This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Tong Van Hoan - Emergency Medicine Doctor - Emergency Department - Vinmec Danang International Hospital. Doctor with 10 years of experience in the field of Emergency Resuscitation.1. Overview of dialysis methods in resuscitation
Hemodialysis in resuscitation are methods performed to filter out endogenous or exogenous toxins, fluids, electrolytes,... Dialysis is performed in emergency cases of critically ill patients with impaired renal function. kidney, liver failure, severe heart failure, blood clotting disorder, acute pancreatitis, multi-organ failure,... Thanks to dialysis methods in resuscitation, the patient's survival rate is much higher than before. . The most commonly used methods of hemodialysis in resuscitation are:Emergency peritoneal dialysis 24 hours continuously. Emergency dialysis by artificial kidney technique.
2. Emergency peritoneal dialysis 24 hours continuously
2.1. Indications for 24-hour continuous emergency peritoneal dialysis Emergency peritoneal dialysis, also known as emergency peritoneal dialysis, is a method of continuous hemodialysis thanks to the exchange of certain substances between blood and dialysis fluid in the abdomen through across the semi-permeable membrane is the peritoneum. Emergency peritoneal dialysis is indicated when the patient has acute renal failure due to various causes.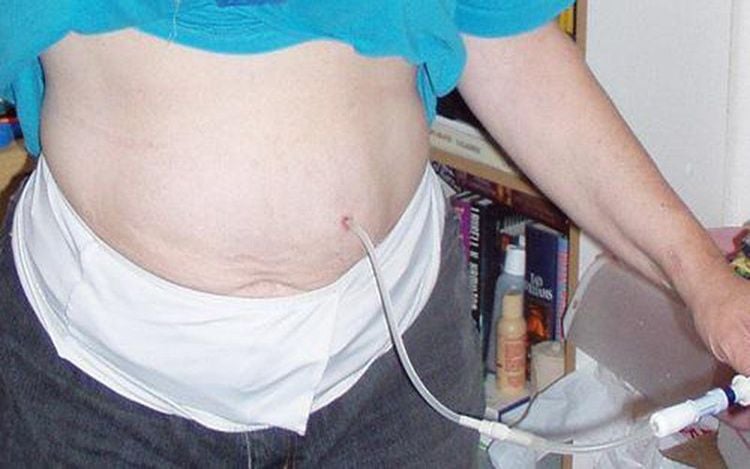
2.2. Steps to conduct continuous hemodialysis by emergency peritoneal dialysis The patient will be clinically examined, blood pressure, urine output, weight measured, and biochemical, hematological, and coagulation tests done. basic blood to ensure health conditions to perform continuous hemodialysis. The medical staff told the patient to fast.
Steps to perform emergency peritoneal dialysis:
The patient is aseptically sterilized the abdominal wall and anesthetized locally around the navel with Lidocaine or Xylocaine; The doctor locates the catheter puncture at the middle white line, 2cm below the navel. Make a skin incision at the midline white enough for Trocat to pass through. Using Trocat to guide the catheter through the peritoneum into the abdomen; Use a metal cannula to guide the catheter under the rectus abdominis muscle, toward the sac with Douglas. When the catheter tip is inserted into the pocket with Douglas, stop and withdraw the metal barrel needle from the catheter. Fix the catheter to the abdominal wall to avoid displacement; Allow 2 liters of 1.5% filtrate to flow into the abdomen with a time of 15 minutes to flow in and 15 minutes to drain, the purpose is to help clean the abdomen. The next fluid bags are 2 liters / time, keep the abdomen for 30-60 minutes and then drain it out to continue filtering. The dialysate can be mixed with Heparin at an appropriate dose to prevent catheter occlusion; The amount of dialysis fluid used daily can be up to 30-40 liters, continuous plasma exchange until the kidney function is restored, the life-threatening condition is over, other indications can be carried out.

3. Emergency dialysis by artificial kidney technique
3.1. Indications for emergency dialysis by artificial kidney technique An artificial kidney is a method where blood is filtered outside the patient's body by a dialysis machine. Blood is drawn from a blood vessel and passed through a synthetic filter called a dialyzer to be cleaned before being returned to the patient's body.Hemodialysis in resuscitation by hemodialysis is performed urgently, sometimes done immediately in parallel with the diagnosis of the cause to temporarily replace the sudden decline in renal function; when the patient has severe salt water overload, blood urea concentration exceeds 30mmol/l, accompanied by increased potassium, severe acid-base metabolism disorder,.... Plasma exchange by emergency hemodialysis is also possible. used in case of drug poisoning (such as barbiturates, ...) or patients with end-stage chronic renal failure develop suddenly, so they have not prepared for an arteriovenous catheter, the first dialysis sessions must be temporary vascular access.
Emergency hemodialysis with hemodialysis has no absolute contraindications, but caution should be exercised in patients with cerebral hemorrhage or hemodynamic disturbances, especially when blood pressure is too low.
