This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Pham Thi Yen - Obstetrics and Gynecology Department - Vinmec Hai Phong International General HospitalThe breech position has the most common ratio among the abnormal fetal positions. The breech delivery technique also has many different and more complicated features than the breech position. Therefore, it is necessary to master the things you need to know about breech delivery below to have a safe labor for both mother and baby.
1. What is a breech fetus?
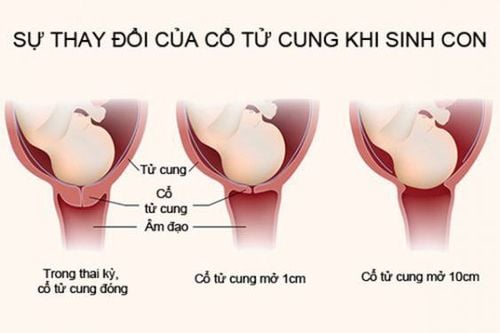
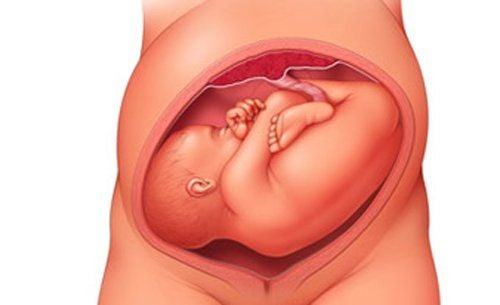
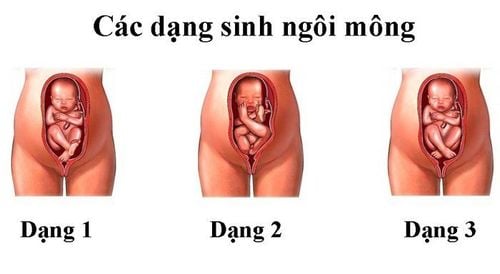
A fetus with a breech or breech position is a vertical position with the head on top, the buttocks or legs below. There are two types of breech position: (1) full breech position with the buttocks and lower limbs flexed, the fetus is sitting cross-legged in the uterus, and (2) breech position is lacking when only the buttocks or legs or head are present. pillow when entering the throne.
The breech position accounts for only 3 to 4% of the total births, much less common than the crown but is the most common abnormality compared to the face and forehead. In which, the lack of buttocks is more common than the full butt. Buttock lacking buttock shape is most common with fetuses over 2500g. In smaller fetuses, breech position lacking breech or leg pattern is common with similar incidence. Missing buttocks are common in people who have given birth; In contrast, the breech position is common in people who have given birth to a child.
The landmark chosen to determine the position and position in the buttock is the sacral crest. The diameter is the diameter of the femur with a length of 9.5cm. Accordingly, the buttock has four styles: the same basin, left front, left back, right front, right back, and two types of pots, left and right, horizontal.
2. Causes of the breech baby
Before the 28th week of pregnancy, the fetus is still small, the size of the head is larger than the body. Meanwhile, the uterus is pear-shaped, with the size of the uterus being quite large at the base and smaller in the lower part. So, during this time, the baby's head tends to rest at the bottom of the uterus, forming the breech position.
When the gestational age is larger, the fetus is getting bigger and bigger, the amniotic fluid is less and less. At that time, the fetal body is larger than the head and will occupy the common basilar area (the wider part), the fetus will be able to adjust itself to the right position.
Therefore, the cause of the breech position may be due to preterm labor when the fetus has not yet adjusted to the right position or there are factors that hinder the normalization of the fetus:
On the mother's side, the cause Causes may be due to the mother's uterus underdeveloped, septate, double uterus, bicornuate uterus. In addition, when the mother has tumors in the pelvis such as uterine fibroids, prostate tumors... It should be noted that the narrow pelvis is not the cause of the buttock. On the fetal side, multiple pregnancies, fetuses with malformations, especially hydrocephalus, most often lead to the breech position. On the side of the appendage is oligohydramnios, placenta previa...
3. How to diagnose breech fetus?
Pregnant women have the ability to self-identify the breech position when seeing that the fetus often tends to kick in the hypogastric region and feels a sense of pressure on one side of the lower abdomen due to the compression of the fetal head. Looking at the abdomen, the uterus is still ovate-shaped, along the longitudinal axis, but the most clear sound of the fetal heart is at the level of the belly button or above the navel.
Touching the upper pole of the fetus at the bottom of the uterus is the head of the fetus, in the form of a round, solid mass, with obvious signs of shaking. The lower pole in the lower part of the uterus is the fetal rump, which has the form of a soft, irregular mass.
