This is an automatically translated article.
Muscular dysplasia is a condition that occurs when a short segment of a blood vessel narrows due to an abnormal thickening of the blood vessel wall. When muscular dysplasia affects the blood vessels that feed the brain, it can lead to a stroke.
1. What are the main symptoms and causes of muscular dysplasia?
Muscular dysplasia is also known in English as Fibromuscular dysplasia – abbreviated FMD. In particular, muscular dysplasia can cause any effect on the blood vessels in the body, but the most common is the blood vessels to important sites such as the kidneys and brain. Not only that, muscular dysplasia can also affect the blood vessels supplying the brain, leading to a sudden stroke.
Not every case of muscular dysplasia has specific symptoms. But when the condition begins to affect blood flow to the brain, the patient will experience headaches, ringing in the ears, neck pain, dizziness or nausea.
Occasionally, the patient may be transiently blind or constantly fall into a sense of loss of consciousness. In many cases, the first symptom of muscular dysplasia is a transient ischemic attack or, more dangerously, a stroke.

Bệnh nhân bị đau đầu chóng mặt do loạn sản cơ
Causes of muscular dysplasia: According to research by scientists, there is a relationship between muscular dysplasia and other genes, hormones or factors, but the main cause of this disease has not been found. Groups of people at high risk for muscular dysplasia:
People who have a habit of smoking, regularly use stimulants that are dangerous to human health High blood pressure People with relatives with dysplasia product
2. Diagnosis of muscular dysplasia?
There are many tests being used in medical facilities and specialized clinics in our country to support the diagnosis and treatment of muscular dysplasia, but perhaps the most commonly used are 2 method below:
2.1 Duplex ultrasound A duplex ultrasound is a test used to check the speed of blood as it travels through a blood vessel. If the patient is suffering from muscular dysplasia, the velocity of the blood will increase rapidly as it passes through the areas narrowed by the thickened blood wall caused by the muscular dysplasia.
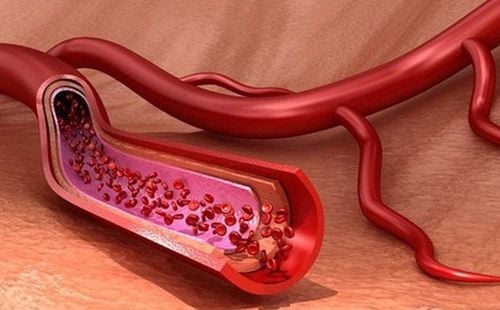
Vận tốc máu trong mạch sẽ bị tăng lên do loạn sản cơ
2.2 X-ray tomography of the blood vessels This test usually involves injecting a contrast agent into the patient's body, entering the areas of blood vessels that are affected by the muscular dysplasia. This substance plays the role of emitting light when it encounters X-ray rays, helping the area to light up and show sharp images inside the blood vessels.
Usually, the most typical shape of blood vessels harboring muscular dysplasia appearing on a CT angiogram will be a “bead” because bright areas in a CT scanner or CAT scan are all imaged. like a string of beads.
3. How is muscular dysplasia treated?
Here are the most commonly used treatment techniques to help promote the dilation of blood vessels carrying muscular dysplasia, readers can refer to:
3.1 Angioplasty through During this procedure, a special wire called an "angiographic catheter" is quickly inserted into the blood vessels in the anus and into the areas where the blood vessels are growing. narrow. At that time, the balloon that acts as a connection to the tip of the catheter will be slowly inflated, and begin to expand in the area of the narrowed blood vessel.
In many cases, a specially constructed wire mesh called a stent will also be placed in those areas to prevent the patient's blood vessels from narrowing again.
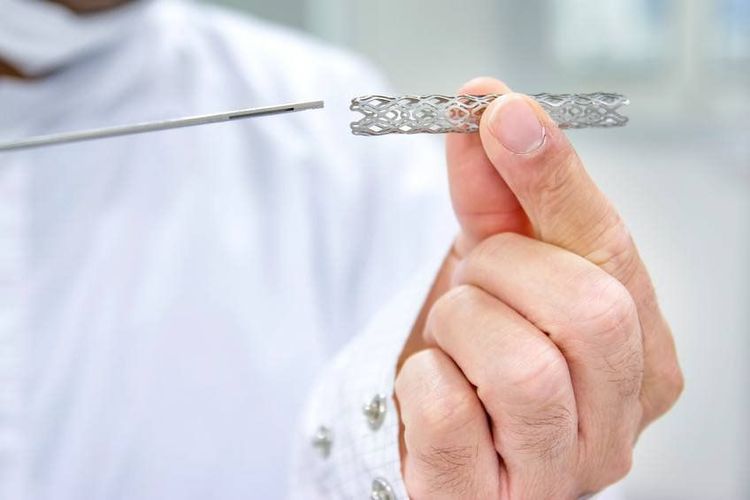

Sử dụng stent để nong mạch vành qua da
3.2 Excision and suture Is a surgical procedure to remove the part of the blood vessel with muscular dysplasia.
3.3 Grafting This is also a surgical procedure to remove diseased parts of blood vessels and replace them with another small piece of a vein, usually from a vein. foot.
3.4 Removal of the inner carotid artery This is a method used to help widen the area of the carotid artery when it is narrowed due to diseases, and one of them is muscular dysplasia. This surgery will remove the area of the narrowed blood vessel.
Customers can directly go to Vinmec Health system nationwide to visit or contact the hotline here for support.