This is an automatically translated article.
The diagnosis of pregnancy requires a multifaceted approach, using 3 main diagnostic tools. This is the history and physical exam, laboratory evaluation, and ultrasound. Now, doctors can use all of these tools to diagnose and monitor pregnancy at an early gestational age and help rule out other conditions.
1. What is early pregnancy monitoring?
Monitoring early pregnancy in the womb of pregnant mothers or having an early pregnancy in the uterus means that a new fetus is formed at a very early stage. Through ultrasound, the structures inside the gestational sac have not been clearly observed, the gestational age has not been determined, usually less than 4 weeks of age.
During pregnancy and during labor, healthcare professionals will want to check on your unborn baby's health. This is done by checking the baby's heart rate and other functions. Fetal monitoring is a very common procedure.
Monitoring can be done in 2 ways. It can be done outside of your belly (external monitoring) or can be done directly on the baby while in your uterus (internal monitoring):
External monitoring: This can be done with a different shaped stethoscope. It can also be done using Doppler. This is an electronic instrument that uses sound waves and a computer. Internal monitoring: A small electrical wire (electrode) is placed over the baby's head while he is in your uterus. Fetal heart rate monitoring (fetal heart rate) is used to check the rhythm and rhythm of heartbeats. It looks for any increase or decrease in the baby's heart rate. It also checks how much the baby's heart rate changes. The average fetal heart rate is between 110 and 160 beats per minute. The fetal heart rate can change as the baby responds to conditions in utero. An abnormal fetal heart rate or pattern could mean that the baby is not getting enough oxygen or has other problems. An abnormal pattern may also mean an emergency cesarean section (cesarean section) is needed.
2. Normal ultrasound image to monitor early pregnancy in the uterus
Fetal ultrasound is a sophisticated imaging technology that uses high-frequency sound waves to monitor early pregnancy in the uterine cavity. The image is generated based on the different echogenicity of the targeted object as well as the tissue between that object and the ultrasound transducer.
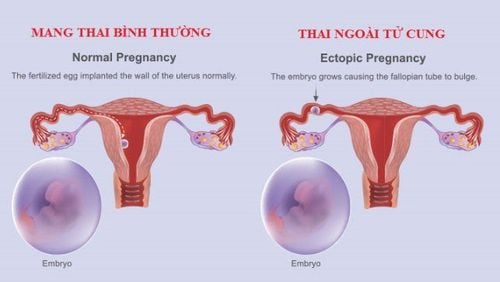
In the early stages of pregnancy, the main use of ultrasound is to determine the presence of a fetus in the uterus. Alternatively, ultrasound may be used to evaluate for the presence of ectopic pregnancy (ectopic, fallopian tube, adnexa, cervix, abdominal cavity, cesarean section), free fluid in pelvis, uterine and adnexal pathology, fetal cardiac activity and rhythm, miscarriage, or gestational trophoblastic disease.
Two anatomical approaches are used to visualize a pregnancy by transvaginal and transabdominal ultrasound. Transvaginal ultrasound is performed using a high-frequency inline transducer inserted into the vagina and visualizes the pelvic organs through the cervix. Conversely, transabdominal ultrasound using lower frequency sound waves can also be used to visualize the pelvic organs but is done by looking through the abdominal wall with a curved transducer. The difference in frequency, coupled with the anatomical position of the transducer during examination, results in the transvaginal approach being superior for earlier pregnancy visualization as well as adnexal assessment.
It is paramount that privacy is provided to the patient when using either form of ultrasound. A curtain should be placed to cover any external anatomy without having to be exposed for patient comfort and privacy.
3. Early pregnancy monitoring by Beta-HCG . diagnostic test
A beta-HCG test that gives a positive pregnancy test will help with further evaluation, especially if the patient has abdominal or pelvic pain and/or vaginal bleeding. The possibility of ectopic pregnancy must be considered, a potentially life-threatening condition that occurs in about 2% of reported pregnancies.
A single beta-HCG level does not provide any information about intrauterine pregnancy. Urgent ultrasound should be performed for any pregnant woman with suspected ectopic pregnancy. Ultrasound may reveal an intrauterine pregnancy, an ectopic pregnancy, findings suggestive of an ectopic pregnancy (solid or complex adnexal mass), or may be indefinable.
If the ultrasound results are inconclusive, the "discrimination zone" can be used to help clinically correlate the ultrasound results with beta-HCG levels. The discriminant region is the approximate beta-HCG threshold that can normally be identified by ultrasound in utero. Transvaginal ultrasound is highly sensitive when beta-HCG levels are above 1,500 mIU/mL, whereas the threshold is much higher when using the transabdominal approach (approximately 6,000 mIU/mL). If a symptomatic patient is ultrasonographically inconclusive with beta-HCG on the "differentiated zone", the diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy must be considered and consulted with an obstetrician-gynecologist.
If the patient does not have a beta-HCG level on ultrasound that is less than the differential region and the patient is hemodynamically stable, without significant pain or vaginal bleeding, then they should be instructed to measure beta-HCG levels. Repeat serum after 48 hours. If this level of repetition increases, ideally doubling every 48 hours, this is highly suggestive of a normal pregnancy. Conversely, if beta-HCG levels decrease or do not double within 48 hours, a miscarriage or unsuccessful pregnancy should be suspected.
4. Significance of early pregnancy monitoring in the womb
Pregnancy test is one of the most important tests to perform early intrauterine pregnancy monitoring for any woman of childbearing age who has problems: pelvic pain, amenorrhea, bleeding vaginal or hemodynamically unstable. This is a highly sensitive and specific test, but limitations should be understood. If the pregnancy is positive, it should be considered as an ectopic pregnancy.
Ultrasound is a widely used diagnostic imaging tool in early pregnancy due to its accuracy and safety advantages for both the patient and the fetus. Information on ultrasound should be interpreted in light of the patient's clinical setting and beta-HCG levels.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.