During labor, vaginal examination when the cervix is dilated will not show a hard round area like the crown but will see the top of the sacrum, the area of the buttocks or the legs. If the water has broken, it will be more palpable with the top of the sacrum, the buttocks with the anus, and the fetal genitals in the middle. If you accidentally put your finger in the anus, you will feel a squeeze.
However, ultrasound is always the commonly used means of determining the breech position, single or twin pregnancy as well as the size of the fetus in order to choose the appropriate delivery method.
4. Mechanism of birth and how to handle it when giving birth to a fetus in the breech position
There is an important difference between first-born and breech-birth. In cephalic birth, when the largest part of the baby's head has been delivered, the rest of the fetus will be born easily. On the contrary, while in the buttocks, following the buttocks, the rest of the parts will get bigger and bigger. Accordingly, breech delivery will include three separate stages including butt delivery, shoulder birth and finally first birth.
However, before going into labor, at the 36th week of pregnancy, women with breech position will be considered to apply the classic procedure of fetal rotation to turn the breech position into a favorable position. Since the pregnancy may continue to normalize into the final weeks of pregnancy, early rotation is not necessary.
In people who have given birth to a premature baby, the breech position is often due to mechanical causes, so the perioperative rotation is often unsuccessful and poses many dangers. In contrast, in pregnant women, it is often easier to rotate the fetus, but it is difficult to fix the fetal position after rotation due to the flaccid uterine muscle tone.
Moreover, the birth of a butt in a child is not as ominous as a child giving birth. Although ectopic pregnancy can face complications such as umbilical cord wrapping, knotted umbilical cord, placental abruption..., many statistics have shown that this procedure does not cause maternal morbidity rates. and the child in the breech increased significantly.
Besides, pelvic irradiation at the end of pregnancy is a necessity, especially in cases where the breech position tends to result in vaginal delivery. In addition, ultrasound is also needed to accurately assess the indications for natural birth through estimating fetal weight, assessing malformations, if any.
When deciding to have a vaginal delivery, there are three ways to give birth:
Natural birth, ie birth without intervention. Partial intervention. Total intervention, ie the great procedure to pull the fetus into the reverse position.
4.1. Natural butt delivery
Natural birth with the breech position is usually only applied to cases of varicocele, small fetus and dilated perineum.The birth proceeds naturally according to the mechanism of breech delivery, without any assistance, nor any surgical intervention on the fetus.
4.2. Partial intervention for the buttock delivery
A fetus with a breech position is allowed to give birth naturally to the navel, the doctor or midwife will assist in the birth of the shoulders, arms and back of the head. When the buttocks have come out of the vulva, if the umbilical cord is tight, it is necessary to gently pull the umbilical cord to relieve the tension. At this time, when pulling the umbilical cord, try not to touch the abdomen and body of the fetus.
When the shoulder is in and ready to go, assist in the delivery of the shoulder by gently lifting the fetal body towards the mother's scapula so that the back shoulder and hand are out. Then, lower the fetal body to open the front shoulder. After releasing the shoulders and arms, gently rotate the fetal body to the prone position, preventing the fetus from rotating back to the supine position.
For the cephalothorax, the midwife's hands hug the fetal pelvis, gently pulling the fetus in an downward and backward direction, at the same time with an assistant pushing on the fundus to help the posterior head bow well. Until the occipital is lowered to the lower border of the joint, the midwife will lift the fetus back towards the mother's abdomen so that the fetal head is tilted back. At this time, the chin, face, and the rest of the head will one by one come out of the vulva.
4.3. Full intervention buttock delivery
The grand operation of breech delivery in a total interventional breech delivery should be performed under anaesthesia and be prepared as a caesarean section.
Today, due to the dangerous nature of cesarean section, the indications for this procedure have been greatly limited and have been replaced by cesarean section.
5. Prognosis of a breech baby

On the mother's side, the relative prognosis is no different from that of a cephalic birth, although labor is somewhat more prolonged. However, women can experience soft tissue tear at a fairly high rate, often due to premature birth.
On the fetal side, there are often many ominous complications such as trauma, umbilical cord prolapse or umbilical cord compression causing asphyxia leading to fetal death.
In short, the breech position is the breech position, making it difficult to give birth, but that doesn't mean it can't be delivered in the breech position through the vagina. Accordingly, all actions and interventions before and during the birth need to be carefully considered, with the right technique and also at the right time to ensure safety for both mother and child.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: medscape.com; ncbi.nlm.nih.gov