This is an automatically translated article.
Ureteral prolapse is dilation of the pseudocyst wall of the submucosal terminal urethral segment. This disease can occur at any age, but is more common in children. Laparoscopic dissection of ureteral prolapse is a commonly used treatment method in ureteral prolapse.
1. What is ureteral prolapse?
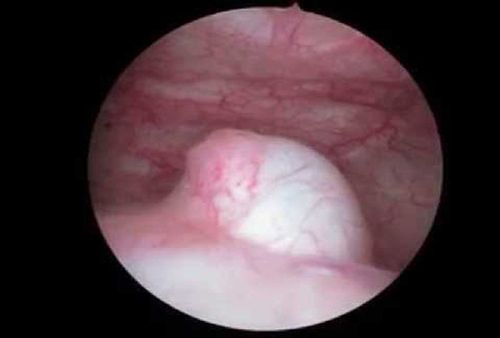
Prolapse of the ureter is a dilatation of the sac-shaped protrusion into the bladder lumen of the ureteral wall of the bladder. This disease is common when the ureter pours out of place, narrowing the point of emptying into the bladder. There are two types of ureteral prolapse: the protrusion is the lining of the bladder or the wall of the ureter.
2. Symptoms of ureteral prolapse
Prolapse of the ureter usually has very few symptoms, if any, it is usually pain, back pain or abdominal pain; Urinary tract infections; fever; painful urination; strong-smelling urine; bloody urine; frequent urination;
2.1 In children In children, symptoms such as: urinary tract infection: high fever, cloudy urine, growth retardation; urinary disorders; Difficulty urinating, frequent urination, painful urination, leaking urine.
2.2 In adults In adults, there may be a dull ache in the low back, sometimes increasing to a sharp pain like renal colic. Urinary tract infections present as recurrent acute or subacute cystitis, recurrent pyelonephritis, or pyuria. There are urinary disorders such as dysuria, urinary incontinence, especially dysuria. Frequent or intermittent dysuria causes chronic incomplete urinary retention.

Tiểu khó là triệu chứng của sa lồi niệu quản ở người lớn
3. Complications of prolapse of the ureter
The most important major complication of ureteral prolapse is damage and infection of the kidney. Prolapse of the ureter obstructs the outflow of urine, which can damage the kidneys as well as reduce the glomerular filtration rate.
Vesicoureteral regurgitation is very common if in a double ureteral kidney. Furthermore, with a single ureteral kidney, reflux can occur on the contralateral side. Can produce urinary stones.
4. Treatment of prolapse of the ureter
Ureteral prolapse can be treated with open surgery or laparoscopic surgery. Open surgery is a technique to cut the prolapsed sac and reattach the ureter to the bladder. Laparoscopic transvesticular surgery is performed by opening the prolapsed sac with an electric knife.
5. Laparoscopic dissection of ureteral prolapse is indicated for which cases?
Prolapse of the ureteric orifice alone or causing complications such as:
Urinary retention Cystitis Renal failure Hematuria Stones in the protrusion of the pouch Laparoscopic dissection of the protrusion of the ureter is contraindicated with:
Uncomplicated systemic diseases are treated such as blood clotting disorders, heart failure, diabetes, urinary infections... Urethral stricture. Hip stiffness.
6. How is laparoscopic dissection of ureteral prolapse performed?
6.1 Before surgery Before surgery, the patient is thoroughly explained about the advantages and possible complications.
For patients on oral anticoagulants, surgery will be performed 3 days after stopping anticoagulation, coagulation tests: prothrombine ratio has increased to the level of normal people; or the patient can be replaced with oral anticoagulants by parenteral anticoagulation.
At the same time, the patient is also asked to stop or change medication for cardiovascular disease, high blood pressure before surgery. Patients at risk of coronary insufficiency, arrhythmia, and respiratory failure should undergo more intensive tests before surgery.

Bệnh nhân mắc rối loạn nhịp tim cần được xét nghiệm chuyên sâu trước khi phẫu thuật
6.2 When performing surgery When performing surgery, the patient is placed on the operating table, buttock closes or slightly exceeds the lower edge of the operating table. The thighs are maximally flexed, but slightly flexed to the abdomen; The two maximum form thighs allow for easy side-to-side movement of the mower. The surgery begins with the technician placing the case through the urethra into the bladder.
Next, the technician locates the bag of prolapse, cuts open the bag, picks up stones in the pouch, if any.
6.3 Postoperatively After surgery, the patient was flushed continuously with isotonic saline solution until the urine was clear and given antibiotics for 3 days for systemic administration;
If you have cystitis or urinary tract infection before surgery, use systemic antibiotics for 1 week. After 6 hours of surgery, the patient can drink water and have a light meal. After 24 hours, eat and drink normally. After 24-48 hours, the urethral catheter was removed, the patient was discharged from the hospital, continued to be monitored and treated as outpatient.
Any questions that need to be answered by a specialist doctor as well as if you have a need for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, please book an appointment on the website to be served.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.