This is an automatically translated article.
There are two main types of lung cancer: small cell lung cancer and non-small cell lung cancer. Non-small cell lung cancer is the most common cancer accounting for 84% of all lung cancer diagnoses. For each type of disease, there will be different treatment methods.1. Non-small cell lung cancer
Non-small cell lung cancer begins when healthy cells in the lungs change and grow out of control, forming a mass called a tumor, with lesions or nodules. A lung tumor can start anywhere in the lung.A tumor can be benign or cancerous. As a lung tumor grows it can slough off the lung tumor. These cells can be carried away in the blood or carried away in the fluid (lymph) that surrounds lung tissue. Lymph flows through the lymphatic vessels into the lymph nodes (small, bean-shaped organs that help fight infection). Lymph nodes are located in the lungs, the center of the chest, and elsewhere in the body. The natural flow of lymph out of the lungs toward the center of the chest may explain why lung cancer often spreads there first. When a cancer cell moves into a lymph node vessel or to a more distant part of the body through the blood, it is called metastasis.
Types of non-small cell lung cancer: Non-small cell lung cancer begins in the epithelial cells. It can also be described based on the type of epithelial cell where the cancer begins:
Adenocarcinoma begins in the mucus-producing cells. Squamous cell carcinoma begins in the cells that line the airways. Large cell carcinoma begins in cells other than the two types described above. To help with diagnosis and treatment, it is most important for doctors to distinguish lung cancer that begins in squamous cells from lung cancer that begins in other cells.
Bệnh lý ung thư phổi cần được phát hiện và điều trị sớm
2. Statistics of non-small cell lung cancer
Non-small cell lung cancer is the most common type of lung cancer, accounting for 84% of all lung cancer diagnoses. The 5-year survival rate for people with all types of lung cancer is 19%. The five-year survival rate for men is 16%. The five-year survival rate for women is 22%. The 5-year survival rate for non-small cell lung cancer is 23%, compared with 6% for small cell lung cancer. However, it's important to note that survival rates depend on several factors, including the subtype of lung cancer and the stage of the disease.
For people with localized non-small cell lung cancer, which means the cancer has not spread outside the lungs, the 5-year survival rate is about 60%. For regional non-small cell lung cancer, which means the cancer has spread outside the lung to nearby areas, the 5-year survival rate is about 33%. If the cancer has spread to distant parts of the body, called metastatic lung cancer, the 5-year survival rate is 6%, but as new therapies work, this number is changing. .
Each year, tens of thousands of people are cured of non-small cell lung cancer in the United States. And some patients with advanced lung cancer can live years after diagnosis. It's important to remember that lung cancer is treatable at any stage, and these treatments have been shown to help people with lung cancer live longer with a better quality of life.
Hình ảnh ung thư phổi giai đoạn 4
3. Symptoms and signs of non-small cell lung cancer
People with non-small cell lung cancer may experience the following symptoms or signs. However, some people don't have any symptoms or the cause of their symptoms is just another medical condition that isn't cancer.
Fatigue Cough Shortness of breath Chest pain, if a tumor spreads to the lining of the lungs or other parts of the body near the lungs Loss of appetite Coughing up phlegm or mucus Coughing up blood Unexplained weight loss Hoarseness For For people with non-small cell lung cancer who have no symptoms, an X-ray or CT scan can be done.
Most people with non-small cell lung cancer are diagnosed when the tumor grows, takes up space, or begins to cause problems with parts of the body near the lungs. A lung tumor can also cause fluid to build up in the lungs or the space around the lungs or push air out of the lungs and cause the lungs to collapse. This will prevent oxygen from entering the body and carbon dioxide from leaving the body by blocking the flow of air into the lungs or using up the space needed for oxygen to enter and carbon dioxide to leave the lungs.
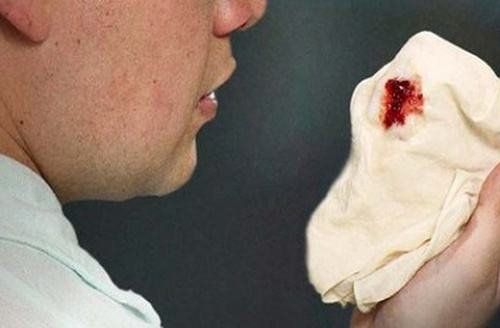
Dấu hiệu ho ra máu ở người bệnh ung thư phổi
Non-small cell lung cancer can spread anywhere in the body through metastasis. The most common sites go to the lymph nodes, other parts of the lungs, bones, brain, liver, and adrenal glands. Metastasis from non-small cell lung cancer can cause:
Shortness of breath Bone pain Abdominal or back pain Headache Convulsions Difficulty speaking
Rarely, a lung tumor can release hormones that cause problems such as low or high blood calcium levels.
Symptoms such as: fatigue, feeling uncomfortable or unwell and loss of appetite are not necessarily due to metastasis. Cancer anywhere in the body can make a person feel unwell in a general way.
If cancer is diagnosed, reducing symptoms remains an important part of cancer care and treatment. This may be called palliative or supportive care. It is usually started soon after diagnosis and continued throughout treatment.
4. The risk of non-small cell lung cancer
Factors that can increase your risk of developing non-small cell lung cancer:
Tobacco and smoking: Tobacco smoke damages cells in the lungs, causing lung cells to grow abnormally. The risk of smoking leading to cancer is higher for people who smoke a lot or smoke for a long time. Regular exposure to secondhand smoke can increase the risk of lung cancer even if the person does not smoke. Smoking marijuana and using e-cigarettes can also increase the risk of lung cancer. Asbestos: These are hair-like crystals found in many rocks and are commonly used as fireproof insulation in buildings. When asbestos fibers are inhaled, they can cause lung irritation. Many studies show that the combination of smoking and asbestos exposure is particularly dangerous. People who work with asbestos in certain things like shipbuilding, asbestos mining, insulation or car brake repair, and smoke have a higher risk of developing non-small cell cancer.
