This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Internal Medicine Oncologist - Internal Oncology Department - Vinmec Times City International Hospital. The doctor has extensive experience in the examination, diagnosis and treatment of cancers.Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common type of primary liver cancer and usually occurs in people with chronic liver disease, such as cirrhosis from hepatitis B or hepatitis C infection.
1. What is hepatocellular carcinoma?
Hepatocellular carcinoma is a type of cancer that begins in the liver. It is different from "secondary" liver cancer, where cancer cells from other parts of the body have spread to the liver. If detected early, the patient will likely be cured by surgery or transplant.Trắc nghiệm: Làm thế nào để bảo vệ lá gan khỏe mạnh?
Làm test trắc nghiệm kiểm tra hiểu biết về gan có thể giúp bạn nhận thức rõ vai trò quan trọng của gan, từ đó có các biện pháp bảo vệ gan để phòng ngừa bệnh tật.2. Who is at risk for HCC?
It is difficult to pinpoint the exact causes of all cases of hepatocellular carcinoma, but in certain groups of people there is a higher chance of developing hepatocellular carcinoma than with hepatocellular carcinoma. ordinary people. The risk is higher in the following groups of people:People with long-term liver disease, patients with cirrhosis: Cirrhosis occurs when liver cells are damaged and replaced by fibrous tissue. It is rooted in causes such as hepatitis B or C infection, alcohol consumption, certain medications, and too much iron stored in the liver.
People with cirrhosis from hepatitis B or hepatitis C infection : Hepatocellular carcinoma can start after hepatitis . To determine whether a patient has hepatitis B or C virus in the body, a blood test is required.
People with a habit of drinking regularly and people with accumulation of fat in the liver: Drinking more than two glasses of alcohol a day for many years increases the risk of hepatocellular cancer. The more alcohol you drink, the higher your risk of disease.
Obesity and diabetes: These are two conditions that increase the risk of liver cancer. Obesity can lead to fatty liver and can lead to hepatocellular carcinoma. For patients with diabetes, the higher risk of HCC may be due to high insulin levels in the patient's body leading to liver damage.

Người béo phì có nguy cơ ung thư gan
3. Symptoms of hepatocellular carcinoma
Patients may not have any symptoms when HCC is in its early stages. As the cancer progresses, the patient may have one or more of the following symptoms:Pain in the right upper quadrant and upper quadrant Sensation of a mass or heaviness in the epigastrium Bloating or distention Loss of sensation appetite and feeling of hunger Weight loss Weakness or extreme fatigue Nausea and vomiting Yellow skin and eyes Weak bowel movements, dark stools and urine Fever.
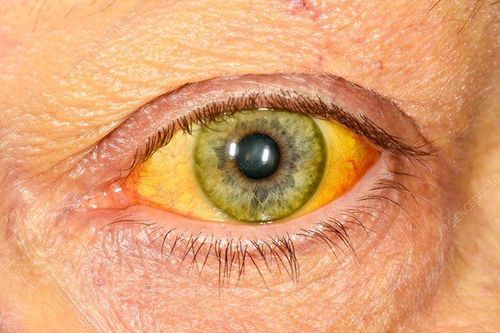
Dấu hiệu da và mắt vàng
4. How to diagnose hepatocellular carcinoma
Tests and imaging used to diagnose hepatocellular carcinoma include:Blood tests to measure liver function : Your doctor will take a blood sample to check for a protein called AFP in the sample. are not. Newborns often have high AFP levels, but it drops in most people soon after birth. If there is a high level of AFP in the blood, it could be a sign of liver cancer. Imaging tests like CT and MRI: Your doctor will likely do an ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI to look for tumors in your liver. Ultrasound, CT scan, MRI to see the liver Liver biopsy: in some cases, the doctor will take a sample of liver tissue and examine it under a microscope for cancer cells. This can be done by taking some liver tissue with a needle that has been placed through the skin and inserted into the patient's liver. Before the procedure, the patient was anesthetized in that area so that he would not feel pain when taking the biopsy sample.
