This is an automatically translated article.
Scabies in children is caused by the parasite Sarcoptes scabiei var hominis, characterized by intense itching, especially at night. The disease, if not detected early and treated properly, causes itching and discomfort for children. Let's learn about the specific medicines to treat scabies in children in the article below.
1. An overview of scabies in children
Scabies in children is caused by the scabies parasite (Sarcoptes scabiei var hominis, scabies). The mite lives in tunnels in the stratum corneum, tunneling and laying eggs and causing an immune response and itching. They are very small and cannot be seen with the naked eye.
Scabies can be spread from person to person through direct skin-to-skin contact, through objects such as clothing, blankets, etc. Anyone can get scabies, but this disease mainly occurs. in children and adolescents. Risk factors for scabies transmission are crowded, cramped living (temporary houses, barracks, kindergartens, households,...), poor sanitation.
Scabies in children if not detected early and treated promptly can persist for a long time and can recur. Treatment of scabies in children is preferred with topical medications used to treat scabies in children, in which the leading drug is Permethrin.
2. Symptoms of scabies in children
Usually, symptoms of scabies appear 4 to 6 weeks after exposure to the pathogen.
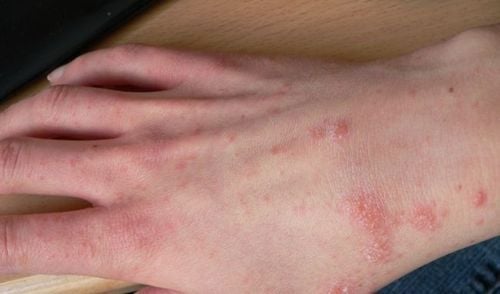
In children under 2 years of age, the rash caused by scabies tends to appear on the head, neck, palms, and soles of the feet. In older children, the rash is usually located in any of the following locations: Hands, between fingers, wrists, waist, thighs, navel, groin area, chest area, armpits.
Below are the common symptoms of scabies, however each child may exhibit different symptoms. Symptoms can be identified as:
Severe itching, especially at night. The rash is accompanied by small bumps or red bumps. Sometimes caves can be seen. Scaly or scaly skin in the worst case scenario. Scabies in children is diagnosed when there are clinical signs of scabies, epidemiological factors, and evidence of the presence of scabies parasites.
3. Cure scabies in children
Scabies is treatable and often all members of a family are treated at the same time. Visitors and caregivers should also be treated.
Children's scabies medicine is prescribed depending on the symptoms, age and general health of the child. It will also depend on the severity of the scabies. Treating scabies in children may include:
Using a prescription skin cream, such as Permethrin. Take medicine to kill ticks. Take an antihistamine by mouth to help relieve itching. Other topical medications can be used as needed to treat scabies in children. Trim your child's nails to help prevent infection. Also, it's important to wash all clothing and bedding in hot water and dry in a hot dryer. Clothes and other non-washable items should be placed in a plastic bag for at least 1 week. These items can include things like pillows and stuffed animals. People with scabies are considered highly contagious. Furniture and carpets should be carefully vacuumed. The itching can persist for weeks after the initial scabies treatment. If the scabies is still there after this time, take the child to the hospital to be examined and treated with special medicines for scabies in children.
4. Special medications for scabies are used in children
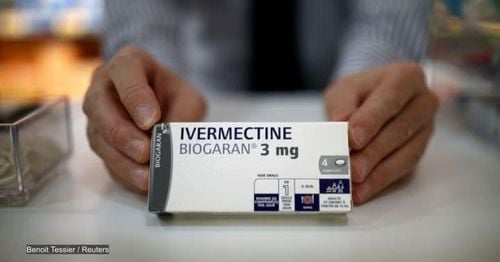
Treatment of scabies in children is initially using topical or oral pediatric scabies medications (Permethrin, Lindane, Ivermectin, D.E.P,...). Permethrin is the drug prescribed first.
For infants and young children: Apply Permethrin to the head and neck, avoiding around the mouth and around the abdomen. Pay attention to the area between fingers, fingernails, toenails, navel. Lindane is not recommended in children under 2 years of age and in people with epilepsy because of its neurotoxic effect. In infants under 2 months of age, sulfur precipitated 6 - 10% in gasoline, administered for 24 hours for 3 consecutive days was safe and effective. For older children and adults: apply Permethrin or Lindane all over the body from the neck down and wash off after 8-14 hours. Permethrin is more commonly used because Lindane can be toxic to the nervous system. These drugs should be repeated in 7 days. Patients who do not respond to topical scabies drugs, or who are immunocompromised to Norwegian scabies, will be treated with Ivermectin. The itching in scabies can be treated with corticosteroid ointments and/or oral antihistamines. Scabies can persist despite the use of scabies medicine for children, the cause of treatment failure may be drug resistance, poor drug penetration through the skin, insufficient course of treatment, recurrence, nodular scabies that is difficult to recognize. Therefore, for persistent scabies, skin testing for scabies parasites is necessary.
Treatment of scabies in children is not only treatment for the child alone, but also for those in close contact with the child and personal items (towels, clothes, blankets, ...) must be treated. Wash in hot water and dry or isolate for at least 3 days.
5. Prevention of scabies in children
The most effective way to prevent scabies in children is to avoid contact with sources of infection, such as people who are sick, not sleeping together, sharing clothes, blankets, ... Personal hygiene is clean every day. With soap every day, pay attention to the position of the folds such as between the fingers, groin, navel, ... In the family or group of people with scabies, it is necessary to treat it completely to avoid spreading.
Reference source: www.urmc.rochester.edu.