This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor II Le Thanh Cam - Department of Pediatrics - Neonatology - Vinmec Danang International General Hospital. Uncle has 15 years of experience in diagnosis & treatment of pediatric diseases; She used to work at the Pediatric Department - Da Nang Hospital and Da Nang Center for Obstetrics and Gynecology. His strength is in the diagnosis and treatment of pediatric pathologies, resuscitation, pediatric emergency.
Hand, foot and mouth disease is an acute infectious disease caused by a virus, which is common in children (over 90%). The disease is usually characterized by fever, sore throat, and a blistering rash on the hands, feet, and mouth, and often progresses to ulcers. These lesions can be on the tongue, gums, and inside the cheeks. Many patients are misdiagnosed with other skin diseases such as impetigo, chickenpox, allergies, ... leading to wrong treatment methods and leading to the spread of the disease.
1. Pathogens
1.1. Definition Hand, foot and mouth disease is caused by a group of viruses belonging to the Enterovirus group. Enteroviruses include four types: poliovirus, Coxsackie A virus (CA), Coxsackie B virus (CB) and Echovirus. The serotypes of species A include: EV68, EV71, EV76, EV89, EV90, EV91 and EV92. While other EV serotypes are under the Enterovirus B or C subspecies.EV71 type is one of the causative agents of HFMD and is sometimes capable of causing central nervous system disease. The pathogenicity of type EV71 has been demonstrated for the first time (1969) when it was isolated from the central nervous system of some cases in California (USA).
Coxsackievirus species belongs to the family Picornaviridae including 29 types. They differ from other enteroviruses in their ability to cause disease in mice, where other enteroviruses are rare or absent. They are divided into 2 groups: Group A and Group B have different pathogenicity in mice. They cause many different diseases: Coxsackie A causes pharyngitis, skin rashes, hand, foot and mouth disease, bleeding conjunctivitis, aseptic meningitis...,Coxsackie B causes myocarditis in infants , upper respiratory tract infection, pericarditis, endocarditis...
Researchers have also reported that the EV71 virus type appeared in Taiwan in 1968 as well as appeared in other countries. Southeast Asia such as: Philippines, Indonesia, Singapore. Although this is not a new type of enterovirus, the characteristics of this virus type are very virulent and are likely to damage the central nervous system, causing severe clinical conditions and consequences. bad, moreover, our country is located in this area, so we need to be alert and cautious when HFMD appears.
1.2. Virus morphology Spherical, 27-30 nm in diameter. The capsid consists of 60 subunits, without an outer layer. Inside contains RNA, which is the genetic component, replication and infection of the virus. 1.3. The viability of the virus in the external environment The virus is excreted to the outside from feces, sneezing, and runny nose. Virus is inactivated by heat 560C within 30 minutes, ultraviolet rays, gamma rays. The virus is tolerant to pH with a broad spectrum from 3-9. Inactivated by: 2% Sodium hyprochlorite (Javel water), Free Chlorine. No or little inactivation by lipid-soluble substances such as: Alcohol, Chloroform, Phenol, Ether. At a cold temperature of 40C, the virus can live for several weeks.

2. Viral pathogenicity
2.1. Epidemiological characteristics 2.1.1. Distribution by time The disease usually occurs all year round, develops in 2 waves: March - May and September - December.2.1.2. Geographical distribution Hand, foot and mouth disease occurs all over the world. In recent times, hand-foot-and-mouth disease is mainly caused by Enterovirus 71 in Southeast Asian countries. The 1998 Taiwan outbreak is considered a major epidemic with more than 100,000 people infected, more than 400 children hospitalized with complications in the central nervous system, up to 78 cases of child deaths.
In Vietnam, hand, foot and mouth disease is common all year round in most localities in the country; In some southern provinces, the number of cases is concentrated from March to May and from September to December.
2.1.3. Distribution by age The disease is often acquired in children under 10 years old, more often in children under 5 years old, concentrated in under 3 years old, with a peak in children 1-2 years old.
2.1.4. Infectious origin The source of the disease is sick, healthy people who carry the virus in secretions from the nose, pharynx, throat, saliva, secretions from burns or feces of the patient. Infectious from the incubation period (3-7 days) before the onset of the disease and the transmission period lasts until the mouth sores and blisters are gone, most contagious during the first week of the disease.
2.1.5. Mode of transmission Hand-foot-and-mouth disease is transmitted by the “fecal-oral” route and by direct contact, but is mainly spread by direct contact with secretions from the nose, pharynx, throat, saliva, secretions from other organs. Burns or contact with secretions and excreta of the patient on living utensils, toys, furniture, floor. Especially when patients have respiratory diseases, sneezing, coughing and talking will create favorable conditions for the virus to spread directly from person to person.
2.1.6. Susceptibility and immunity Hand, foot and mouth disease has a high susceptibility, everyone is susceptible to the virus that causes hand, foot, and mouth disease, not everyone infected with the virus has symptoms, but most people with the disease have symptoms. hidden form, no symptoms, this is a dangerous source of infection; The disease is common in children under 15 years old, especially those under 5 years old with a higher incidence.
People of all ages can be infected with Enterovirus but not all get sick, the disease only occurs in bodies that do not have a strong enough immune system to fight Enterovirus. Statistics show that babies, children and even teenagers and adults who are not immune can get the disease.

