This is an automatically translated article.
Thyroid cancer rates seem to be increasing. Thyroid cancer occurs in the cells of the thyroid gland - a butterfly-shaped gland located in the neck of the body. Most cases of thyroid cancer can be cured with treatment. The following information will provide insights into the survival chances of thyroid cancer patients.
1. Thyroid cancer
1.1. Concept of thyroid and thyroid cancer The thyroid gland is part of the endocrine system in the human body. The endocrine system is responsible for producing substances called hormones that help regulate all life activities of the body. The thyroid is a small butterfly-shaped gland at the base of the throat consisting of 2 lobes, left and right, connected by the waist. The thyroid gland produces the hormone thyroxine, which helps the body regulate:
Metabolism
Blood pressure Heart rate Body temperature Body weight Thyroid cancer is one of the most common endocrine cancers. and is increasing gradually over time in part because today thyroid cancer can be easily diagnosed and detected.
1.2. Symptoms of Thyroid Cancer Diagnosis of thyroid cancer in the early stages is often difficult because there are no noticeable symptoms. During the progression of the disease, some of the following symptoms may appear:
Feeling of something blocking the throat Prolonged cough, unknown cause Hoarseness Sore throat, neck Difficulty swallowing, pain when swallowing Lymph nodes swollen neck blood

Người bệnh có thể gặp triệu chứng của ung thư tuyến giáp như khó nuốt hoặc đau khi nuốt
1.3. Risk factors for thyroid cancer Risk factors that can lead to thyroid cancer include:
Family history of thyroid cancer Many studies have shown that women are at increased risk of developing thyroid cancer. higher than men Have a history of breast cancer Have a history of radiation exposure. Age: People over the age of 40 have been shown to have a higher risk of developing thyroid cancer than those under this age. 1.4. Types of Thyroid Cancer Across all cancers, thyroid cancer is relatively rare. The incidence of thyroid cancer is only one-tenth that of breast cancer and one-fifth of lung cancer
Thyroid cancer is classified based on the appearance of the cancer cells. Cancer cells usually don't have much difference from normal cells and they are called differentiated cells. These differentiated cells grow more slowly than undifferentiated cells in other cancers.
Types of thyroid cancer include:
Papillary thyroid cancer: Papillary thyroid cancer is the most common type of thyroid cancer, usually appearing in women of childbearing age. Papillary thyroid cancer is less dangerous than other forms because the cancer cells grow slowly and are easy to treat. Medullary thyroid cancer: It is a relatively special and very rare form of thyroid cancer, accounting for only about 3% of all thyroid tumors. In some cases, this type of cancer is genetic. Medullary thyroid cancer arises from the C cells of the thyroid gland. This is a dangerous cancer with a relatively low cure rate.
Thyroid cyst: Thyroid cyst is the most likely type of tumor to spread and recur. They arise from hurthle cells and account for about 3 to 10% of all differentiated thyroid cancers. Undifferentiated thyroid cancer: The starting point of undifferentiated thyroid cancer is follicular cells, which tend to grow and metastasize very quickly, so treatment often does not bring good results. Thyroid lymphoma: A rare form of cancer, also known as non-Hodgkin lymphoma, that originates in white blood cells.
