This is an automatically translated article.
Psoriasis is one of the causes of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. This is the accumulation of fat in the liver cells that is not caused by alcohol abuse.
1. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and psoriasis
1.1 What is non-alcoholic fatty liver disease? The liver is one of the largest organs in the body and is extremely important for our survival. The liver is responsible for producing bile, which helps break down fats and remove waste from the body. Perform drug and toxin metabolism, balance fluid levels in the body through the production of proteins that process hemoglobin and store iron. At the same time, this organ helps to convert blood ammonia into harmless urea for excretion, storage and release of glucose (sugar) when needed for energy. Perform cholesterol production and immune factors production to fight infection, regulate blood clotting
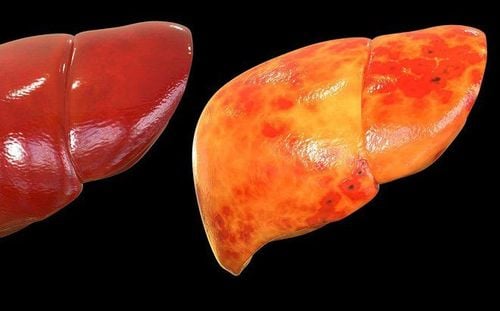
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a common disease in the world. Fatty liver disease is related to the accumulation of fat in liver cells. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) was defined after other causes were excluded such as alcoholic fatty liver, autoimmune hepatitis, hepatitis C, primary biliary cirrhosis, and Wilson's disease.
NAFLD is usually asymptomatic. Therefore, the diagnosis is only started after the patient has a blood test and the liver enzyme levels are found to be higher than normal. High levels of liver enzymes can be a sign of many liver diseases. Therefore, your doctor will rule out other conditions before diagnosing NAFLD. Liver ultrasound can also help reveal excess fat in the liver.
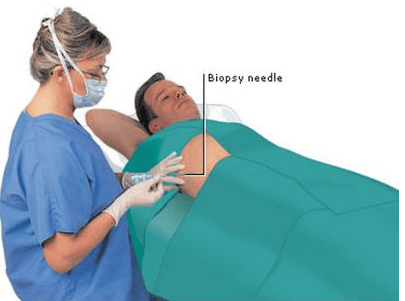
Sinh thiết gan là một trong những phương pháp chẩn đoán bệnh gan nhiễm mỡ không do rượu
Liver biopsy is one of the methods to diagnose nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Your doctor will take a small sample of liver tissue with a needle from your abdomen. The sample is studied in the laboratory for markers of inflammation and scarring.
If you have symptoms like right side abdominal pain, jaundice or swelling, see your doctor. Because if nonalcoholic liver disease is not detected and treated early, it will cause many dangerous complications. Among them is cirrhosis of the liver, which reduces liver function. Cirrhosis can sometimes progress to liver cancer or liver failure. In some cases, liver failure can be treated with medication, but usually a liver transplant is needed.
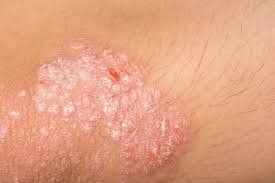
1.2 Learn about Psoriasis Psoriasis is an autoimmune disease that results in systemic inflammation in which the body overproduces skin cells. In healthy people, it takes 3 weeks to 4 weeks to grow cells in the deeper layers of the skin. As the skin matures, they slowly rise to the surface. However, in a person with psoriasis, immature skin cells reach the surface for less than a week, then they die and fall off. This leads to red, itchy patches of skin.
Psoriasis usually appears on the palms, soles, elbows, scalp or lower back. Currently, drugs can only treat the symptoms of the disease, but not completely. Therefore, treatment tends to continue throughout the patient's life.
Psoriasis can develop for a variety of reasons, including a complex link between genetics and environmental exposure. Psoriasis was previously thought to affect only the skin and joints. However, more evidence suggests that chronic psoriasis can lead to other diseases in which inflammation is important.
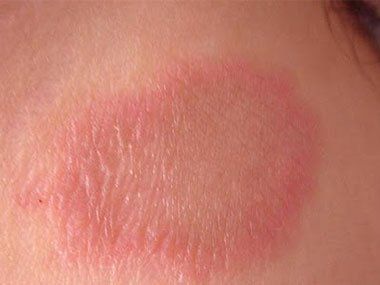
Bệnh vẩy nến có thể phát triển do nhiều nguyên nhân
2. The relationship between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and psoriasis
Patients with psoriasis may also have a number of other diseases at the same time such as: cardiovascular disease, stroke, uveitis, obesity, metabolic syndrome, gout, .. especially liver disease. non-alcoholic steatosis.
Up to 47% of patients with psoriasis develop nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Patients with concomitant nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and psoriasis have a greater risk of severe cirrhosis than patients without psoriasis and are more likely to have metabolic syndrome, higher C-reactive protein. and psoriasis area and severity index (PASI) were higher than in psoriasis patients without NAFLD. Because, both psoriasis and NAFLD are associated with metabolic conditions like metabolic syndrome and obesity
3. Measures to improve non-alcoholic fatty liver and psoriasis

Bổ sung vitamin E giúp giảm viêm
Here are some measures to help patients with psoriasis and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease improve their condition at the same time:
Weight loss: This is the most effective method to help patients control or reverse the disease non-alcoholic liver disease. Losing 10% of total body weight, even a 3% to 5% loss has been shown to improve liver health. To achieve the safest and best weight loss results, you should consult your doctor. Adjust the scientific diet: Eat a lot of foods rich in fiber; Eat more fruits and vegetables. Limit your intake of sugar, saturated fat, salt, and carbohydrates. Drinking a cup of coffee in the morning will work to reduce liver inflammation. Vitamin E supplementation helps reduce inflammation and fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Maintain exercise. Special treatment for other health problems such as; Diabetes; High cholesterol; High triglycerides (fat in the blood); Polycystic ovary syndrome; underactive thyroid, hypothyroidism; Underactive pituitary gland, or hypopituitarism Reduce stress Stay away from alcohol: Alcohol can cause fat to accumulate in liver cells and damage many other organs. If you can't stop drinking completely, keep it to a minimum, such as drinking less than one drink per day if you are a woman and less than two drinks per day if you are a man. Talk to your doctor about all the medications and supplements you take. Patients with liver disease should not take non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen and naproxen Vaccinations to prevent hepatitis A and B viruses Vinmec International General Hospital with facilities, website With modern medical equipment and a team of experts and doctors with many years of experience in medical examination and treatment, patients can rest assured that they will be examined and treated at the Hospital.
If you have a need for consultation and examination at the Hospitals of the National Health System, please book an appointment on the website for the best service.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References: ncbi.nlm.nih.gov, webmd.com, healthline.comMORE
Relationship between psoriasis and depression Genetic factors in atopic dermatitis Psoriasis is difficult to definitively treat