This is an automatically translated article.
Postpartum complications can occur in the uterus, in the placenta, in the cesarean section or in the perineum. Some common postpartum complications related to the placenta such as retained placenta, retained placental membranes, bleeding after placental abruption...1. Common complications after giving birth are related to the placenta
Giving birth is an arduous and not easy process. In addition to ensuring the health and safety of the life of the mother and the baby, in each birth, it is necessary to pay attention to monitor the possible risks of postpartum complications on the mother and baby.On the mother's body, postpartum complications can occur at the perineal incision (for normal delivery), at the cesarean section (for cases of cesarean delivery), or complications in the uterus. and complications related to the placenta.
Common clinical complications after birth such as:
1.1 Remaining placenta or placental membranes in the uterine cavity The placenta is the link between the mother and the fetus, usually being pushed out within the first half hour. postpartum by the force of contractions of the uterus. However, in clinical practice, due to many factors, the placenta is not completely pushed out, but a part remains in the uterine cavity. That is called the residual phenomenon.
Missing placenta can lead to inflammatory problems in the uterus or even cause postpartum haemorrhage, which can lead to death.
Manifestations of retained placenta : Dull, continuous abdominal pain with a feeling of tightness, poor uterine contraction, blood loss may lead to dizziness and fatigue, severe may shock.
Treatment:
Place an intravenous line, give pain medication if the mother has a lot of pain. If there is no associated bleeding: manage uterine control, push placenta and residual membranes out of uterine cavity, inject uterine contractions and systemic antibiotics. If the pregnant woman has haemorrhage: conduct resuscitation for the mother, combine with mechanical hemostasis, control of the uterus, injection of uterine contractions and use of antibiotics to prevent infection.
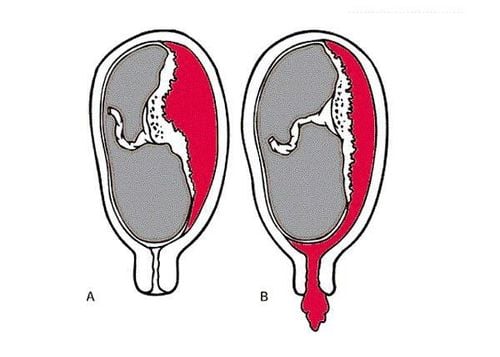
Sót nhau có thể dẫn tới các vấn đề viêm nhiễm trong buồng tử cung
Manifestations: placenta is still attached to the uterus, there is no bleeding. In some cases, the placenta is partially implanted, after the pregnancy is delivered, the placenta is not completely detached, so it may be accompanied by more or less bleeding depending on the wide or narrow area of the placenta. If it is a full-fledged placenta, it usually does not cause bleeding.
Treatment:
Carry out placental abruption, control the uterus. If bleeding occurs, mechanically stop the bleeding by massaging the uterus. Use uterine contractions. Anti-infective antibiotics. If there is bleeding in the partial placenta, or if the total placenta is present, a hysterectomy is required. Intensive resuscitation if the mother shows signs of respiratory failure, organ failure. 1.3 Hemorrhage after a placental abruption Hemorrhage is an intense bleeding from the vagina to the outside, usually occurring within 24 hours of giving birth. Hemorrhage is one of the most common obstetric complications in clinical practice, and is the leading cause of death in the majority of postpartum cases.
Postpartum hemorrhage occurs because the mother's uterine muscles do not contract after birth, due to uterine malformations or large fetus, there are fibroids in the uterine cavity... Hemorrhage can also be caused should be by vegetable cake.
Manifestations: postpartum bleeding continuously in the first 24 hours accompanied by other manifestations such as rapid pulse, low blood pressure, dizziness, pale skin, sweating, thirst... Postpartum haemorrhage may occur. may lead to the risk of shock due to hypovolemia, renal or multi-organ failure, and death.
Treatment:
Ensure vital indicators for pregnant women: pulse, blood pressure, temperature, breathing rate, immediately establish an intravenous line. Intensive resuscitation if the pregnant woman has severe symptoms such as respiratory failure, circulatory failure, multi-organ failure... Carry out mechanical hemostasis by a number of techniques such as: uterine massage, abdominal aortic block , two-handed ectopic compression, or internal or external compression. Monitor the uterus to treat blood clots inside the uterine cavity and residual membranes if present. Give oxytocin, if there is no response, you can give misoprostol or ergometrin. Antibiotics to prevent superinfection.
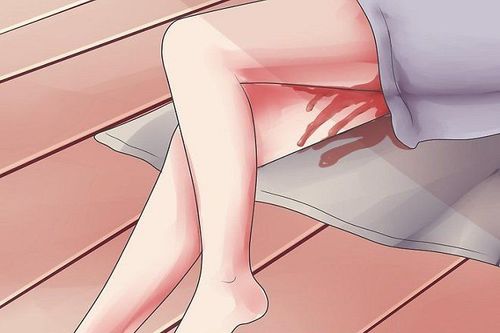
Băng huyết là hiện tượng máu chảy dữ dội từ trong âm đạo ra ngoài, thường xảy ra trong vòng 24 giờ sau sinh
2. Prevention of complications after birth
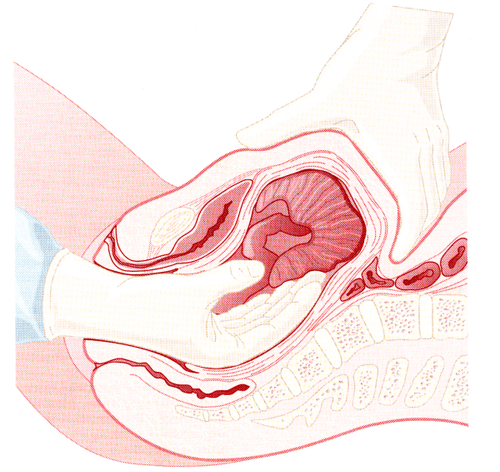
In order to avoid complications related to the placenta after birth, every birth, especially a vaginal birth, needs to be checked for placenta. Checking vegetables is an operation that helps to observe and evaluate all problems of the placenta, including:Checking the placenta. The following issues should be observed:
Observe and assess whether the placenta is sufficient or lacking. Observe and check the location of the amniotic fluid hole. The attachment site of the umbilical cord is adjacent, plaque or central. Blood vessels from the base of the umbilical cord to the placenta so that accessory placentas can be detected. For multiple pregnancies, the membrane dissection should be observed to assess the number of placentas. Check the veggie Check the veggie zones from the center to the periphery to see if any are missing. The quality of the placenta is an important factor to help predict the risk of later diseases such as infarcts, fibrosis or calcium deposits on the placenta. Checking the umbilical cord The condition of the umbilical cord knot. Examine the umbilical cord cross-section to see the umbilical blood vessels. Measure the length of the umbilical cord. Besides checking the umbilical cord, mothers need to note a few things as follows to limit complications during and immediately after birth:
Ensure the health of both mother and baby, provide adequate nutrition during pregnancy. Go for regular antenatal check-ups as prescribed. Giving birth in a reputable and professional medical facility.

Đi khám thai định kỳ để hạn chế những tai biến sản khoa có thể gặp
At Vinmec International General Hospital, there is a package maternity service as a solution to help pregnant women feel secure because of the companionship of the medical team throughout the pregnancy. When choosing Maternity Package, pregnant women can:
The pregnancy process is monitored by a team of qualified doctors Regular check-up, early detection of abnormalities Maternity package helps to facilitate the process. birthing process Newborns get comprehensive care
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.