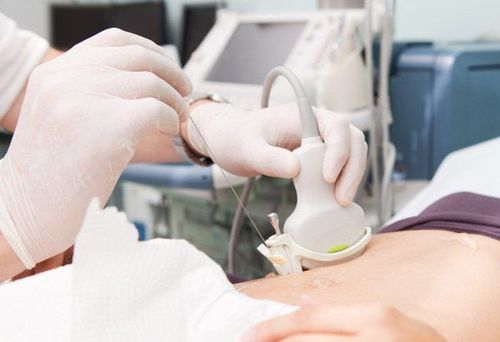
Sinh thiết gan giúp chẩn đoán ung thư biểu mô tế bào gan
5. Treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma
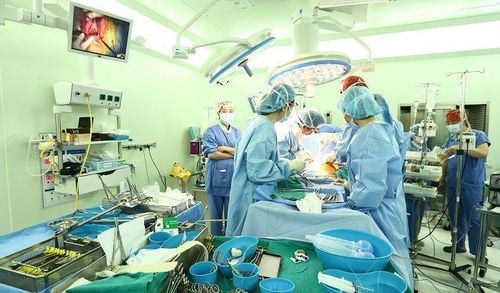
Depending on the size and location of the cancer cells, the liver's ability to function, and the patient's health conditions, the doctor will choose the right treatment for each patient. Commonly used treatments include:5.1 Surgery Surgery to remove the cancer and a portion of the healthy tissue surrounding it may be an option for people with functional early-stage liver cancer. normal liver function.
Liver transplant surgery is removing the entire liver and replacing it with a healthy liver from a donor. This may be a viable option if the patient's cancer cells have not spread beyond the liver.
Liver transplant is a major surgery and a donor liver needs to be taken from someone with the same blood type and similar body size as the recipient. After a liver transplant, a patient may need to stay in the hospital for up to 3 weeks after surgery and it can take 6 months to a year to return to a normal lifestyle. After the transplant, the patient will need to take medication to prevent the body from rejecting the new liver.
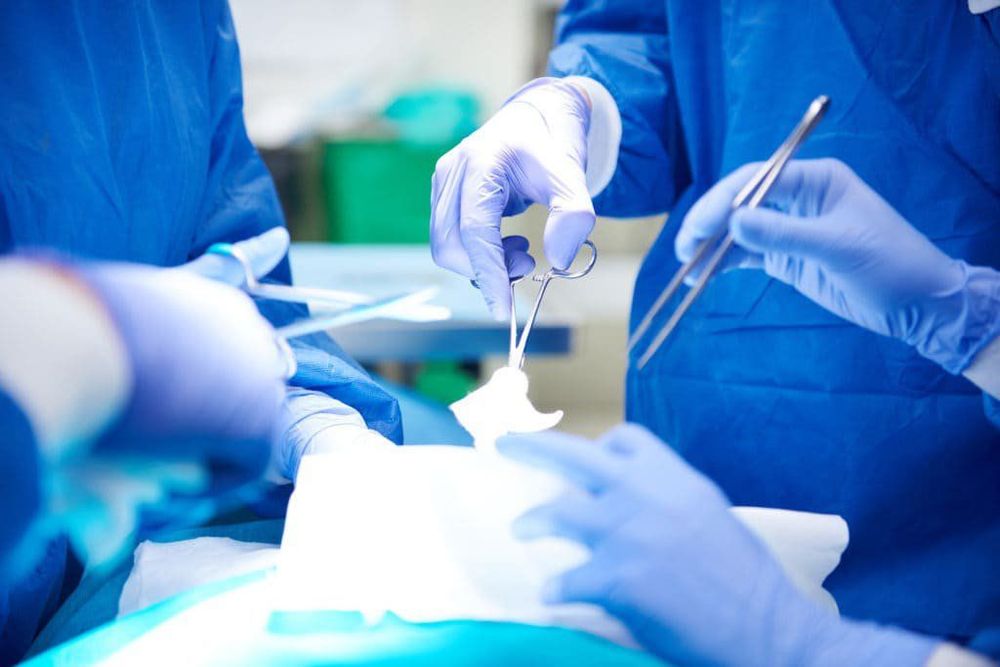
Phẫu thuật loại bỏ ung thư
In this method, the doctor destroys the tumor by freezing it with a thin metal probe. Once the patient is under anesthesia, the doctor places a probe into the tumor and delivers a cold gas that kills the cancer cells. A similar method, called radiofrequency ablation, uses an electric current to destroy cancer with heat.
