This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Vu Huu Thang - Emergency Resuscitation Doctor - Emergency Resuscitation Department - Vinmec Ha Long International General Hospital. The doctor has nearly 10 years of experience in Emergency Resuscitation.Coma is a common clinical emergency, appearing in many different conditions. The cause of a coma can come from many causes, it may be after an injury or some other medical condition in the body that leads to this condition. However, in order to diagnose coma most accurately, it is necessary to perform a comprehensive examination and perform some necessary laboratory tests for the diagnosis.
1. What is a coma?
Coma is defined as a phenomenon in which the patient has reduced responsiveness or inability to respond to external stimuli. Coma is a disturbance of consciousness that occurs in a patient in which, when external stimuli are applied, the patient does not show any signs of recovery or response.
Some clinical manifestations of coma include:
Unable to wake the patient up No intentional actions and movements of the patient Easy to confuse with a sleeping patient When performing To stimuli, even painful stimuli, the patient is still unresponsive. Coma needs to be diagnosed promptly because it can lead to death if emergency treatment is delayed. In case patients receive early intervention, they can fully recover within 2-4 weeks. Therefore, in order to save the patient's life, finding the exact cause of the coma is extremely important, making a great contribution to the successful treatment of this medical condition.
2. Cause of coma

Some common causes of coma are found clinically:
Due to cerebrovascular damage: can be cerebral infarction or cerebral hemorrhage, subarachnoid hemorrhage causing coma. Patients often present with coma, focal paralysis of a body part accompanied by signs of cardiovascular disease. Due to infection or meningitis: some diseases can have signs of infection and meningitis such as encephalitis, cerebral thrombophlebitis or malignant malaria. Caused by convulsions: convulsions can appear in many different conditions such as epilepsy, hypoglycemia, eclampsia in pregnant women, brain tumor or brain abscess, causing mass shock as well. lead to convulsions in the patient. Due to a number of metabolic disorders: typically diabetic endocrine disease, coma occurs in many forms such as coma with increased osmotic pressure, coma with ketoacidosis or hypoglycemia. Diseases such as liver disease, hyperuricemia syndrome, electrolyte disturbances including hyponatremia, hypokalemia, or hypothyroidism, adrenal insufficiency, and polyglandular failure are also causes of coma. Caused by poisoning: usually in clinical practice, patients are poisoned with sleeping pills, opioid pain relievers or toxic chemicals such as drugs, organophosphates, alcohol,... coma phenomenon. Caused by traumatic brain injury: patients with traumatic brain injury leading to brain contusion often have a coma that lasts from the time the patient is traumatized until the patient wakes up for the first time, coma in a state of unconsciousness. This is often accompanied by a subdural hematoma.
3. Diagnosis of coma
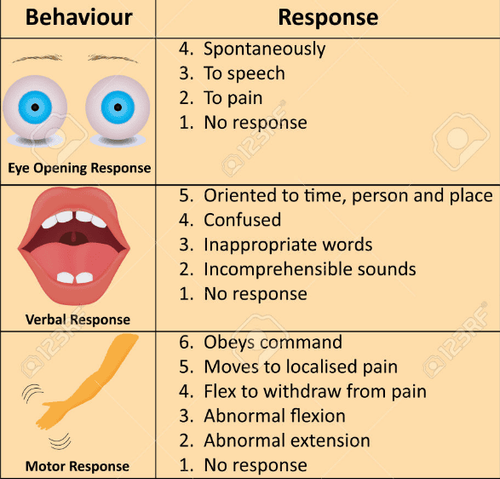
Diagnosis of coma should be based on clinical and subclinical:
Clinical:
Functional and physical symptoms include loss of consciousness, inability to wake up. In particular, the state of consciousness loss was assessed by the doctors using the Glasgow scale based on 3 main factors that need to be investigated, which are eye-opening response, motor response and speech response, the maximum score of the scale. Glasgow score is 15 points.
Subclinical:
Some subclinical tests need to be done to diagnose and find the cause of coma, including:
Liver function tests, kidney function tests, electrolytes, blood glucose levels, blood calcium levels . Blood tests 10 Urine tests Computed tomography or cranial magnetic resonance imaging to see how much brain structures are damaged. A lumbar puncture is performed in patients with headache, fever, and suspected CNS-level infectious disease. EEG measurement to examine the electrical activity in the brain, from which it is possible to evaluate coma due to diseases of brain infections, brain metabolic disorders or convulsions. In the face of a comatose patient, it is necessary to control a number of issues such as:
Respiratory function: the patient needs to open the airway to aspirate sputum, remove foreign objects from the pharynx, provide oxygen through the nose or a mask. oxygen, intubation, or artificial ventilation. Circulatory function: patients can use drugs to regulate blood pressure and prevent cardiovascular collapse and shock in necessary cases.

Prevent cerebral edema, increase intracranial pressure by increasing ventilation for the patient, lying with the head about 20° - 30° above the bed, intravenous infusion of some solutions such as Mannitol or Sodium Chloride 3% . Anticonvulsants: Use anticonvulsants such as Diazepam 10mg IV or Phenobarbital IM. Hemodialysis, detoxification by some means such as intravenous infusion of hypertonic sugar solutions, use of some drugs with Naloxone antagonists in patients with opiate poisoning. Some other management such as rehydration, electrolytes, urinary catheterization, anti-ulcer, occupational therapy, eye protection, anti-inflammatory vascular thrombosis, correction of hyperthermia or hypothermia, parenteral or intravenous feeding to ensure patient energy.
Coma is a danger sign that should not be ignored clinically because it may be a warning of a medical condition that is progressing to a severe stage. Patients admitted to the hospital because of a coma need to be treated promptly, find and detect the cause of the coma for the most effective treatment.
The Emergency Department of Vinmec International General Hospital operates 24/24 on all days of the week, including Saturday and Sunday as well as holidays of the year. The team of emergency doctors and nurses at the Department are professionally and thoroughly trained, able to receive and handle urgent cases of patients, and always coordinate with all specialties in a timely manner. fast.
With modern equipment and a team of experienced doctors, the Emergency Department has conducted emergency and saved the lives of serious and complicated patients. At the same time, patients at the Emergency Department are always coordinated care by many other specialized specialties (Team Base Care). Therefore, at the Emergency Department, patients will be examined, diagnosed, accurately and quickly, with high reliability and intensive treatment right from the emergency stage to help them quickly get out of the critical stage. dramatic and stable.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.