This is an automatically translated article.
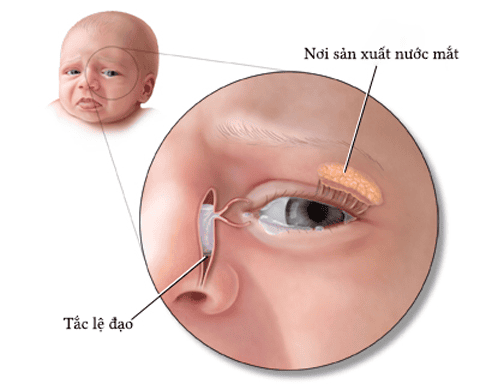
Occlusion of the lacrimal sac or occlusion is a complete obstruction of the physiological tear drainage path from the lacrimal sac to the nasal cavity causing frequent lacrimation and may be accompanied by complications, such as acute pouchitis. or chronic, conjunctivitis, recurrent corneal disease, decreased vision,... affecting the patient's quality of life.
1. What is the lacrimal sac or lacrimal function and how to recognize it?
When there is partial or complete obstruction of the tear drainage system, we call it lacrimal occlusion/tissue occlusion. When this phenomenon is encountered, tears do not flow down the nose as usual, but cause watery tears. From there, it irritates or can lead to chronic eye infections. The tear gland is located at the top of each eye, our tears will be secreted from this location. Every day, tears are still secreted continuously to help lubricate and protect the surface of the eyeball, then drain into 2 small tear points at the inner end, between the upper and lower eyelids. Then, tears will flow through the 2 tear ducts on the inside of the eyelids to drain into the tear sac located on the side of the bridge of the nose, then into the nose through the lacrimal duct. Tears can be reabsorbed or evaporated.
Tracheal obstruction occurs in 20% of births, but it only lasts until 1 year of age. Meanwhile, in adults, it only occurs due to eye infections, swelling due to trauma or possibly due to tumors blocking the tear duct. The phenomenon of tear duct obstruction in 20% of newborns is due to a thin membrane covering the lacrimal duct while in the fetus. If this membrane does not open automatically at birth, it will lead to congenital tear duct obstruction. In adults with rhinitis, sinusitis, this condition will stimulate scar tissue thereby also obstructing the tear duct. In addition, some other causes that may be encountered in people with blocked tear ducts are:
Abnormalities in the development of the skull and face causing malformations of the skull, face as well as tear ducts. This phenomenon is seen in people with Down syndrome or other disorders. Aging: The tear point of the elderly tends to narrow with age, which leads to blockage, making it impossible for tears to flow down the lacrimal duct. Injury to the nose: For example, in the case of nasal fractures, irritation of scar tissue and blocked tear ducts. Nasal polyps: Formed from the lining of the nose, nasal polyps can block the tear ducts. Conjunctivitis: Viral conjunctivitis can affect the lacrimal gland and lead to tear duct obstruction. However, this does not happen often. Tumors: Tumors can press on the lacrimal duct causing obstruction of the lacrimal duct. Some signs of blocked tear ducts:
When the tear duct is blocked, it can cause live tears. This means that tears are produced more frequently and more frequently than usual. This can be aggravated by a cold, sinusitis or out in cold air
A blocked tear duct can lead to an infection due to bacterial stagnation, so some of the symptoms of inflammation may be present. experience such as: Swelling, tender red in the corner of the eye, in the area between the eyes and nose. Recurrent eye infections, mucous discharge from the eyes, scaly eyelashes, blurred vision, tears with blood streaks or possibly fever.
The diagnosis of lacrimal occlusion is made by injecting fluid into the lacrimal system from the lacrimal point and monitoring for drainage. If this amount of fluid does not drain, you have blocked tear ducts. In addition, for a deeper diagnosis, you may also be assigned to perform a contrast X-ray or CT scan of the lacrimal system.
