This is an automatically translated article.
Neonatal sepsis is an acute illness that can lead to multiple organ failure, septic shock, and high mortality. The disease needs to be detected and treated promptly to avoid life-threatening complications.1. How dangerous is bacteremia in newborns?
Neonatal sepsis is an acute bacterial disease circulating in the blood, causing diverse clinical symptoms, multi-organ failure, and septic shock. The bacteria that cause bacteremia are usually E.coli, streptococcus, Listeria, Klebsiella, staphylococcus, Pseudomonas,... Factors that increase the risk of bacteremia in babies are: Premature birth, low birth weight. ; mother has fever, infection before birth; time of rupture of membranes more than 12 hours before birth; amniotic fluid is dirty, cloudy, and has a bad smell; there is resuscitation at birth,...
Neonatal sepsis can occur as early as 1 - 2 weeks after birth. New-born babies are susceptible to neonatal infections because reproductive conditions (tools, environment, birth attendants themselves) are not hygienic, making it easy for germs to pass through the skin, umbilical cord into the bloodstream, and spread. throughout the body, including the brain, causing encephalitis - meningoencephalitis, easily leaving sequelae even after being actively treated. The mortality rate due to sepsis accounts for about 20 - 50% of the cases and this is also the answer to the question Are newborns with sepsis dangerous? In particular, septic shock is a severe manifestation of sepsis.
2. Symptoms of sepsis in infants
If more than one of the following signs is present at the same time, the newborn may have sepsis:
Signs of fetal distress ; Fast fetal rate, meconium-colored amniotic fluid; Temperature disturbances: Fever (over 38 degrees Celsius) or hypothermia (under 35 degrees Celsius); Digestive: Abortion, vomiting, abdominal distension, diarrhea, hepatosplenomegaly, gastrointestinal bleeding; Respiratory: Shortness of breath, groaning, rapid breathing, chest tightness, cyanosis, possibly stopping breathing; Circulatory: Rapid pulse, blue-violet skin, purple veins, cold skin, rash, hemorrhage, pus-filled blisters, possibly septic shock; Nervous system: Lethargy or irritability, convulsions, tremors, possibly coma, paralysis, dystonia. The fontanel bulges if there is purulent meningitis; Skin: diffuse inflammation or purulent ulceration; Scleroderma, acute renal failure, or oliguria if the infection is severe. Depending on the type of bacteria entering the blood, children will have different early or late clinical manifestations, different prognosis and different treatment methods. If the child has sepsis due to group B strep infection, the symptoms usually appear 3-4 hours after birth or as late as 1-2 weeks after birth with manifestations of pneumonia, purulent meningitis such as stopping breathing, low blood pressure,... If a child has staphylococcal bacteremia, it usually shows up in the bones and skin (infective dermatitis).
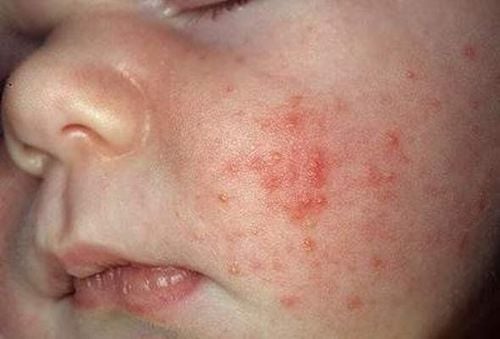
Trẻ bị viêm da, mủ nhiều
3. Diagnosis of sepsis in neonates
Test of blood count, platelets; Chest X-ray; Blood culture; Culture of infected foci: Skin, umbilicus, feces, urine; Spinal puncture if meningitis is suspected, then check for cells, proteins, sugars, and salts in the cerebrospinal fluid.
4. How to manage sepsis in babies
4.1 Antibiotics Administer antibiotics as soon as sepsis is suspected. Usually use broad-spectrum antibiotics, a combination of 2 antibiotics or based on the type of bacteria the child is infected with to use the appropriate antibiotic according to the antibiotic chart.
If the child has not been treated with antibiotics: Ampicillin at a dose of 100mg/kg/24 hours and Gentamicin at a dose of: 5mg/kg/24 hours; If the child has been treated at the lower level with the above drug but does not improve, it is necessary to combine Tacefoxym at a dose of 100mg/kg/24 hours and Amikacin at a dose of 15mg/kg/24 hours; When there are results of antibiogram: Treat according to the antibiotic chart; The duration of antibiotic treatment is 10-15 days and until the blood culture results (-) all clinical signs of sepsis disappear. In case of septicemia accompanied by purulent meningitis, the duration of specific antibiotic treatment lasts at least 3 weeks. 4.2 Supportive treatment against respiratory failure; Fully nourished; Replenish electrolytes, water, acid-base balance if there are disorders; Shockproof if available. Note: Perform emergency treatment if the child has temperature disturbances, respiratory disorders, circulatory disorders, convulsions, purulent meningitis, disseminated intravascular coagulation, coagulopathy, loss of balance. by acid-base, metabolic disorders, water and electrolyte disturbances,...
5. Prevention of bacteremia in infants
Neonatal sepsis is closely related to the conditions and environment of the child's upbringing, the time of rupture of membranes, the time of labor, the state of intervention during delivery,... Therefore, to prevent dangerous diseases This danger in children, mothers should pay attention to:Improve knowledge about pregnancy care, periodical antenatal check-ups; If there is a vaginal infection or a sexually transmitted disease, it should be thoroughly treated before becoming pregnant; Choosing a reputable hospital when giving birth, delivery tools must be sterilized, the birth attendant must ensure hygiene; If a pregnant woman breaks water early, antibiotics must be used immediately to prevent infection; When taking care of a newborn, you must wash your hands thoroughly with antibacterial soap to avoid spreading and re-infecting the baby; Use clean diapers and hats.

Rửa tay sạch sẽ, dùng tã lót và áo mũ sạch sẽ cho trẻ sơ sinh
At Vinmec International General Hospital, pediatric patients will be examined and treated for respiratory infections and bacteremia in a sterile, quiet space to help them recover quickly.
Disinfectant medical instruments, international standard clinic equipment and inpatient rooms are arranged at the hospital according to specific areas
Dedicated team of doctors with many years of experience Experience from leading pediatric hospitals in Vietnam.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.