This is an automatically translated article.
HIV is a dangerous virus that can infect both sexes, attacking and destroying the immune system. So what are HIV symptoms in women?1. What is HIV?
HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) is a virus that causes human immunodeficiency. A special feature of HIV is that unlike other viruses that are attacked and eliminated by the human immune system, HIV has the ability to attack and weaken the immune system by destroying CD4 cells, eliminating defense capacity of the human body.
The way HIV is transmitted is through bodily fluids, including:
Blood; Sperm; Vaginal and rectal discharge; Mother milk. HIV infection is a chronic condition for which there is currently no cure. However, if detected early and treated according to the right regimen, HIV can be controlled, patients will have a long life time almost like people without HIV.
Normal progression of HIV goes through three stages: acute HIV infection, asymptomatic stage, and late AIDS stage.
2. HIV symptoms in women
Each person is different when infected with HIV will show different symptoms. Symptoms usually appear 2 to 4 weeks after being infected with HIV, and they are easy to miss because they are mistaken for a cold or the flu. Symptoms of HIV vary depending on the stage of the disease.2.1 Acute stage of HIV infection The most common early signs of HIV in women include:
Rash on body: most HIV patients have dermatological problems, and rash is the symptom common; Fever: patients often have prolonged fever, low fever (37.7 - 38.2°C); Sore throat; Severe headache.
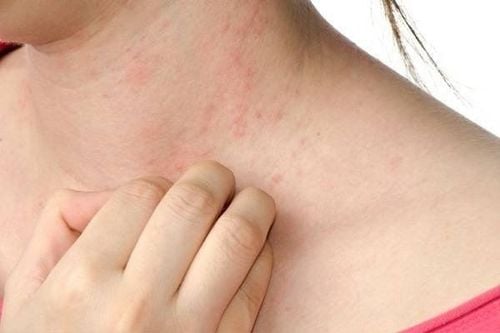
Phát ban trên cơ thể: đa số các bệnh nhân HIV đều gặp các vấn đề về da liễu, và phát ban là triệu chứng phổ biến
Less common symptoms include:
Swollen lymph nodes: lymph nodes are present all over the body (neck, nape, armpits, groin,...), play a role in immunity, protecting the body. against pathogens. When infected with HIV, the immune system is activated, leading to enlarged lymph nodes, causing swollen lymph nodes, which can last up to several months; Nausea, vomiting; Tired; Mouth sores; Bacterial vaginosis: The vagina can become inflamed due to bacteria or a fungal infection. Symptoms of vaginal yeast infection include: burning sensation inside and outside the vulva - vagina, pain during sex, pain when urinating, cloudy vaginal discharge. Although bacterial vaginosis or vaginal yeast infection are both common in normal women, in HIV-infected women, repeated infections are more frequent; Night sweats; Muscle pain, joint pain. Symptoms of the acute phase usually disappear after one to two weeks.
2.2 Asymptomatic phase When the symptoms of acute HIV infection disappear, the disease progresses to the asymptomatic stage. During this stage, the patient will not show any signs or symptoms, and this phase lasts for years, possibly up to 10 years or longer. Although the patient looks completely normal on the outside, inside the patient's body, HIV continues to multiply and attack, destroying the immune system, and HIV has the ability to infect others.
2.3 End stage - AIDS If left untreated, the patient will progress to the end stage of the disease - Acquired Immuno Deficiency Syndrom (AIDS). By this time, the body's immune system has been destroyed, the body completely loses its ability to fight pathogens, including agents that are normally not strong enough to cause disease in humans.
Symptoms in women at this stage include:
Persistent diarrhea; Nausea, vomiting; Rapid weight loss; Tired; Ulcers in the oral cavity; Vaginal infections caused by fungal or bacterial infections; Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID): This is a bacterial infection in the pelvic area, including inflammation of the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries. This infection is difficult to treat and often recurs; Recurrent fever; Recurrent chills; Recurrent night sweats; Shortness of breath; Cough; Persistent or persistent lymph node swelling; Dementia, psychosis or other mental disorders.
3. Timing of HIV testing for women
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends that everyone between the ages of 13 and 64 get tested for HIV at least once in their lives. Pregnant women are also recommended to be tested for HIV.
Women with risk factors should be tested for HIV more often. Those risk factors are:
Vaginal or anal sex with someone whose HIV status is unknown or with someone who has HIV but is not receiving antiretroviral therapy;

Quan hệ tình dục qua đường âm đạo hoặc hậu môn với người không biết rõ tình trạng nhiễm HIV
Injecting drugs using shared needles; You yourself have contracted a sexually transmitted disease (eg, syphilis); You yourself have tuberculosis or hepatitis.
4. How to prevent HIV in women
Some basic HIV prevention strategies for women include:
Do not use drugs, do not share and do not reuse needles; Use of HIV-exposure prophylaxis for those with risk factors; Do not douche after sex, because this will change the natural balance of the flora in the vaginal environment, making it easier to become infected, especially increasing the risk of HIV infection as well as other diseases. sexually transmitted diseases ; Be faithful to a partner who is neither HIV-infected nor infected with other sexually transmitted diseases; Safe sex, using condoms is the simplest, most convenient and cheapest way. Non-HIV-infected women with HIV-infected partners will not be afraid of infection if their partners receive antiretroviral therapy according to the correct regimen, and the measured viral load is less than 200 copies/mL of blood. However, condoms are still recommended to be used.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References: Healthline, Medical News Today.