The article is professionally consulted by doctors of the Department of Pediatrics - Neonatology - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.
Dengue fever is an acute infectious disease, often causing epidemics, caused by 4 strains of Dengue virus (Arenavirus, Bunyaviridae, Filoviridae and Flavivirus). The disease can appear at any age, rarely appearing in infants. Dengue fever in infants as well as other subjects often has symptoms of high fever leading to skin and mucous membrane hemorrhages and cardiovascular collapse leading to death if not treated promptly.
1. Causes of Dengue Fever in Infants
Whether it is infants, children or adults, there are 2 common causes of the disease:
- Caused by the Dengue virus.
- Mosquitoes that suck the blood of infected people spread the disease to healthy people.
Of course, dengue fever will not be transmitted from person to person as parents often worry. Usually, children with dengue fever need to be identified within the first 3 days from the day the child has a fever. In addition, mothers should also note whether at that time there is a dengue fever outbreak, or whether anyone around them has the disease.
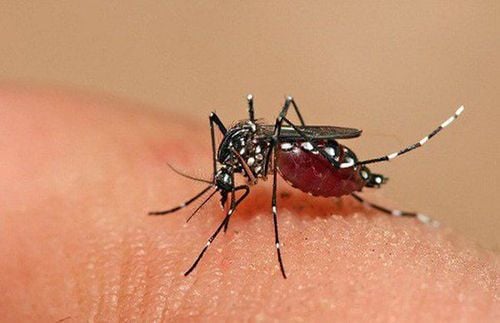
Dengue fever is often prevalent in tropical regions, mainly in Southeast Asia and the Western Pacific. Vietnam is one of the countries with severe outbreaks. In the North, the epidemic season usually starts from June to July and peaks in August, September, October, and November. In contrast, in the South, the epidemic tends to appear all year round, and often tends to increase during the rainy months with high humidity.
2. Signs of dengue fever in children
Dengue fever in infants, young children, children or adults is manifested by the following symptoms:
- High fever, sudden and continuous for 2-7 days.
- Difficulty reducing fever, muscle pain, joint pain, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, headache.
After a few days, the patient will see signs of rash, bleeding in many different forms such as nosebleeds, petechiae under the skin, vomiting, blood in urine, and leukopenia (4000/mL) ... In infants, the disease occurs at a lower rate, often with symptoms that need to be distinguished from other diseases such as Sepsis, meningitis, respiratory infections, gastrointestinal infections ...
Note the stages of dengue fever in children:
Usually, children with dengue fever need to be identified within the first 3 days from the date of fever.
- Day 1: The child has a high fever, suddenly, red face, red throat but no pain. At this stage, it is not necessary to take the child to the hospital but can stay at home to monitor further.
- Day 2: If the child still has signs of high fever, the mother should try to look for signs of subcutaneous bleeding on the abdomen, limbs, neck, and eyelids.
- Day 3: Symptoms of dengue fever become more obvious. In addition to high fever, the child may have mucosal bleeding such as bleeding gums, and nosebleeds.
- Day 4, 5: Symptoms are more obvious when the child has red rashes all over the body, high fever, nosebleeds…
Usually, children under 12 months old with dengue fever will have symptoms of high fever, cough, runny nose, many subcutaneous hemorrhages, hepatomegaly, Low red blood cell volume, decreased platelets, and a very high tendency to shock.
Therefore, during the dengue fever season, parents (and medical staff) need to be careful because this disease is easily confused with children under 12 months of age with symptoms of respiratory infection. If treatment is delayed, it can lead to unpredictable consequences.
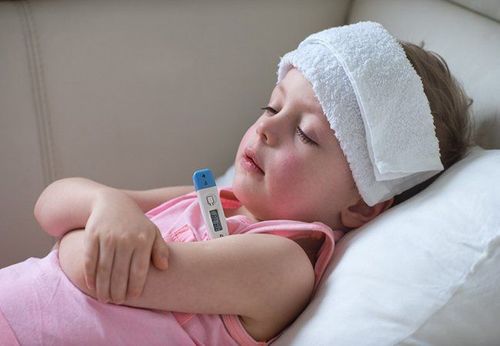
3. Treatment measures for dengue fever in young children
Most cases of dengue fever in the early stages (without signs of bleeding) are treated at home. But this doesn’t mean that complications do not occur. Therefore, children need to be closely monitored to promptly handle complications. Mothers should take their children to the hospital as soon as they notice unusual signs such as fatigue, lethargy, abdominal pain, vomiting, heavy bleeding, and cold hands and feet.
For the patient's family, it is important to note:
- Home care: Let the child rest and drink plenty of water. Food should be in liquid form so that the child can swallow easily and not vomit. If the child is still breastfeeding, the number of feedings should be increased. Dengue fever makes the blood thick and difficult to circulate so the child needs to drink plenty of water to avoid shock because shock is the leading cause of death in people with the disease.
- Dengue fever usually progresses within 7 days and mostly heals on its own, and the rate of severe complications is only 3% -5%. People with the disease must go to the doctor if severe symptoms such as abdominal pain, restlessness, bleeding gums, nosebleeds, and cold hands, and feet appear, they need to be taken to the hospital immediately.
- It is necessary to monitor to promptly handle when the child shows signs of shock. If the child has abdominal pain, vomiting, and cold hands and feet, the child needs to be taken to the emergency room immediately. Another sign of shock is that the child suddenly becomes lethargic, sometimes struggling and not alert. The child may also have reduced urination but feel very thirsty. Bruising of the skin and gray lips are also signs of shock.
- The red spots on the skin are caused by some red blood cells escaping from the blood vessel wall to the outside, accumulating under the skin, and causing subcutaneous hemorrhage. These signs will disappear in 5-7 days. Therefore, it is not recommended to treat them with folk remedies such as rubbing betel leaves on the skin or scraping the skin, which can damage the child's skin.
- Children should be given antipyretics as prescribed by the doctor, and should not have a high fever that can easily lead to convulsions.
Families should take their children back to the doctor immediately if they show signs of vomiting a lot, no fever but fatigue, cold hands and feet, or bleeding. - Remember to schedule a follow-up visit: every day until the fever has been gone for > 48 hours.
4. Criteria for children to be discharged from the hospital
- Children have no fever for at least 24 hours without the need for antipyretics.
- Children have signs of appetite, good urination, and significant clinical improvement.
- No signs of respiratory failure due to pleural or peritoneal effusion.
- Platelet count 50,000/mm3.
If there are positive signs of progress as above, the child can be discharged by the family and treated at home.
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.







