This is an automatically translated article.
The article was written by Dr. Le Tuyet Nga - Specialist I Pediatric Doctor at Vinmec Gardenia Clinic.Lactose intolerance occurs when the body cannot digest the lactose in milk. Children with lactose intolerance have symptoms of bloating, gas, and diarrhea. This situation recurs causing intestinal dysbacteriosis, absorption disorders, growth retardation for children. With infants and young children with lactose intolerance, parents need to know how to handle it properly to prevent dangerous complications, ensure that the child is still provided with adequate nutrients and develops normally.
1. What is Lactose?
Lactose is the main form of sugar found in milk and dairy products and is digested in the intestines with the help of an enzyme called lactase. The enzyme lactase is a substance that helps to cut the lactose molecule in half into two more easily absorbed components, galactose and glucose. Therefore, without or deficient in this enzyme, the child's body will not tolerate lactose, leading to a state where the lactose (not absorbed) will ferment and cause a series of unpleasant symptoms such as bloating. , nausea, diarrhea, abdominal pain,...2. What causes lactose intolerance?
There are four causes of lactose intolerance. Specifically as follows:Primary lactose intolerance: Most babies are born with a normal amount of lactase enzyme. However, as children grow older with a changed diet (less dairy products), so does lactose intolerance. Secondary Lactose Intolerance: Lactose intolerance can be caused by damage to the small intestine or digestive problems such as enteritis, stomach ulcers, ... that children have. Once these issues are resolved, the lactose intolerance should also go away. Congenital Lactose Intolerance: These are cases where a child is born normally with a deficiency of lactase enzyme (inherited from parents). Lactase deficiency: Common in premature babies. Because the amount of lactase enzyme usually thrives in the last 3 months of pregnancy before the baby is born. Therefore, in premature babies, the baby's digestive system may be unstable, not providing enough lactase enzyme. However, even in a normal newborn, the digestive system in the first 2 years of life does not fully activate the necessary digestive enzymes. The lactase enzyme needed for the digestion of lactose is only 70% active, making it difficult for children to digest products containing this sugar.

Có 4 nguyên nhân chính là không dung nạp lactose nguyên phát, không dung nạp lactose thứ phát, không dung lactose bẩm sinh và thiếu hụt men lactose.
3. Manifestations in children with lactose intolerance
Children with frequent flatulence and bloating: After each feeding or drinking milk, children often have a feeling of bloating, prolonged abdominal distension. Lactose that is not absorbed when reaching the colon is fermented anaerobically, creating a lot of gas in the abdomen. Children with prolonged diarrhea, loose, watery stools, mild sour smell. Occasionally, stools are mucusy, foamy, or bloody. Lactose, when not absorbed, is eliminated directly in the feces. In the colon, lactose is a strong water absorber. Here, lactose interacts with microorganisms, fermenting to make stools loose, mucus, effervescent, sour and acidic. Children with nausea, vomiting, regurgitation of milk: Flatulence, abdominal distension, poor ability to contain milk, food in the stomach of children, easily stimulated to push back into the esophagus causing vomiting. Babies cry more. Abdominal pain, cramps. Children often have expressions of arching their backs, clenched fists, and bent limbs. When your child has the above 5 symptoms, you need to immediately recognize the signs of lactose intolerance for immediate handling. Lactose intolerance for a long time makes digestive disorders worse, children reduce nutrient absorption, lack nutrients, stunted, slow growth. More dangerous, the longer it lasts, the severe damage to the digestive system, easily turning into chronic enteritis.4. What to do when your child is lactose intolerant?
For breastfed babies: Maintain breast milk for babies. Breastfeeding can be alternated with lactose-free formulas. Depending on the digestive disorder to decide whether it is necessary to change to lactose-free milk lines or not.For babies taking formula milk: It is recommended to use lactose-free formula (lactose free milk). Pay attention to the ingredients in the milk label and nutritional information when giving any type of milk to your baby. Avoid milk containing a lot of lactose such as cow's milk, goat's milk for babies.
For older children who have eaten solids: Limit the use of products containing a lot of lactose until the baby's digestive system is completely recovered. When children drink milk but have bloating, abdominal pain, diarrhea, it can first be improved by:
Give the child milk to drink at the same time as eating solid foods: Bananas, cereals, ... because solid foods are good. Slow absorption will make lactose intolerance better controlled. Give your child milk one spoon at a time, dividing the milk into small portions. Give your baby extra butter because it contains all the nutrients that milk has, but with less lactose. Give your child extra yogurt because yogurt also has many of the nutrients in milk, but the good bacteria in yogurt help digest the lactose. If the above symptoms persist, quickly take the child to see a doctor for examination and advice on a suitable diet, providing adequate nutrients for the development of the child. Consequences of lactose intolerance are severe malnutrition in children, poor appetite, and poor dietary habits, which slow down the recovery of intestinal mucosa. Therefore, parents absolutely must not be subjective when their children encounter this situation.

