This is an automatically translated article.
Posted by Master, Doctor Huynh Vu Khanh Linh - Doctor of Obstetrics and Gynecology - Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology - Vinmec Phu Quoc International General Hospital
Semen analysis is a type of paraclinical test to check whether a man's fertility and spermatogenesis are normal or not? This is an important test for most couples who want to have children.
1. Definition of infertility
Infertility is currently a burden on the Vietnamese health sector, affecting about 15-20% of couples of reproductive age. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), infertility is a disease of the reproductive organs, a couple is said to be infertile when they are unable to get pregnant after a year or more of living together, having intercourse. regularly and without using any contraception. For couples with wives over 35 years old, the time limit is 6 months. Therefore, when the wife is over 35 years old, after 6 months of trying for a baby but still unable to get pregnant, she should be examined and treated early. However, for cases where the cause of infertility is relatively clear, the timing is no longer set.
2. Infertility groups
Infertility is divided into 2 groups, namely:
Primary infertility: a couple who have never gotten pregnant after a year of living together without using any contraception. Secondary infertility: a couple who have not become pregnant again after a previous pregnancy for at least 1 year living together without using any contraception. The cause of infertility is usually about 35-40% female, 30% male, 20% both husband and wife, and the remaining 10-15% of unknown cause. In which:
Ovulation disorder (15%). Fallopian tube disease and pelvic adhesions (30-40%). Factor due to husband (30-40%). No cause can be found (5 - 25%).
3. Causes of infertility due to husband
Common causes of male infertility are: oligospermia, low sperm count, anti-sperm antibodies, undescended testicle, varicocele, specifically:
Undescended testicle: occurs in 3% of full-term infants, 21% of babies born prematurely and 0.8-1.8% of 1-year-olds. According to Dang Quang Tuan's research, laparoscopic surgery proved to be more effective than open surgery in diagnosing and treating undescended testicles, the rate of undescended testes being lowered through laparoscopy was 90%. Varicose veins: this is a common disease in men causing 15-25% of primary infertility cases and 75-81% of secondary infertility. This pathology can be effectively treated with microsurgery. Other causes of male infertility include: trauma to the testicles, chromosomal abnormalities, blockage of the vas deferens, retrograde ejaculation, endocrine disorders, orchitis. In addition, factors that reduce sperm quantity and quality such as: Occupational influences: working in high temperature environments, exposure to toxic chemicals...
There are many causes of male infertility. Gender and each group of causes need different treatment methods. Currently, the indications for treatment of infertility are built on the value of semen analysis results.
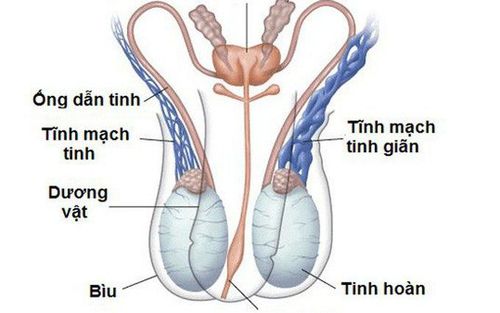
Giãn tĩnh mạch thừng tinh là một trong các nguyên nhân hiếm muộn do chồng
4. Male infertility and semen analysis indicators that need to be evaluated in the semen chart
4.1. Macroscopic assessment Lysis
It is the phenomenon that semen after ejaculation will liquefy itself at 37oC. Average lysis time in 15 minutes at laboratory temperature or 37oC incubator. This phenomenon is mainly caused by the enzymes fibrinolysin and aminopeptidase of the prostate to break down fibrin, liquefying semen to release sperm.
If lysis does not occur after 60 minutes, it is usually due to an abnormality of the prostate gland (such as prostatitis). Sperm that is not motile or difficult to move may be due to a condition in which the semen has not fully dissolved. For samples that do not lyse after 60 minutes, this should be noted in the results. However, some authors suggest using yeast to facilitate lysis by diluting semen with 10 IU/ml bromelain, stirring, and incubating prior to evaluation.
Viscosity
Assessed by observing the elongation of the droplet of semen being dispensed from the tip of the Pasteur pipette. Viscosity is normal when the droplet of semen drops sporadically, whereas the viscosity is considered high when the droplet is longer than 2cm. High viscosity is usually due to abnormal components in semen secreted by accessory glands.
High viscosity will make it difficult to evaluate sperm motility and density by affecting sample homogeneity. The method of reducing the viscosity is similar to that of undissolved samples. Viscosity-reducing needles can affect sperm motility and morphology.
Volume
In the sample after ejaculation will include sperm and semen. About 90% of semen is produced from the seminal vesicles and prostate gland. The rest is secreted by the testes, epididymis, and bulbar urethra. Accurate measurement of semen volume is important, as this metric affects how the total sperm count and the total number of foreign cells in an ejaculate are calculated.
According to the latest WHO recommendations, the volume of the ejaculate sample should be calculated by the weight of the sample in the container. Semen volume was calculated using sample weight, with the convention that the density of semen was equal to 1g/ml.
The volume of semen is expressed in ml with a minimum standard value of ≥ 1.5 ml. A large volume of semen is often seen in those who have a long period of abstinence from ejaculation. In the case of semi-obstruction of the seminal vesicles, there is usually a very small volume of semen. The absence of semen (Aspermic) is usually due to obstruction or retrograde ejaculation.
pH
pH is measured at certain times at 30 minutes to no more than 1 hour after ejaculation. The pH determination should take place within 30 seconds because semen can oxidize when exposed to air, which will change the pH. The minimum pH value is 7.2 as recommended by WHO 2010.
pH varies depending on the acidic prostate secretions and the alkaline seminal vesicle secretions. A pH below 7 is commonly seen in the presence of azoospermia which may be due to obstruction or absence of bilateral vas deferens.