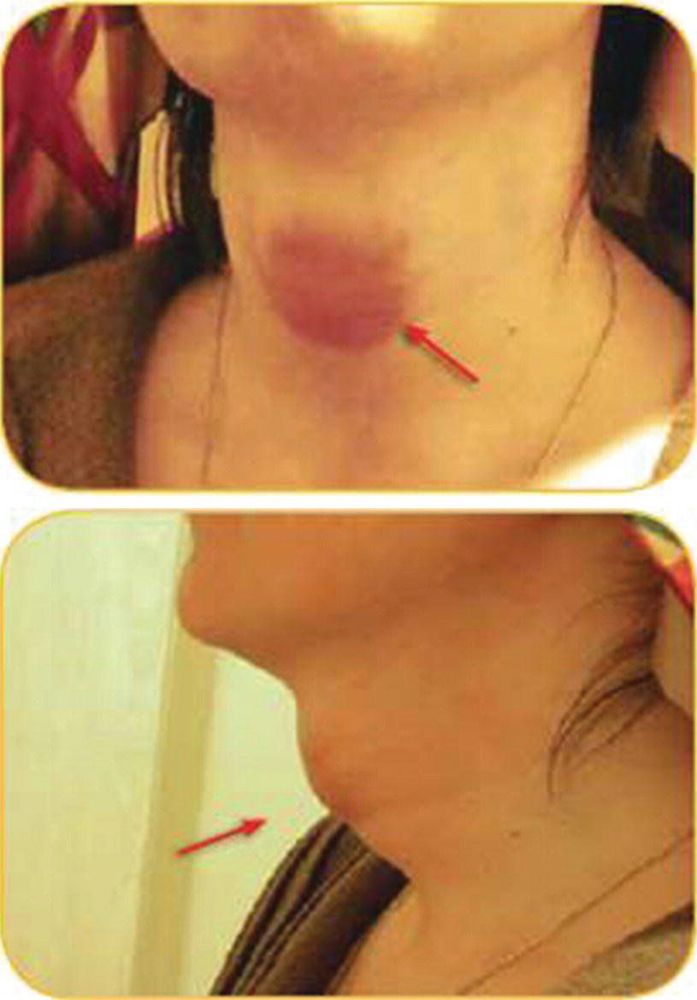
Hình ảnh bệnh nhân mắc U lympho tuyến giáp
1.5. Diagnosing thyroid cancer Routine checkups and certain tests can help detect thyroid cancer. Physical examination of the neck may reveal a small mass in the thyroid gland in addition to enlarged lymph nodes.
Tests used to diagnose thyroid cancer include:
Thyroid function tests
Thyroglobulin tests used in papillary cancers or thyroid cysts
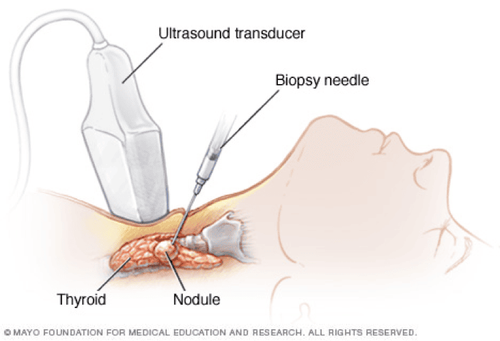
Computed tomography of the thyroid gland Super thyroid tone Thyroid biopsies Measure calcium and phosphorus levels in the blood Laryngoscopy .
1.6. Thyroid cancer treatment The treatment for thyroid cancer depends on the form of cancer. In most cases, surgical removal of part or all of the thyroid gland is indicated. In this condition, the amount of hormone produced by the thyroid gland will not be guaranteed and the patient will be supplemented orally for life.