Với trẻ bú mẹ không dung nạp lactose, bạn cần tiếp tục cho bé bú mẹ xen kẽ với bú sữa ngoài không chứa lactose.
5. Common mistakes made when babies are lactose intolerant
5.1. Failure to comply with nutritional adjustments In many cases, babies are prescribed lactose-free milk to limit digestive disorders and diarrhea. Lactose-free milk is a line of milk that has limited lactose and/or added lactase enzyme to support the digestion of milk sugar. Lactose free milk still ensures to provide the necessary nutrients for the baby. Many mothers are concerned that lactose-free milk will not provide enough nutrients for the baby, so they do not comply with the treatment regulations. This affects the effectiveness of the treatment of lactose intolerance.5.2. Excessive abstinence According to the old concept, when a nursing infant has diarrhea, the mother can only eat "healthy" foods such as: Pork, green vegetables. However, according to the new scientific point of view, it is the most important nutrient supplement. Mothers should choose a variety of foods to ensure adequate nutrition for their children. Only limit unhealthy foods such as hot spicy foods, stimulants (alcohol, tobacco, coffee).
5.3. Confusing with other conditions With symptoms such as diarrhea, sour-smelling stools, it is easy for mothers to confuse them with other conditions such as digestive disorders due to intestinal dysbiosis or cow's milk protein allergy.
It is necessary to clearly distinguish the above conditions for appropriate treatment.
Lactose intolerance Babies have diarrhea after about 30 minutes - 2 hours after drinking breast milk or regular formula. The number of bowel movements depends on the amount of milk the baby drinks.
Cow's milk protein allergy Unlike lactose intolerance, a milk allergy can be life-threatening. Therefore, you need to see a doctor early and correctly diagnose the symptoms, especially in children. Milk allergy and lactose intolerance have a lot in common, but allergies are genetic.
Milk allergy is a condition in which a child's immune system fights against certain proteins contained in milk. That is, the body in these children is born with an allergy and cannot adapt to some proteins in milk. There are 2-3% of children under 3 years old are allergic to milk. Heredity is also a factor that causes milk allergy in children, that is, if one parent has been allergic to milk, about 50-80% of their children will also be allergic from childhood.
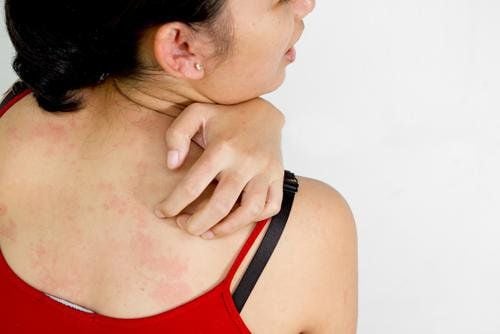
The culprits that cause allergic reactions in babies are certain proteins such as casein protein and whey protein in milk. Allergy to milk proteins can directly affect the digestive system and other parts of the body such as the skin and respiratory system. Allergies have two levels, the first is a rapid and sudden allergy such as vomiting, wheezing, red rash, swollen face, diarrhea, even the skin will become red if it comes in direct contact. with milk. Secondly, the reaction is slow, making children often uncomfortable, vomiting, stomach pain, bloody stools, slow weight gain, slow growth. The solution to this milk allergy is that the mother needs to know exactly which protein her child is allergic to on the label of dairy products to make the best choice.
Children with milk allergy have very obvious symptoms as soon as they drink cow's milk or foods made from cow's milk from a few minutes to a few hours. In addition to diarrhea, the baby may be accompanied by a rash, difficulty breathing,... These symptoms will disappear if cow's milk is stopped and switched to formulas containing hydrolyzed protein.

Trẻ dị ứng đạm sữa bò thường bị nhầm lẫn với không dung nạp lactose.
The severity of lactose intolerance symptoms varies from child to child. Therefore, the family should monitor to soon recognize and adjust the diet and milk selection accordingly.
Please follow the website: Vinmec.com regularly to update many other useful information.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.