This is an automatically translated article.
Urticaria angioedema is a reaction characterized by short-term swelling of the skin and mucous membranes. Urticaria angioedema can lead to many dangerous complications, even death.1. What is angioedema urticaria?
Urticaria angioedema, also known as angioedema, angioedema urticaria, is a reaction to swelling of the skin and mucous membranes in a short time. This is a disease with symptoms similar to urticaria. However, urticaria manifests mainly as a rash, papules in the epidermis and dermis, while angioedema often causes red, swollen masses in the dermis, accompanied by pain and tenderness. While urticaria affects only the surface of the skin, angioedema can affect all organs of the body, most commonly the lips and eyes. In severe cases, the disease can cause respiratory and gastrointestinal edema, which can easily lead to death.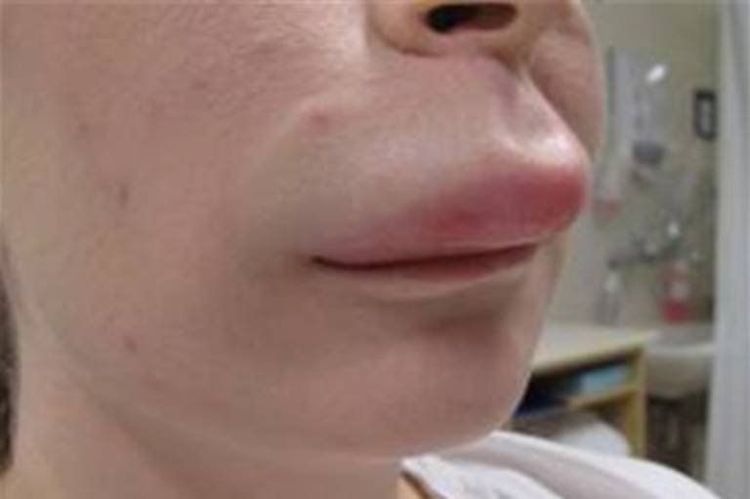
Mề đay phù mạch
2. Causes of angioedema urticaria
The cause of angioedema depends on the different types of angioedema. Specifically:Acute allergic angioedema: Usually occurs with urticaria about 1-2 hours after exposure to the allergen. The cause of this condition is mainly food allergies (seafood, eggs, milk, peanuts,...), pollen, drugs (Penicillin, vaccines, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, ...) , insect stings, allergy to contrast material, latex particles,...; Drug-induced angioedema: This is a non-allergic drug-induced reaction that can develop several days after the first dose. The cause of drug-induced angioedema is the patient's use of certain drugs such as ACE inhibitors or a series of effects of kinin products, metabolites of arachidonic acid and nitricoxide; Spontaneous angioedema: Usually chronic, recurrent and occurs with urticaria. The cause of self-recognized angioedema remains unclear. Many studies indicate that about 30 - 50% of cases of idiopathic angioedema urticaria are due to autoimmune disorders, including systemic lupus erythematosus; Hereditary angioedema: is an autosomal dominant inherited disease, quite rare. The cause of this condition is a genetic abnormality that causes a deficiency of normal proteins in the blood; Acquired C1 inhibitor deficiency: Due to lymphoma or the body has antibodies against C1 inhibitor. For these reasons, substances such as bradykinin cause vasodilation, increased permeability, and leakage of fluid through the vessel wall, leading to angioedema and urticaria.
3. Symptoms of urticaria angioedema
Throat, tongue, lips, eyelids, hands, feet, and genitals may become swollen; The skin is swollen, sensitive and painful. A swelling may appear for 1-2 days, then spread to other areas, persist for several days and may become chronic; Angioedema of the throat and tongue can cause breathing difficulties, even asphyxiation and death; Angioedema in the gastrointestinal tract causing abdominal pain, diarrhea; Patients with hereditary angioedema may experience headaches, visual imbalance, and anxiety.4. Method of diagnosing angioedema urticaria
Based on medical history, family history, allergy history; Check the skin for swelling and the sensitivity of the swelling; Skin testing to identify allergens; Test blood levels and function of specific proteins if hereditary angioedema is suspected.
Xét nghiệm máu nếu nghi ngời phù mạch di truyền
5. Treatment of angioedema urticaria
Depending on the cause of the disease, the patient's location and the severity of the disease, the doctor will recommend an appropriate treatment for angioedema. Specifically:Cases of angioedema of the respiratory tract: Need to give first aid to the airways, take the patient to the emergency room; Mild angioedema: Treatment is similar to urticaria and other allergic reactions. Specifically, it is possible to apply cold packs to the patient. The use of topical drugs or lotions do not promote much effect because they are difficult to penetrate deep into the dermis; In case of prolonged angioedema: Adrenaline subcutaneous injection, systemic corticosteroid therapy, systemic antihistamine therapy. If the disease does not respond to antihistamines, cyclosporine, an anti-IgE drug (Omalizumab) can be used. Alternatively, other measures such as plasmapheresis or intravenous immunoglobulin can be used. The goal of chronic angioedema treatment is to reduce itching, pain, swelling, and help patients maintain daily activities; Other therapy: Intravenous C1 inhibitor, bradykinin or kallikrein inhibitors, and anabolic steroids (eg, stanozolol, oxandrolone and danazol) to increase C1 inhibitor levels, tranexamic acid used in prepubertal children for the treatment of hereditary angioedema type 3.
6. Measures to prevent and stop the progression of angioedema urticaria
Avoid factors that cause allergic angioedema such as food, some drugs, chemicals,...; Apply a cold pack to the swollen skin; Take the medicine according to the dose prescribed by the doctor; After drug treatment, if the disease does not improve, you should contact your doctor for further examination and advice. Angioedema urticaria needs to be detected early for timely and effective treatment. Therefore, when there are warning symptoms of the disease including skin swelling, red heat, ... the patient should go to the hospital for timely examination and treatment.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.