This is an automatically translated article.
Hand, foot and mouth disease in children is an infectious disease caused by enteroviruses including: coxsackieviruses and enterovirus 71. The disease is transmitted by the gastrointestinal tract, but viruses present in respiratory secretions can be transmitted directly through these fluids.
1. Manifestations of hand, foot and mouth disease in children
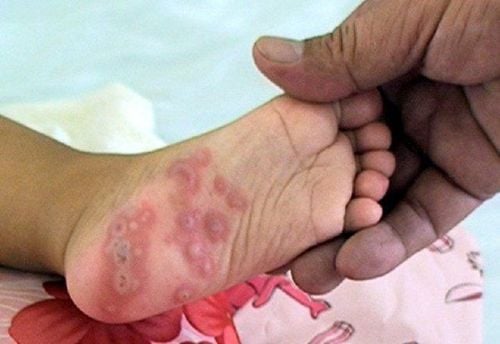
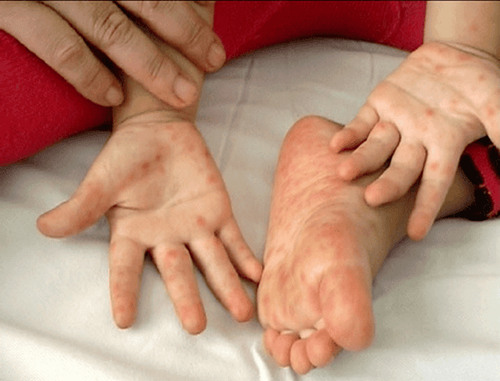
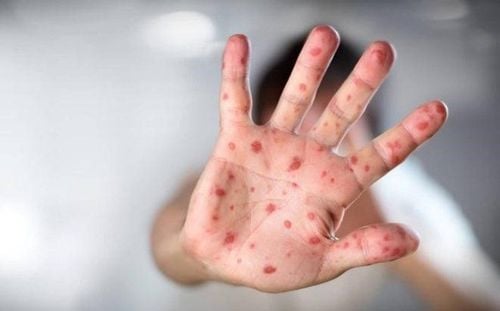
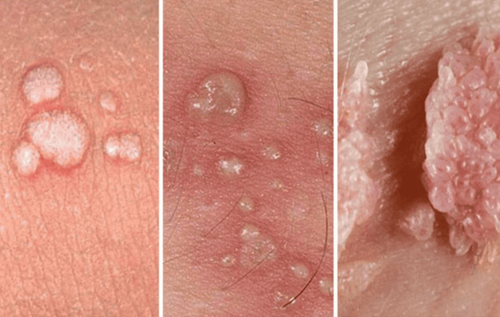
The main manifestation of hand, foot and mouth disease in children is skin lesions in the form of blisters, existing in special locations such as mouth, palms, soles, buttocks, knees. Hand, foot and mouth disease in children can cause many dangerous complications such as encephalitis, myocarditis, acute pulmonary edema and can lead to death if not detected early and treated promptly...
Communicable disease through the fecal-oral route and by direct contact, but mainly by direct contact with secretions and secretions of the patient on living utensils, toys, furniture, floors...
Bệnh chân tay miệng ở trẻ có thể gây nhiều biến chứng nguy hiểm
2. The causative agent of hand, foot and mouth disease in children
The two main groups of common pathogens are Coxsackievirus A16 and Enterovirus 71 (EV71). Disease caused by strain EV71 often causes severe neurological complications in hand, foot and mouth disease and can lead to death. Cases of severe complications are usually caused by the EV71 strain.
Hand, foot and mouth disease occurs sporadically all year round in most localities, in the South often increases from March to May and from September to December. The disease is common in children under 5 years old, especially in the age group. under 3 years old.
3. Complications can be encountered when the baby has hand, foot and mouth disease
Although hand, foot and mouth disease in children can go away on its own without intervention. However, many cases of the disease progress to severe and lead to dangerous complications. Therefore, it is necessary to actively monitor abnormal manifestations in children, because neurological, cardiovascular and respiratory complications often appear 2 to 5 days early of the disease. At that time, it is necessary to take the child to medical facilities for timely examination and treatment.
3.1. Neurological complications and signs to recognize Meningitis lesions with signs indicating that the virus has entered include: children with high fever, lethargy or irritability, delirium, headache, stiff neck, bulging fontanelles, fear of light, weakness in limb movement or possibly coma Inflammation in brain parenchyma, brain stem... with signs that the virus has invaded include: short intermittent myoclonic tremor 1-2 seconds (mostly tremors in the arms and legs, occurs when the baby is starting to sleep or when lying on his back), the child is sleepy, restless, tossing, unsteady, shaking limbs, looking backwards, nystagmus, weakness, limb paralysis, cranial nerve palsy, convulsions, increased muscle tone. Finally, the child may be comatose, this is a serious sign, often accompanied by respiratory and circulatory failure. Neurological complications in hand, foot and mouth disease are the most serious complications, threatening the patient's life. or cause irreversible brain damage.
