This is an automatically translated article.
Leukemia is one of the leading malignancies with a high mortality rate. To detect the disease, patients need to do blood cancer tests. for early detection and prompt treatment.1. What is blood cancer?
Blood cancer (acute leukaemia) is a disease that occurs because blood cells are cancerous in the process of creating cells, they will multiply very quickly and if not treated in time, it will stagnate. deposits in the bone marrow, interfering with the subsequent production of normal blood cells.Blood cancer is not a single disease but includes many diseases, including 2 main types:
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML): Due to cancerous myeloid cells such as granulocytes , red blood cells, platelets but not lymphocytes Acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL): Due to cancerous damage to lymphocytes. Today, science has not found the exact cause of the disease. The treatment of blood cancer is also very complicated, expensive and has a very high mortality rate.
2. Signs that the patient has had blood cancer
Blood cancer patients often have the following manifestations:Fever or chills. Fatigue, persistent weakness. Frequent infections. Losing weight unintentionally. Swollen lymph nodes, enlarged liver or spleen. Easy bleeding or bruising. Small red spots on the skin (petechiae). Excessive sweating, especially at night. Bone pain. In leukemia, symptoms are often vague and unclear. Early leukemia symptoms can be ignored because they can resemble those of the flu and other common illnesses.
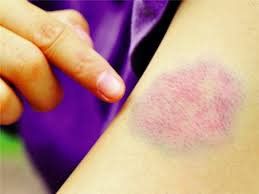
Người bệnh ung thư mái thường dễ chảy máu hoặc bầm tím
3. Diagnosis and detection of blood cancer
Ways to detect blood cancer include:3.1. Based on Clinical Symptoms In acute leukemia, many symptoms appear not only because of insufficient production of normal blood cells in the marrow, but also because cancer cells have spread throughout the body. Symptoms due to a decrease in normal blood cells include:
3.1.1. Vulnerability to infection Fever is a common symptom. This is a symptom associated with a decrease in the number of white blood cells in the peripheral blood. Possible infection in a certain organ: Respiratory, urinary tract... Sometimes no infection can be detected. Infections respond poorly to antibiotics. The function of white blood cells is to protect the body against infection. against foreign pathogens such as bacterial agents, so the white blood cell count is reduced, leading to insufficient resistance, as a result, blood cancer patients are susceptible to infections.
3.1.2. Anemia symptoms Irreversible anemia with features Rapid and worsening Anemia Anemia disproportionate to the extent of bleeding The patient is poorly adapted to anemia due to the acute nature of the disease A Poor response to blood transfusion Anemia often manifests as: dizziness, palpitations, tachycardia, and syncope. Pale skin with pale mucous membranes. This is a symptom associated with a decrease in the number of red blood cells. Because the function of red blood cells is to carry oxygen throughout the body, any deficiency of red blood cells results in hypoxia in the target organs of the body, causing symptoms such as rapid breathing or shortness of breath when breathing. movement, dizziness, fatigue, paleness.
3.1.3. Risk of bleeding Spontaneous bleeding with characteristics of thrombocytopenic purpura Subcutaneous hemorrhage is the most common condition, multiform, multi-age. Mucosal bleeding: Bleeding gums, nosebleeds, women can bleed from the uterine lining: Menorrhagia, menorrhagia. Visceral bleeding: Possible gastrointestinal bleeding, urinary tract bleeding, myocardial hemorrhage, pericardial, cerebral hemorrhage, meningeal. If there is a very high risk of death, the prognosis is severe. This is a symptom related to a low platelet count. Since the function of platelets is to stop bleeding, any platelet deficiency increases the risk of bleeding even with minor trauma, and results in small petechiae, ecchymoses, and bleeding. from the gums or from the nose. Visceral bleeding can occur in severe cases.
3.1.4. Infiltrative syndrome The liver and spleen are often enlarged at a small or moderate level (3-4 cm below the costal margin) There are cases that are larger but less common. Enlarged lymph nodes in many locations: neck, inguinal armpit.. Bone pain: due to infiltration into the periosteum Gum hypertrophy Subcutaneous granuloma Enlargement of internal organs and other organs due to invasion of cancer cells into organs such as liver, spleen, lymph nodes. In some cases, these cells can invade the central nervous system, which can manifest as meningeal irritation, causing headaches and vomiting.
3.1.5. Oral and pharyngeal necrosis and ulcer syndrome Poor response to antibiotics
3.1.6. Atypical form Lack of symptoms or unclear symptoms easily missed or misdiagnosed, or rare symptoms due to malignant cell infiltrate causing paralysis of half of the person, arthritis, clitoral testicles, bone tumors, subcutaneous tumors...
3.2. Based on blood cancer test results 3.2.1 Blood cell-blood test
Có thể chẩn đoán ung thư máu dựa vào xét nghiệm tế bào máu
3.2.2 Marrow test- bone marrow aspiration Bone marrow aspiration is the removal of a small amount of marrow tissue in the form of a liquid to determine the presence of cancer cells, which is crucial for the diagnosis. acute leukocytes.
3.2.4 Serum and Urine Analysis- Biochemistry Test This test analyzes blood and urine components. Uric acid concentration in plasma and urine, LDH concentration will be increased in blood cancer.
3.2.6 Cell classification test - cell surface antigens The antigens on the cell membrane surface are specific for each cell line.
3.2.7 Gene Abnormalities Test- Chromosome Abnormalities Gene and chromosomal abnormalities can be found in malignant white blood cells.
Blood cancer is an extremely dangerous disease, so we ourselves should take the initiative to go for an annual health check and go to the doctor as soon as we see the above signs to help detect blood cancer early, thereby providing timely and effective treatment.
The general health checkup package at Vinmec International General Hospital fully provides customers with examination benefits and is completely different from performing a regular health check. The program is scientifically and practically designed to approach your entire health condition, and at the same time, early detection, timely intervention and treatment to minimize the complications of diabetes. Critical illnesses threaten your life. The general health examination should be carried out periodically from 6 months to 1 year / year to ensure that the body is always healthy and can detect and prevent diseases as soon as possible.
Customers can register for a general health checkup package in the Vinmec International General Hospital system here.
Articles refer to the source: webmd.com
SEE MORE:
High white blood cells warn of what disease? Diagnosis of acute leukemia (blood cancer) Development of CAR-T cell therapy technology for the treatment of blood cancers