This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Cardiology & Thoracic Surgery doctors - Cardiovascular Center - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.Tetralogy of Fallot is the most common cyanotic congenital heart disease, accounting for about 10% of congenital heart diseases. This heart disease causes changes in the structure of the heart.
1. Congenital heart disease
Congenital heart disease in children (or congenital heart defects) are abnormalities of the heart that occur in the fetus. Because the heart structure is defective, the function and activity of the heart is affected, blood circulation in the body works abnormally.
Congenital heart disease in children is the most common form of birth defect and the leading cause of death from birth defects. Currently, thanks to ultrasound technology, congenital heart defects can be detected at 18 weeks of pregnancy.
2. What is Tetralogy of Fallot?
Tetralogy of Fallot is a common congenital heart disease in our country as well as worldwide. The incidence is 10% of all congenital heart diseases. It is also one of the most common cyanotic congenital heart diseases, accounting for 75% of cyanotic heart diseases in children over 2 years of age.
The disease often shows early cyanosis right from the first months after birth, with gradual progression with age, greatly affecting the physical, mental and operational development of the child. Without early surgical intervention, children with tetralogy of Fallot often die before adulthood from many serious complications caused by severe hypoxia. Children can die from acute hypoxia or from infective endocarditis, cerebral thrombosis, brain abscess.
Because of the severe nature of the disease, tetralogy of Fallot needs to be diagnosed as soon as possible, assessing the severity of the disease based on clinical, echocardiography and cardiac catheterization, thereby posing the problem of intervention. timely surgery, help children lead a normal life.

Tứ chứng Fallot cần phải được chẩn đoán càng sớm càng tốt nhằm can thiệp ngoại khoa kịp thời
3. Symptoms of tetralogy of Fallot
Tetralogy of Fallot includes 4 lesions Right ventricular outflow tract stenosis: The relationship between the right ventricle and the lung is narrowed, causing blood flow to the lungs to decrease. The main narrowing area is just below the pulmonary valve, causing this muscle to thicken. The pulmonary valve can also become narrowed. Ventricular septal defect: There is a hole between the right and left ventricles of the heart. Aorta deviates to the right and "rides" just above the ventricular septal defect: The aorta is often heavily displaced to the right and is often located just above the ventricular septal defect. Right ventricular hypertrophy: The right ventricular muscle is thicker than normal due to outflow obstruction. Recognizing children with heart disease tetralogy of Fallot Cyanosis of the skin and mucous membranes is the main sign. The time of appearance is not certain, it may be immediately after birth (if tight) or later (after 4-6 months). Cyanosis increases with exertion (cry, suckling, etc.). The degree of cyanosis more or less often depends on the degree of pulmonary stenosis. Shortness of breath, fatigue on exertion. Signs of squatting when the child is walking: the child suddenly squats down, raises his buttocks, lowers his head, and hugs his knees during exertion. Syncope due to lack of brain oxygen. Thirst due to increased blood concentration. Cupped fingernails, clubbed fingers and toes, appear after 2-3 years. There are many red spots in the eye conjunctiva. Slow physical and mental development. Non-cyanotic: Systolic murmur due to ventricular septal defect and funnel stenosis, can be heard along the left sternal border and the patient is not cyanotic (clinical signs of tetralogy of Fallot 4 are not cyanotic similar to a small foramen ventricular septal defect). ).
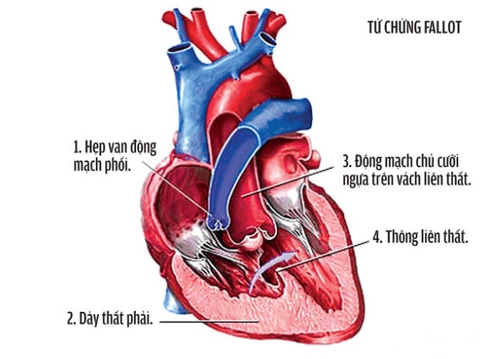
Tứ chứng Fallot bao gồm 4 tổn thương
Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital has routinely performed patients from small children to adults with congenital heart disease tetralogy of Fallot and achieved very positive results with a success rate of surgery up to Up to 95%, the rate of pulmonary valve preservation is high. (If pulmonary valve preservation cannot be achieved during complete surgical repair of tetralogy of Fallot, most patients require multiple hospitalizations in their lifetime for biological pulmonary valve replacement every 8-10 years.)
The surgeries are performed by a team of highly qualified doctors with many years of experience in the field of cardiovascular surgery. Along with that is the support from a system of modern equipment and machinery invested by the hospital to serve the surgery: Maquet's HR20 artificial heart and lung system, Avance CS2 Anesthesia Machine, R860 ventilator of GE, the world's most modern IGS730 Hybrid Operating Room
The advantages of tetralogy of Fallot congenital heart surgery are:
After the repair in the heart, the oxygen level in the blood increases and the patient's symptoms decrease. Helps restore cardiovascular functions, prolonging patient's life
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.