Other treatments include:
Radiation External beam radiation Chemotherapy
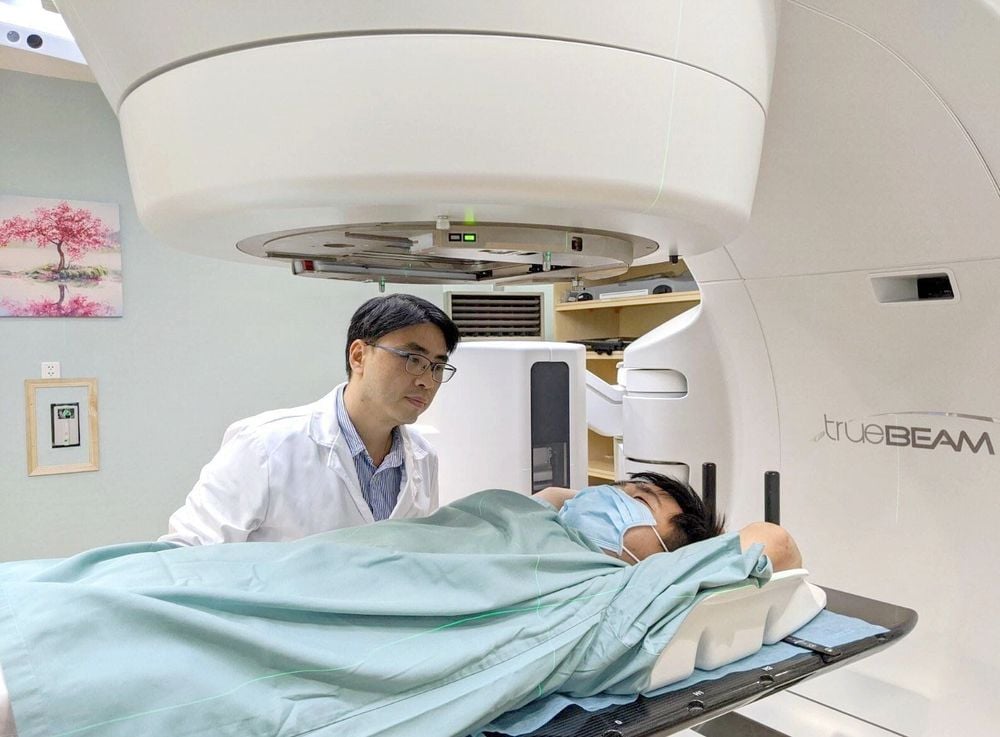
Người bệnh có thể điều trị ung thư bằng phương pháp xạ trị tại cơ sở y tế uy tín
2. Life chances of thyroid cancer patients
In general, the prognosis of thyroid cancer is very good, especially for patients under 45 years of age and the tumor size is small.
Patients with papillary thyroid cancer have the best prognosis when the cure rate is very high.
The 5-year survival rate shows what percentage of people live at least 5 years after cancer is found. Typically, the 5-year survival rate for people with thyroid cancer is 98%. However, this rate is also based on many factors such as the specific type of cancer as well as the advanced stage of the disease.
For localized thyroid cancer, the cancer cells have not metastasized, the 5-year survival rate is almost 100% with papillary, medullary thyroid cancer and thyroid cyst. This rate is only 31% for undifferentiated thyroid cancer cases.
If the tumor has spread to nearby organs or to the lymph nodes around that area, it is also called regional thyroid cancer. In this case, the 5-year survival rate for papillary thyroid cancer was 99%, for thyroid cysts it was 96%, for medullary carcinoma it was 90%, and for thyroid cancer. Undifferentiated this rate is only 12%.
In cases where the tumor has spread to other parts of the body, the 5-year survival rate for papillary thyroid cancer is 78%, thyroid cyst and 63% and medullary thyroid cancer is 39%. Particularly in the case of undifferentiated thyroid cancer, the 5-year survival rate of the patient is only 4%.
Thyroid cancer is the most common of all endocrine-related cancers and is on the rise, especially for women aged 40 and over. Although there are many factors to determine the likelihood of cure, such as the type of cancer or the advanced stage of the cancer, in general, thyroid cancer is easy to treat and often has a good prognosis. People who are diagnosed with thyroid cancer early often respond well to treatment, so screening and timely detection of thyroid cancer is important, giving patients a higher chance of survival.
Vinmec International General Hospital is equipped with advanced modern equipment and a team of leading experts with high expertise. The hospital now has an effective screening and screening package for thyroid diseases, helping to check thyroid function, screening & early detection of common thyroid diseases such as simple goiter, hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism, thyroiditis, thyroid nodules, thyroid cancer, ... so that appropriate and timely treatment measures can be taken.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE.
References: cancer.net, healthline.com