Radon: This is an invisible, odorless gas released naturally by some soils and rocks. Exposure to radon increases the risk of certain types of cancer, including lung cancer. Other chemicals: Other chemicals such as gases, chemicals in the workplace or in the environment can increase the risk of lung cancer. In some parts of the world, people exposed to coal or wood cooking flames may have an increased risk of lung cancer. In addition, smoke from diesel gas or from welding metal can also increase the risk of lung cancer. Or exposure to certain substances such as radiation, arsenic, nickel, chromium also increases the risk of lung cancer Genetics: Some people get the disease may be genetic. If you have a parent, brother, or sister with lung cancer, you may also have a higher risk of developing lung cancer.
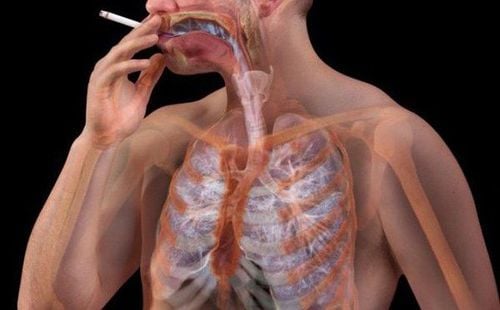
Người hút thuốc lá có nguy cơ cao mắc bệnh ung thư phổi
5. Non-small cell lung cancer stages
Non-small cell lung cancer is divided into 5 stages:
Stage 0: The disease at this point is cancer in place and has not grown into nearby tissues and has spread beyond the lungs Stage 1: Cancer Non-small cell lung cancer at this stage is a small tumor that has not spread to any lymph nodes, so the doctor can remove it completely. This stage is divided into two stages according to the size of the tumor: Tumor IA is less than 3cm and Tumor IB is larger than 3cm but smaller than 4cm. Stage 2: This stage is also divided into two stages: IIA cancer with tumors larger than 4cm but smaller than 5cm (haven't spread to nearby lymph nodes) and IIB cancer with tumors that are small in size. 5cm or less in size that has spread to lymph nodes or tumors larger than 5cm but has not spread to the lymph nodes.
Stage 3: This stage non-small cell lung cancer is classified as IIIA, IIIB, or IIIC. The stage of non-small cell lung cancer is based on the size of the tumor and the lymph nodes the cancer has spread to. Stage 3 cancer has not spread to other parts of the body. Stage 4: Means the lung cancer has spread to more than 1 location in the lungs, the fluid surrounding the lungs or heart, or distant parts of the body through the blood. Non-small cell lung cancer is more likely to spread to the brain, bones, liver, and adrenal glands.
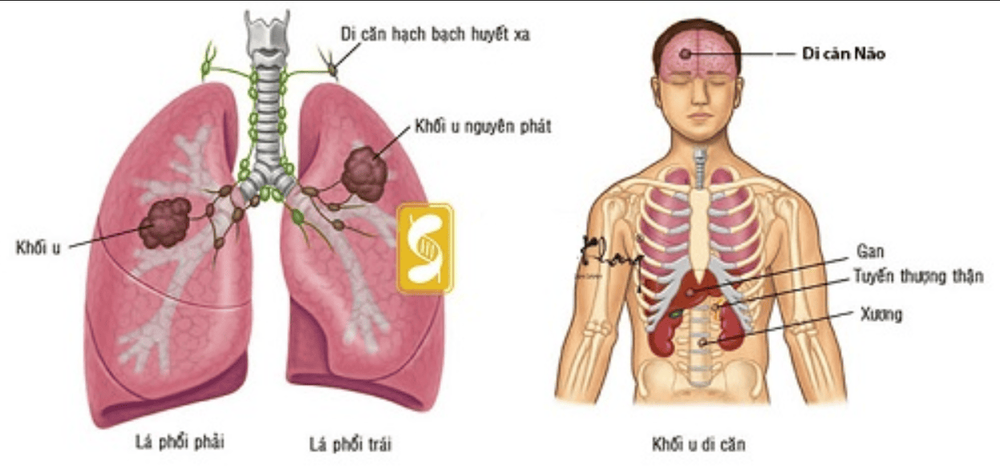
Giai đoạn 4 của ung thư phổi, tế bào ung thư di căn đến cơ quan khác trong cơ thể người bệnh
6. Prevention of non-small cell lung cancer
Lung cancer in general and non-small cell lung cancer in particular are caused by different factors. Researchers are constantly looking at these factors to possibly prevent the risk of disease. Although there is no proven way to completely prevent this disease, taking some preventive measures advised by a specialist can reduce your risk.
The most important way to prevent lung cancer is to avoid secondhand smoke. Statistics show that non-smokers have a very low risk of lung cancer. Smokers can reduce their risk of lung cancer by stopping smoking, but their risk of lung cancer will still be higher than that of never-smokers.
Detecting lung abnormalities early will increase the cure rate and prevent the disease from progressing to cancer. Therefore, it is necessary to perform periodic lung cancer screening, which can detect early signs of lung abnormalities as well as lung-related diseases, helping to detect and treat early. promptly avoid unfortunate things from happening.
Customers wishing to examine and treat lung-related diseases can directly go to Vinmec Health System nationwide or book an appointment online HERE.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: cancer.net, cancer.net