between the brain and the gut, improve gut health and reduce symptoms of stress, fatigue, anxiety, headaches; Using drugs to treat postpartum depression such as: Sertraline, paroxetine, nortriptyline and imipramine; In case the mother has postpartum psychosis, intends to commit suicide or murder her child, she should be immediately hospitalized for specific treatment. To prevent postpartum complications after giving birth, it is necessary to pay attention to the health of pregnant women. Careful care helps pregnant women recover quickly and avoid dangerous complications. In particular, when there are postpartum diseases, both the patient and the family need to carefully monitor the symptoms and perform the right treatment as prescribed by the doctor.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.