5.3 Radiation Therapy Radiation therapy using energy from X-rays or protons may be recommended if the patient is unwilling or unable to have surgery. Your doctor will use a specialized type of radiation therapy, called body-positioning radiation therapy (SBRT), which involves focusing multiple beams of radiation simultaneously at one point in the body. There are two types of radiation therapy that can be used to treat HCC:
External beam radiation therapy: The patient will lie on a table while the radiotherapy machine will deliver radiation beams to specific points on the chest or belly. Internal radiation therapy: The doctor injects small radioactive particles into a blood vessel to the liver. These radioactive particles block or destroy the blood supply to the tumor in your liver. Radiation therapy can cause side effects such as nausea, vomiting, or fatigue, but these symptoms should go away when treatment is complete.
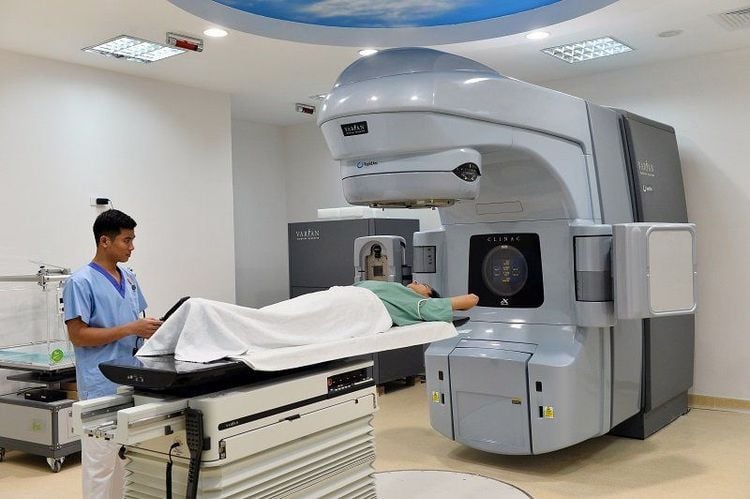
Phương pháp xạ trị giúp điều trị ung thư gan
Patients usually receive chemotherapy in an outpatient setting, ie the patient does not need to stay overnight in the hospital. Common side effects are nausea and vomiting, loss of appetite, fever and chills, headache and weakness, possible infection, bruising, bleeding, and fatigue.
5.5 Percutaneous ethanol injection The doctor will first perform ultrasound to determine the location of the tumor, then use a fine needle to inject ethanol to destroy cancer cells. When performing this operation, the patient will be given local anesthesia to avoid pain.
5.6 Drug Targeted Drug Targeted Drug Therapy is a method of using drugs to attack specific points in cancer cells to slow disease progression in people with advanced liver cancer. The therapy also stops the growth of new blood vessels or proteins that help tumors grow.
Side effects may include: fatigue, rash, decreased appetite, diarrhea, pain, bleeding, blistering of the hands, and inflammation of the stomach or intestines.
5.7 Immunotherapy Immunotherapy may be an option for treating advanced liver cancer. Doctors use drugs that stimulate the patient's immune system so that it finds and destroys cancer cells. Immunotherapy drugs are called tumor cell growth inhibitors. Side effects of this procedure can include: fatigue, fever, rash, decreased appetite, pain, and autoimmune reactions involving the lungs, liver, intestines, kidneys, and other organs.
For some people, treatment makes the cancer go away completely. But for others, the cancer may not go away completely or may return, so regular treatment is needed to keep it under control for as long as possible. Patients may not have control of their cancer, but they can control their lifestyle choices. Joining a support group or requesting care after treatment is essential for patients to maintain a healthy and optimistic life.

Liệu pháp miễn dịch trong điều trị ung thư
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Article reference source: mayoclinic.org, webmd.com