3.2. Respiratory complications Shortness of breath: the child with hand, foot and mouth disease has symptoms of rapid breathing, chest indrawing, wheezing, laryngeal stridor, irregular breathing, shallow breathing, abdominal breathing. Acute pulmonary edema: manifests as pink foaming, shortness of breath, cyanosis, the lungs hear many moist rales, when intubated, blood or pink foam is observed.
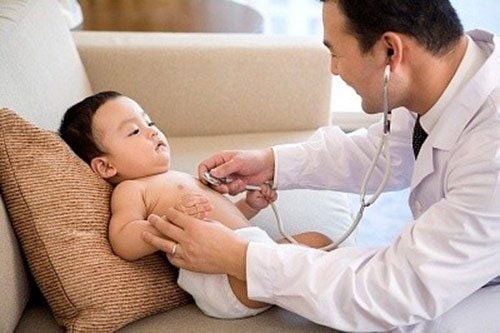
Trẻ bị chân tay miệng có biểu hiện thở nhanh, rút lõm lồng ngực
3.3. Circulatory complications: Myocarditis, hypertension, heart failure, pulse collapse In severe cases, children may show symptoms of wheezing, shortness of breath, chest indrawing, cyanosis, rapid pulse... no Prompt emergency can lead to acute pulmonary edema, heart failure, myocarditis... life-threatening. Symptoms of children with circulatory complications include:
The child's pulse is fast: >150 beats/minute Capillary filling time >2 seconds Purple veins, sweating, cold extremities, vasomotor disorders ( may be localized in an elevated blood pressure in the early stages (systolic blood pressure of children under 1 year of age >110 mmHg, children aged 1 to 2 years >115 mmHg and children over 2 years of age >120 mmHg). and unmeasured blood pressure These circulatory complications usually appear within 2-5 days of illness and require intensive treatment in the emergency department.
3.4 Other complications of hand disease Foot-and-mouth disease in children Superinfection complications Superinfection occurs when bacteria attack on broken blisters, manifesting as red, hot, painful skin with yellow or pus discharge. life-threatening but makes children uncomfortable, fussy due to fever and pain. Treat superinfection complications by using antibiotics and closely monitoring by specialists.
Complications disappear. Water Mouth sores cause pain and affect the child's eating, such as difficulty swallowing, refusing to eat, refusing to breastfeed and as a result, dehydration. To prevent this complication, parents should give the child enough water to drink and depending on the level, the child can be monitored and supplemented with water at home or in a medical facility. In addition, parents should encourage children to drink little by little and drink several times a day.
When there are signs of severe dehydration below, it is necessary to take the child to a medical facility immediately:
The child is fussy, tired, lethargic. Dry skin, wrinkles, skin pinch disappear slowly. Sunken eyes. Urinating little or no urine.
Trẻ có thể bị biến chứng viêm cơ tim khi bị chân tay miệng
4. Treatment for children with hand, foot and mouth disease
Currently, there is no specific medicine to treat hand, foot and mouth disease in children. Therefore, treatment for children is mainly symptomatic treatment such as fever reduction, pain relief, support to improve health and monitoring, early detection of complications for timely treatment and adequate nutrition.
Most cases of baby with hand, foot and mouth disease will be treated as outpatients at home. Parents are the ones to directly monitor and take the child for re-examination as soon as there are severe signs such as: High fever ≥ 39oC, difficulty breathing or breathing. weakness, startling, struggling, tremors, irritability, trouble sleeping, weakness in the limbs, convulsions or coma.
The use of Immunoglobulin is not routine, requires a doctor's prescription in certain cases. In addition, hand, foot and mouth disease is a viral disease, so antibiotics are not required unless bacteremia, meningitis or bacterial superinfection are not excluded.
The virus that causes hand, foot and mouth disease in children has not yet been prevented by specific vaccines. Therefore, the main prevention is to limit contact with sick children, clean the body and improve the health and resistance of the children.
Vinmec International General Hospital is a high-quality medical facility in Vietnam with a team of highly qualified medical professionals, well-trained, domestic and foreign, and experienced.
A system of modern and advanced medical equipment, possessing many of the best machines in the world, helping to detect many difficult and dangerous diseases in a short time, supporting the diagnosis and treatment of doctors the most effective. The hospital space is designed according to 5-star hotel standards, giving patients comfort, friendliness and peace of mind.