From sepsis, viruses to oral mucosa and skin. The incubation period usually lasts from 3 to 7 days.
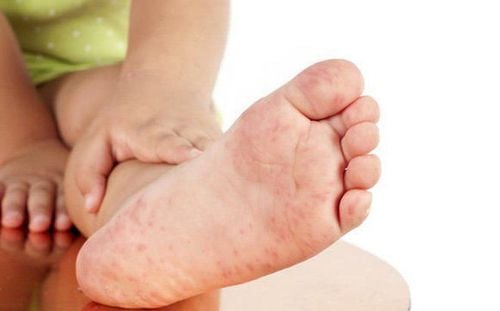
2.2.2 Manifestations of HFMD The initial manifestation is fever, then blisters appear on the oral mucosa (in the gums, tongue, inside the cheeks) and a rash begins to appear on the hands, foot. These erythema may form blisters. The hallmarks of HFMD are usually non-pruritic and do not appear on the palms of the hands or soles of the feet. Thus, the rash and blisters mainly appear on the hands, feet and mouth, so it is called HFMD. In addition, in rare cases, it can appear in some other places on the body such as the buttocks.
The blisters in the mouth often burst and cause ulcers, making the child painful, cry a lot, eat poorly or fear not to eat, so the child loses weight quickly. If the blisters on hands and feet break, if not kept clean, it can lead to a bacterial infection that causes festering and makes the disease more complicated. Most cases of HFMD will recover, but there are a few, if the cause of the disease is EV71, the disease may become more complicated, especially when the virus damages the central nervous system, which will show a disease. Meningitis typically presents with high fever, headache, stiff neck, nausea, and vomiting.
2.2.3. Summary of manifestations of mouth ulcer disease: The appearance of blisters with a diameter of 2-3 mm It is often difficult to see the blisters on the oral mucosa because it ruptures very quickly to form ulcers, the child is very painful when eating, increased salivation. Blisters: From 2-10mm, gray, oval. Blisters of the buttocks and knees often appear on an erythematous background. Blisters of the palms and soles may be raised above the skin to the touch or hidden under the skin, usually painless. The disease may present atypically such as: blisters very rarely interspersed with erythema, some cases only show erythema and no bullous manifestations or only simple mouth ulcers. The prognosis for HFMD depends on whether the etiology is Enterovirus A16 or EV71. If caused by Enterovirus A16, the disease is usually mild and can resolve on its own after 7-10 days, but due to EV71, there can be dangerous complications such as pneumonia, myocarditis or meningitis, even death. for sick people.
2.2.4. Differential diagnosis with some similar diseases 2.2.5. Complications
Common complications are: meningitis, meningoencephalitis, acute flaccid paralysis, myocarditis, acute neurogenic pulmonary edema Complications can be combined such as: Meningoencephalitis, edema pneumonia and myocarditis in the same patient. These complications are often fatal and progress rapidly, possibly within 24 hours. According to studies in Taiwan, serious complications are often caused by Enterovirus 71.
3. Laboratory diagnosis

Gathering a team of leading pediatricians: including leading experts with high professional qualifications (professors, associate professors, doctorates, masters), experienced, worked at major hospitals such as Bach Mai, 108.. Doctors All are well-trained, professional, with a mind - range, understanding young psychology. In addition to domestic pediatric specialists, the Department of Pediatrics also has the participation of foreign experts (Japan, Singapore, Australia, USA) who are always pioneers in applying the latest and most effective treatment regimens. . Comprehensive services: In the field of Pediatrics, Vinmec provides a series of continuous medical examination and treatment services from Newborn to Pediatric and Vaccine,... according to international standards to help parents take care of their baby's health from birth to childhood. from birth to adulthood Specialized techniques: Vinmec has successfully deployed many specialized techniques to make the treatment of difficult diseases in Pediatrics more effective: neurosurgery - skull surgery, stem cell transplantation. blood in cancer treatment. Professional care: In addition to understanding children's psychology, Vinmec also pays special attention to the children's play space, helping them to have fun and get used to the hospital's environment, cooperate in treatment, improve the efficiency of medical treatment.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.