This is an automatically translated article.
Nail fungus is a fungal infection of the nails that is rare in children and increases in frequency with age. This is a common, insidious, chronic inflammatory nail disease. So how to treat nail fungus like?
1. Causes of nail fungus disease
Nail fungus is caused by many fungal strains and has diverse clinical lesions. The most common fungal strains that cause nail fungus include:
Dermatophytes account for over 90% of nail fungus cases. Mainly caused by some strains of Trichophyton spp. such as T. rubrum, T. violaceum, T. mentagrophyte, rarely caused by E. floccosum. Yeast: Mainly caused by some strains of Candida such as C. albicans, C. tropicalis... In addition, it can also be caused by Malassezia spp. like M. furfur but rare. Non dermatophyte moulds: Uncommon nail fungus, can be caused by Fusarium spp., Aspergillus spp., S. hyalinum, H. toruloidea... Grows include:
Lives in hot and humid environments. Work frequently in contact with water. Wear rubber gloves for hours at a time. Sharing nail care tools or towels with someone who has a fungal nail infection. The nail has just been injured. Someone in the family often suffers from nail fungus. Elder. Smoke. People with diabetes. People with cancer and undergoing chemotherapy. Psoriasis disease. Poor blood circulation. Organ transplant. HIV-infected people.

Sau khi biết nguyên nhân thì các bác sĩ sẽ lựa chọn cách điều trị nấm móng
2. Symptoms and diagnosis of nail fungus like?
Common symptoms of nail fungus are:
The nail surface is rough, covered with a layer of fine bran-like scales, the nail has longitudinal or transverse stripes. The part of the nail that is infected with the fungus is yellowish, or brownish-black. Fingernails are fragile and break easily. Underneath the nail can also be damaged and the nail peeled. Initially, the patient only has 1 or 2 nails, but if left untreated, it gradually spreads to other nails. On each nail, the fungus will attack from the edge of the nail inward and will not become inflamed around the nail if caused by Dermatophytes. Or the fungus invades from the base of the nail and there is inflammation around the nail if it is caused by Candida. When the toenail inflammation is very painful, red, swollen, pus and a lot of itching around the nail. Your doctor can diagnose nail fungus based on clinical symptoms or do some additional tests. The simplest is that the doctor can cut and scrape the discolored surface of the nail and take the debris and send it to the microbiology laboratory for examination and fungal culture.
3. Nail fungus treatment regimen
Topical drugs to treat nail fungus include:
Ciclopiroxolamine 8% solution applied daily until cured. Amorolfin (loceryl) 5% applied once a week. If the fingernails are in good condition, with only minor lesions on the outer margin or mild periungitis in 1-2 nails, antiseptic and antifungal creams can be used. If the damage to many nails or inflammation of 3 or more nails, a combination of topical and oral antifungal drugs.
Oral drugs to treat nail fungus include:
Fluconazole 150 - 200 mg/week × 9 months. Griseofulvin 1-2 g/day until the nail returns to normal. Itraconazole 200mg/day × 12 weeks or 200mg twice daily × 1 week/month for 23 months. Terbinafin 250mg/day × 12 weeks or 250mg/day x 4 weeks, then 4 weeks off, 4 weeks of treatment. These drugs should not be used by pregnant or lactating women.
For nail fungus in children, use one of the following:
Fluconazole 6 mg/kg/week × 12 - 16 weeks. Griseofulvin 20mg/kg/day until cured. Itraconazole 5 mg/kg/day (50 kg) × 1 week/month, used for 2 consecutive months. Terbinafin 62.5 mg/day (40 kg) × 6 weeks. Supportive treatment of nail fungus includes
Nail erosion. Remove much damaged nail by surgery, apply 40% urea. Although nail fungus disease is not life-threatening, it reduces working capacity and causes cosmetic loss, affecting the patient's quality of life. Nail fungus progresses silently, cannot heal on its own, and can lead to nail loss.
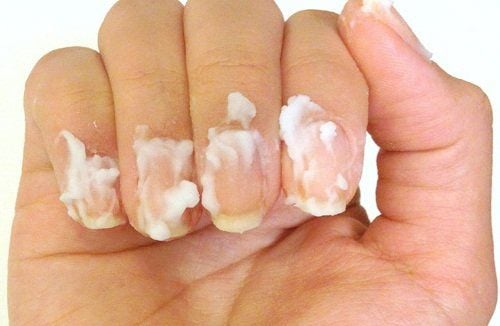
Bôi thuốc tại chỗ là một trong các cách điều trị nấm móng
4. Prevent recurrence of nail fungus
To prevent recurrence of nail fungus, if possible, change jobs or wear gloves when working to avoid wet nails. Besides, should limit contact with water with detergents such as soap, dishwashing liquid. Only contact with water when absolutely necessary such as bathing, do not wash hands and feet when not necessary, because doing so will create a humid environment for the fungus to grow again.
Although nail fungus is a disease that is not dangerous, it is unhygienic, aesthetic and very difficult to treat. Therefore, you need to treat early, timely, and with the right method to avoid severe cases that require long-term and expensive treatment. You should remember not to self-medicate without a doctor's prescription.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.