This is an automatically translated article.
This article is professionally consulted by Resident Doctor of Pediatrics - Neonatology - Department of Pediatrics - Neonatology - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.
Neonatal pathological jaundice is a condition that needs to be examined and treated early by doctors at a pediatric hospital. If not treated in time, severe disease can cause many serious complications.
1. Overview of neonatal jaundice
Jaundice is quite common in newborns. In premature infants, 2-3 days after birth, jaundice often appears. In term infants, jaundice is quite rare and accounts for only about 25 - 30%. The cause of physiological jaundice in newborns is the accumulation of Bilirubin - the yellow substance produced when red blood cells are broken down and released. Jaundice is common in newborns because they have a high number of red blood cells, which are often broken down and replaced. Meanwhile, the newborn's liver is not mature enough to remove all bilirubin from the blood and thus causes jaundice. When babies grow up to about 2 weeks old, the liver will develop more fully to be able to process and filter out all bilirubin. Therefore, physiological jaundice in newborns will go away on its own without leaving any danger.
However, infants can have both physiological and pathological jaundice - a sign of an underlying disease. While physiological jaundice in newborns will clear up on its own after about 2 weeks, pathological jaundice requires long-term treatment by a specialist with various methods depending on the severity of the disease.
Trắc nghiệm: các chỉ số cần chú ý về sự phát triển thể chất của trẻ
Chiều cao, cân nặng của bé ở từng giai đoạn nên là bao nhiêu là bình thường, bao nhiêu là bất thường? Cùng ThS.BS Ma Văn Thấm điểm lại xem bạn đã nắm được các chỉ số phát triển thể chất của bé chưa nhé!The following content is prepared under supervision of Thạc sĩ, Bác sĩ y khoa, Ma Văn Thấm , Nhi , Phòng khám Đa khoa Quốc tế Vinmec Dương Đông(Phú Quốc)
2. Pathological Jaundice and Physiological Jaundice of Newborns
2.1. Physiological jaundice in newborns is common. Simple jaundice of the face, neck, chest and abdomen above the navel; Appears about 48 -72 hours after birth; It resolves spontaneously within 1 week for full-term infants and 2 weeks for premature infants; Do not combine other unusual symptoms; Dark or yellow urine and pale stools; The baby is still growing well and gaining weight evenly.
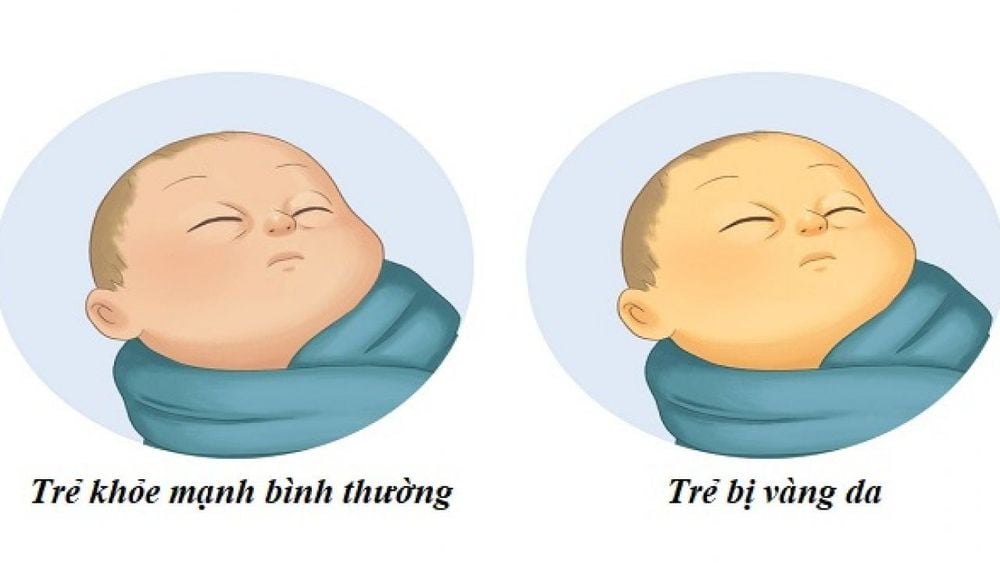

2.2. Warning signs of pathological jaundice in newborns Jaundice in newborns is considered pathological when there are abnormal warning signs as follows:
Very dark jaundice, whole body and eyes ; Appears early from the first day after birth; Does not resolve after 1 week in term infants and 2 weeks in preterm infants; There are other accompanying symptoms such as: Skipping or poor feeding, fever, crying a lot, lethargy, apnea, rapid breathing, change in body temperature, ... Bilirubin blood test is higher than normal.
3. Dangerous complications from neonatal jaundice
Neonatal pathological jaundice is a condition that cannot be ignored because it can lead to some serious complications such as:
3.1. Acute Cerebral Bilirubin An acute cerebral Bilirubin condition should be immediately considered when a child has jaundice in combination with the following signs:
Lethargy; Unfocused; Crying Quit suckling; High fever. Torsion Convulsions Doctors say Bilirubin is very toxic to the cells of the brain. Therefore, severe jaundice can cause bilirubin to enter the brain and cause many other serious complications.
3.2. Nuclear jaundice (Bilirubin encephalopathy) Newborns will have nuclear jaundice when the substance Bilirubin exceeds the allowable limit, causing the liver to not be able to excrete it in time and potentially seep into the brain. The result is brain damage that is irreversible. Therefore, if the neonatal pathological jaundice has been confirmed, it must be treated as soon as possible. Specifically, before 7 days postpartum to prevent the risk of brain damage.

4. Prevention of pathological jaundice of newborns
If neonatal jaundice is not detected and treated in time, it can cause neurotoxicity and lifelong sequelae of cerebral palsy, even death.
The mother's adherence to the doctor's antenatal care schedule is the best way to prevent neonatal jaundice. Especially pay attention to a reasonable diet and rest in the last months of pregnancy to avoid premature birth. When detecting abnormal symptoms during pregnancy, it is necessary to go to a medical facility immediately to be monitored by an obstetrician.
For cases of physiological jaundice in infants should be monitored. Breastfeed and sunbathe the baby properly every morning. However, if you see a lot of and prolonged jaundice in your baby, you should soon take it to a pediatrician for examination and treatment.
In short, parents need to know very well the warning signs of neonatal jaundice in order to closely monitor the baby. In particular, it is important to avoid the case that pathological jaundice is mistaken for physiological jaundice in newborns, thereby subjectively not treating it in time and leading to unfortunate consequences.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online.