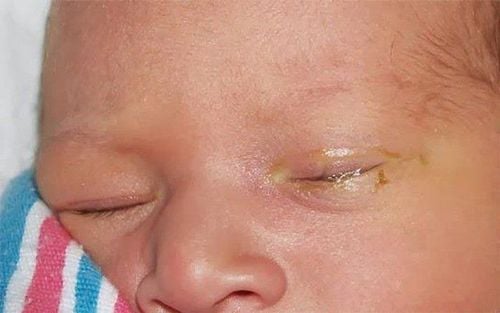
Tình trạng tắc túi lệ có thể làm cho mắt bị nhiễm trùng mãn tính
2. Laparoscopic lacrimal sac surgery
Laparoscopic lacrimal sacectomy is surgery to create a direct passage from the lacrimal sac to the nasal cavity to create a shortcut to conduct tears from the eye to the nose. Nasal sacral bypass is indicated when other methods have failed. In this surgery, the opening from the lacrimal sac to the nose is created from the side of the nose without having to make an external skin incision. It is contraindicated in patients with occlusion of the nasolacrimal duct with acute pouchitis or progressive lacrimal abscess. Or the general condition does not allow surgery.
2.1. Steps to perform laparoscopic lacrimal anastomosis Step 1: Anesthesia
Anesthetize the inner corner of the upper and lower eyelids, the anterior epiglottis with a vasoconstrictor anesthetic (can use 2% lidocaine mixed with adrenaline or drugs with similar effects) Anesthesia if the patient is young or uncooperative. Anesthetize the nasal mucosa by placing gauze impregnated with a local anesthetic such as 2% lidocaine. Place a nasal constrictor. Step 2: Technique
Put the light tube into the nose Dilate the lacrimal hole and the lacrimal canal Then insert the light tube through the lacrimal hole and into the lacrimal sac Cut the nasal mucosa Cut the mucosa corresponding to the lacrimal bone. Exposing lacrimal bone Osteotomy: Locate the lacrimal and thicker parts of the jawbone by moving the tip of the light guide and using a periosteal separator to determine the bone structure. First, remove the tear bone. Remove any bone fragments to avoid clogging the stoma later. Enlarge the bone hole. Partial resection of the jawbone (lateral branch) may be required. Lacrimal sac mucosal resection: Move the tip of the light tube to locate the lacrimal sac area. Use the tip of this tube to inflate the lacrimal sac and cut the mucosa. Cut the upper part of the lacrimal duct mucosa and lacrimal sac from bottom to top, in front of the guiding light source. If the lacrimal sac is dilated, resect the nasal mucosa horizontally. Avoid allowing the nasal mucosa to create an excess flap because this flap will block the opening. During surgery, it is necessary to use a suction tip to suck blood or mucus from the mucosa and lacrimal sac. The nasal mucosa and bone can be cut with conventional instruments or with a YAG or NdYAG laser. Place the silicone tube: Insert the tube from the lacrimal side, through the opening into the nose. Tie both ends of the tube in the nasal cavity.
2.2. Follow-up after laparoscopic lacrimal anastomosis Routine post-operative broad-spectrum antibiotics, combined with low-dose corticosteroids for 7-10 days Take medication to reduce edema, possibly in combination with systemic antibiotics Periodic monthly examination Withdrawal average tube after 3 months During the time when the tube has not been removed, it is possible to pump the test tube.
Possible complications and treatment
Whole body: Use broad-spectrum antibiotics within 5-7 days In eyes: Use a mixture of corticosteroids and antibiotics for 4 weeks Avoid blowing your nose for 5-7 days. Complications: Bleeding, if there is bleeding, it is necessary to endoscopy, check the bleeding site and stop the bleeding.

Sau khi thực hiện phẫu thuật thông túi lệ nội soi, cần theo dõi tình trạng bệnh nhân và tuân thủ theo hướng dẫn của bác sĩ để tránh gặp các biến chứng
To examine and treat eye diseases, you can go to the Eye specialist - Vinmec International General Hospital. The department has a comprehensive vision and eye health care function for children, adults and the elderly including refractive error testing, general examination, diagnostic ultrasound, laser treatment and surgery. In addition, ophthalmology also has the task of coordinating with other clinical departments in the treatment of pathological complications and eye injuries caused by accidents.
Why should you choose to examine and treat eye diseases at Vinmec International General Hospital?
Simple and quick procedure. Enthusiastic advice and support, reasonable and convenient examination process. Comprehensive facilities, including a system of clinics and consultations, blood collection room, dining room, waiting area for customers... The medical staff has high professional qualifications, style. Professional, caring way of working.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.