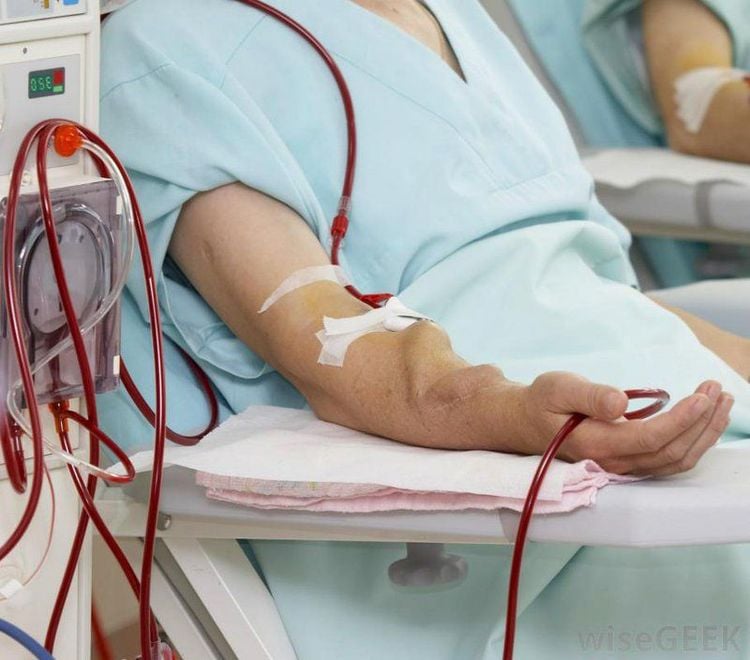
To conduct a blood transfusion with emergency hemodialysis, the doctor will choose the way into the blood vessel. The vascular access routes that can be used are the femoral vein, the subclavian vein, the internal vein, etc. In which, entering the femoral vein by placing a catheter using the Seldinger technique is the most common method. Due to its ease of implementation, it is suitable for emergency dialysis, ensuring good and stable blood flow.
Steps to establish the extracorporeal circulation:
Step 1: install the kidney filter Step 2: expel the vapors Step 3: check the operation and safety of the extracorporeal circulation. Step 4: Insert the patient into the extracorporeal circulation in the following order: Inject a loading dose of heparin, then a maintenance dose of heparin if continuous hemodialysis is used.
Set the blood pump at 100ml/min, when the blood reaches the venous bulb, connect the venous wire to the IV FAV needle.
Check and adjust parameters such as blood speed, ultrafiltration coefficient, dialysis time, ... then conduct dialysis.
Medical staff closely monitor the patient during dialysis, at the end of dialysis write all data on the dialysis monitoring sheet.
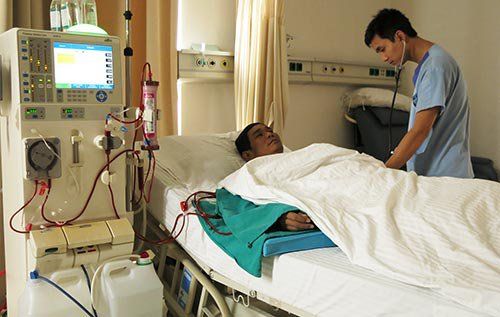
3.3.1. Intermittent emergency dialysis Patients will have dialysis sessions lasting from 4-6 hours. Dialysis specifications include:
Temporary vascular access; Blood flow 200-300ml/min depending on the patient's condition; Bicarbonate renal filtrate with a filtrate flow rate of 500 ml/min. 3.3.2. Continuous emergency dialysis Continuous dialysis (LMLT), also known as continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT) includes multiple modalities such as intravenous-intravenous (TM) ultrafiltration. - continuous veno-venous hemofiltration (CVVH), continuous veno-venous hemodialysis (CVVHD), ultrafiltration combined with continuous veno-venous hemodialysis hemodiafiltration - CVVHDF).
LMLT is a dialysis technique that allows to eliminate from the patient's blood continuously (24/24 hours) water and solutes with molecular weight (TLPT) less than 50,000 daltons, especially with The large volume of replacement fluid (> 35 mL/kg/hour) through diffusion - dialysis, ultrafiltration - convection and membrane adsorption mechanisms helps to eliminate solutes with small TLPT (BUN, creatinine) ...) to medium and large aphrodisiacs (cytokines, inflammatory mediators...). Multiple organ failure, septic shock, acute pancreatitis, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) are mostly associated with systemic inflammatory responses and cytokines.
On the other hand, LMLT technique also helps to correct water-electrolyte disorders, acid-base balance and is safe for hemodynamically unstable patients through convection, ultrafiltration and dialysis.
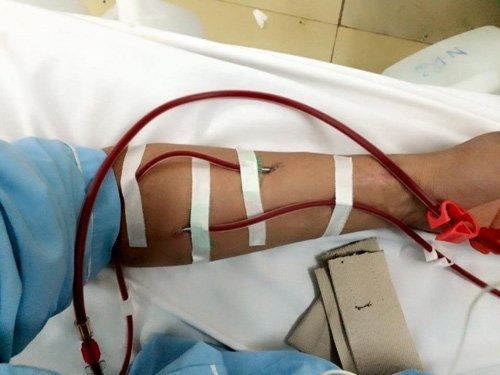
When the patient has high blood pressure, the patient can be given oral antihypertensive drugs or injecting antihypertensive drugs in an emergency. In the intermittent emergency dialysis method, each dialysis session takes about 10-13 grams of amino acids and about 30 grams of glucose, so the doctor will prescribe an infusion of amino acid solutions and 10% and 20% hypertonic glucose solutions. , 30% for the patient.
Dialysis needs to be done in a medical facility with adequate equipment, medical professionals with solid knowledge and skills to avoid causing dangerous complications for the patient.
Vinmec International General Hospital is a high-quality medical facility in Vietnam with a team of highly qualified medical professionals, well-trained, domestic and foreign, and experienced.
A system of modern and advanced medical equipment, possessing many of the best machines in the world, helping to detect many difficult and dangerous diseases in a short time, supporting the diagnosis and treatment of doctors the most effective. The hospital space is designed according to 5-star hotel standards, giving patients comfort, friendliness and peace of mind.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.