4.2. Microscopic examination Motility
Motility was investigated by observing the natural motility of sperm, then calculating the ratio of motile sperm to the total number of sperm observed and expressed as a fraction hundred. The rate of progressive sperm motility was found to be related to the pregnancy rate. Sperm motility can be influenced by many factors such as a man's age and health status. Factors such as duration of abstinence from intercourse, sampling method, and time from ejaculation to survey can also affect the results. Therefore, sperm motility should be assessed immediately after complete dissolution of semen, within 30 minutes but not more than 1 hour after ejaculation.
In the latest version of WHO, sperm motility is classified into 3 categories: progressive (PR-progressive), non-progressive (NP-non-progressive) and immotile (IM-immotile) ). The minimum cut-off value for total motile sperm (PR+NP) is 40%, for advanced motile sperm is 32%.
Sperm survival rate
This ratio is very important in cases where the sperm is completely immobilized in the ejaculate sample. A high percentage of dead and immobilized spermatozoa may be suggestive of epididymal disease. In addition, survival assessment results allow cross-checking of mobility outcomes. Normally, the percentage of dead sperm does not exceed the percentage of motile sperm, and the percentage of live sperm is often more than the percentage of motile sperm.
Semen analysis is a basic test for the general assessment of male fertility. A semen analysis shows the quantity and quality of sperm present in the semen, and can diagnose other causes of abnormalities, guide further tests, and prescribe appropriate treatment. . Therefore, in the examination and diagnosis of an infertile couple, semen analysis is a mandatory routine test.
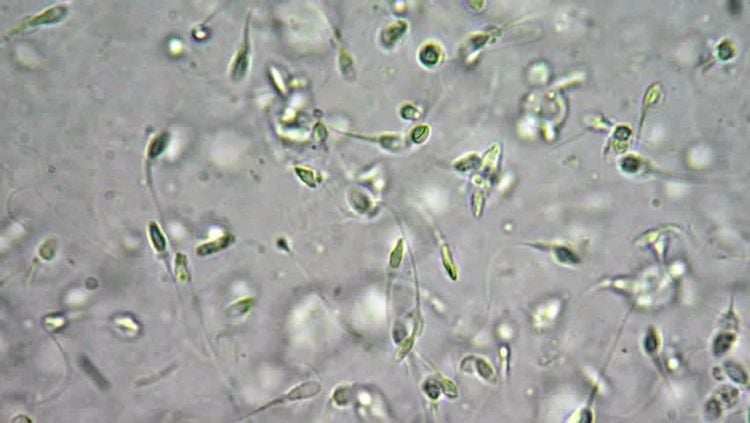
Tinh dịch đồ là một trong các xét nghiệm giúp đánh giá tình trnajg hiếm muộn nam
Sperm density
Many studies show that the total number of sperm in an ejaculate and sperm density are related to the pregnancy rate and are the basis for predicting the possibility of pregnancy. The minimum limit of sperm concentration in the sample is 15 x 106/ml.
Sperm shape
Sperm were determined to be of normal shape when the head, neck, midsection and tail were all normal. The sperm head is oval with clear lines, 3.7-4.7μm long, 2.5-3.2μm wide, the ratio of length to width is 1.3-1.8. In which, the head pole accounts for 40-70% of the volume of the head region. The head pole has no large vacuoles or more than 2 small vacuoles and does not occupy more than 20% of the head region volume. The posterior pole region does not contain any vacuoles.
The midsection is considered normal when tapered, 0.5-0.7μm wide, 3.3-5.2μm long, axially attached to the head. The residual cytoplasm is 1/3 smaller than the head size (mature spermatozoa are no longer visible). In addition, the tail should be straight, even, tapering than the middle, not coiled, about 45-50μm long.
According to the latest WHO recommendations (2010), sperm shape should be assessed according to the strict Kruger criteria. Accordingly, all sperm with the wrong shape as described above are considered abnormal sperm. In addition, any sperm with a suspicious shape should be classified as abnormal.
Foreign cells
Foreign cells also known as round cells, include epithelial cells, white blood cells, immature sperm and sometimes red blood cells. Normally, white blood cells are not present in semen, if present, only in very small quantities. A large number of leukocytes present in an ejaculate may indicate pathology, usually originating in the prostate or seminal vesicles. Meanwhile, normal erythrocytes are absent in semen or may be present in very small quantities but have no pathological significance. The presence of multiple immature spermatozoa and immature germ cells in semen indicates tubular dysfunction, often in varicocele.
Semen analysis is very important for couples who are expecting a baby. The results of semen analysis partly reflect the quality of sperm, helping doctors to diagnose infertility and other diseases more effectively.
Vinmec Reproductive Center is the leading modern center in Vietnam, built and applied a comprehensive medical examination and treatment process, combining both male and female obstetrics and gynecology to offer the optimal plan. for each patient case. In particular, at Vinmec, there are all kinds of testing machines and methods to find out the cause of infertility in both men and women. Up to now, Vinmec IVF fertility center has provided fertility support to over 1000 infertile couples with a success rate of over 40%. This rate is equivalent to developed countries such as UK, USA, Australia,...
With high professional level and extensive experience, Vinmec's team of experts is capable of deploying. Synchronize and comprehensively the most advanced assisted reproductive techniques today, helping to realize the dream of parenthood of hundreds of families across Vietnam.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.