This is an automatically translated article.
Laparoscopic pituitary surgery is the most common surgery used to remove pituitary tumors. Using endoscopic devices, the neurosurgeon removes the tumor with minimal trauma.
To do so, patients need to be examined and properly diagnosed, properly consider indications for pituitary tumor surgery before intervention.
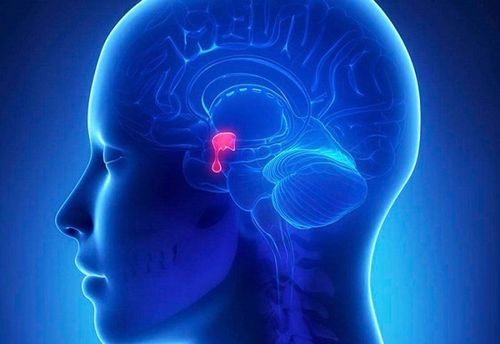
1. What is a pituitary tumor?
Pituitary tumors, also known as adenomas, are benign, noncancerous growths from the pituitary parenchyma cells that make up the majority of cases of pituitary adenomas. Less than 1% of pituitary adenomas are cancerous in nature.
The effects of a pituitary tumor may be structural or functional, or both. Specifically, a large pituitary tumor can put pressure on the optic nerve and affect vision. It can also cause damage to the surrounding normal pituitary tissue and lead to a deficiency in some or all of the hormones produced by the pituitary gland. Even large pituitary tumors also compress the surrounding brain parenchyma.
On the other hand, although rare, a pituitary adenoma can still produce abnormal hormones. The most common is a prolactin-producing pituitary tumor. Others produce steroid hormones, which cause Cushing's disease, or growth hormone, which causes acromegaly.
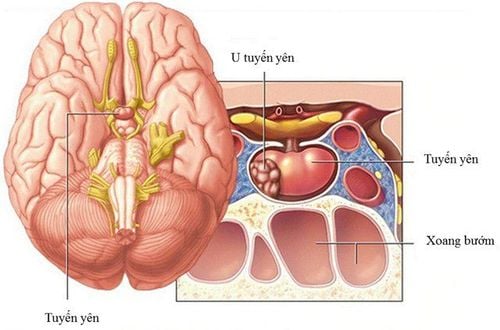
U tuyến yên thường lành tính, hiếm khi là ác tính
2. Endoscopic pituitary surgery: Indicated when?
A pituitary tumor if discovered incidentally and not causing any effect then only need to be monitored. Meanwhile, pituitary tumors with the following characteristics should be considered for surgery for pituitary tumors:
2.1. Visual influence
If the pituitary tumor is too large, it may press on the optic nerve located just above the pituitary gland. This can affect vision and can cause any of the following symptoms:
Pituitary tumors narrow the field of view. The patient feels like he is looking down a tunnel. This usually affects one eye more than the other. Pituitary tumors reduce vision. The patient cannot clearly see the details of pictures or words. Large tumors can cause double vision but are very rare.
2.2. Hormonal disorder
Pituitary adenomas are often found in the background because they cause an overproduction of a specific hormone. In contrast, some other pituitary adenomas can also produce more than one hormone at the same time.
The three most common types of hormone overproduction adenoma are:
Prolactin-secreting pituitary adenoma Tumor of the pituitary gland that overproduces the hormone ACTH, which in turn increases the release of cortisol in the adrenal glands, causing Cushing's disease. Pituitary tumors secrete growth hormone, causing acromegaly. There are a few pituitary tumors that produce other hormones, but they are much rarer.
Pituitary adenomas that do not produce hormones are called inactive pituitary adenomas. This condition leads to hormone deficiency symptoms as the tumor presses on the remaining pituitary gland. This condition is often diagnosed late because it does not produce specific symptoms when there is an excess of hormones.
2.3. Causing pressure
A pituitary tumor can also be detected when an increase in its size has an effect on other functions in the brain in addition to limited vision.
For example, pituitary tumors can be so large that they block the flow of cerebrospinal fluid in the brain, leading to a condition called hydrocephalus or hydrocephalus.
Another example is a large pituitary tumor that increases cranial pressure, causing headaches, dizziness, hearing loss or other symptoms. If detected late, these symptoms become progressively worse, the brain parenchyma is compressed, which can lead to permanent loss of function.
2.4. Biopsy of pituitary gland
The removal of a small piece of cells from the pituitary gland for biopsy is one of the indications of pituitary endoscopy. Under the analysis of pathology, in addition to the above-mentioned characteristics, if the result is malignant, even though it is small in size, the patient also needs early intervention to remove the tumor.
Thus, when the patient has a pituitary tumor and has one of the above indications, it is necessary to arrange early laparoscopic pituitary surgery before the pituitary growth causes more serious complications. At the same time, any delay may cause the surgery to exceed the indications of the laparoscopic approach; Instead, the patient had to have an alternative intervention with craniotomy.
Sinh thiết là một trong những phương pháp điều trị u tuyến yên
3. What is the goal of laparoscopic pituitary resection?
The goal of pituitary tumor surgery is to safely remove as much of the tumor as possible. During this procedure, the surgeon must ensure that the delicate nerves and blood vessels in the area are not damaged and that the remaining brain parenchyma is intact in general.
The pituitary tumor surgery to remove the tumor not only helps to release the pinched part of the brain, especially the optic nerve, but also helps to re-establish the balance of secretion of pituitary hormones in the body.
Moreover, compared with surgical removal of pituitary adenomas by opening the skull cap, the laparoscopic approach to pituitary tumor also aims to provide optimal recovery time for the patient, minimize trauma as well as reduce trauma. to achieve the highest aesthetic effect.
4. Contraindications to laparoscopic pituitary resection
Similar to other surgical interventions, patients cannot perform laparoscopic pituitary tumor surgery if it is not possible to ensure that the surgery goes smoothly before. Specifically, the patient has cardiopulmonary disease or serious chronic diseases, is having an acute illness, has a hemostasis disorder, a history of allergy to anesthetics, poor quality of life or prognosis. limited long-term...
In terms of local expertise, there is no absolute contraindication to surgery for pituitary tumors, especially with laparoscopic techniques when interventions are minimal. However, some difficult cases, which need to be considered when appointing laparoscopic pituitary surgery, are on patients with facial and nasal deformities, no sphenoid sinus or too small sphenoid sinus, crooked septum or have an active ENT infection.
Laparoscopic surgery to remove pituitary tumors is considered the safest and most effective method in the treatment of pituitary tumors today. However, to know laparoscopic pituitary tumor removal: Indicated when? It is necessary to carefully consider and consider each case, avoid any contraindications before performing it to ensure convenience for the surgery as well as minimal trauma intervention on the patient.
Customers who have needs of examination and treatment can directly go to Vinmec Health System nationwide or contact for an appointment HERE.
MORE:
Are pituitary tumors dangerous? Symptoms of Pituitary Tumors Pituitary Tumor Surgery
Close-up of prostate cancer treatment with robotic laparoscopic surgery
In April & May 2021, when there is a need for examination and treatment of pituitary tumor at Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital, customers will enjoy double incentives:
- Free specialist examination
- 50% discount for customers with post-examination treatment indications. The program is limited to the corresponding technique of each hospital and to customers who perform this treatment technique for the first time at Vinmec.