This is an automatically translated article.
The article is expertly consulted by MSc, Dr. Huynh An Thien - Neurologist, Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine, Vinmec Danang International General Hospital.VII nerve palsy is a common disease of all ages, regardless of sex, and is not contagious. So what is the cause of the disease? Is 7th nerve palsy dangerous and how should treatment be oriented? Follow along in the following article.
1. What is the 7th nerve palsy?
Nerve VII is a motor nerve that controls facial movements. Peripheral cranial nerve palsy, also known as peripheral facial palsy, is a state of complete or partial loss of movement of the muscles of the half of the face, due to damage to the facial nerve. This condition is in contrast to central facial paralysis which is damage to the brain.Little is known that the facial nerve has a complex path from the central nervous system through the temporal and parotid glands to the muscles of the face. That is why the motor damage of the half face has many causes such as from the brain stem, in the VII nerve, in the stony bones or in the parotid gland...
Causes:
Central VII nerve paralysis : Typical facial paralysis due to localization in the skull causes cerebrovascular accidents, tumors of the central nervous system, and auditory nerve tumors. Peripheral nerve palsy: Damage to the VII nerve from the temporal bone outward is also known as Bell's facial paralysis, usually due to cold, or inflammation.
2. How is 7th nerve palsy diagnosed?
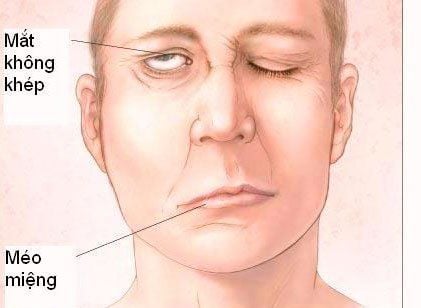
With VII nerve palsy, the diagnosis is mainly based on clinical signs. The doctor will ask specifically about the patient's case of facial paralysis, identify the lesion to help diagnose and locate the lesion through the appearance of facial paralysis, accompanying symptoms such as ear discharge, trauma, taste disturbances, decreased tear secretion...
Besides, the doctor can diagnose the disease clinically by:
Identify peripheral facial paralysis with characteristic signs of lesions lesions such as Charles bell sign, the patient cannot close his eyes At rest, the patient's face is asymmetrical, pulled to the healthy side, forehead wrinkles are erased compared to the opposite side, the eyebrows are drooped, The paralyzed side's edge is lowered relative to the other side, the cheeks are flat and bulging on expiration. For closed lesions, the doctor can see by the sign that when the eyelids are tightly closed, the eyelashes on the paralyzed side are longer than the healthy ones. In general, in order to accurately diagnose VII nerve palsy, the treating doctor needs to rely on factors of muscle tone at rest, study the muscle group in the face, and perform other physical examinations. Other m such as:
Ear examination: Finding the uvula, ear discharge and tympanic condition allows the diagnosis of the cause. Throat and neck examination: Palpate the face and neck to rule out a parotid gland tumor. Neurological examination: Look for other associated cranial nerve lesions. Patients with signs of 7th nerve palsy are not only clinically diagnosed, but also performed paraclinical tests to accurately determine the condition and cause of the disease.
Cranial magnetic resonance imaging with cerebral blood vessels to determine central or peripheral lesions Other tests: Blood count, Blood sugar, Sedimentation blood, Biochemistry...
3. Is VII nerve palsy dangerous?
VII nerve palsy can cause various serious sequelae such as:
Eye complications: conjunctivitis, keratitis, corneal ulcer, eyelid droop. These complications can be prevented with protective eye drops, glasses, complete or partial eyelid cartilage sutures. Synergism: manifests involuntary muscle contractions associated with involuntary actions such as edge pulling with eyes closed. Failure of treatment, rehabilitation can alleviate this discomfort. Posterior hemifacial spasm: This complication occurs in severe forms due to nerve damage with partial nerve redistribution. Crocodile tear syndrome: rare, presenting with tears when eating.
4. How to treat VII nerve palsy?
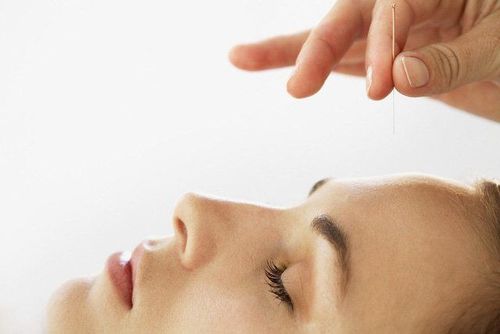
With the state of cranial nerve VII, treating doctors will treat medically and combine surgery to bring quick and comprehensive results to the patient. Depending on the case of peripheral or central paralysis, there are different treatment directions:
Peripheral paralysis VII: First of all, medical treatment is indicated, patients with 7th nerve palsy will be used early corticosteroids, high dose (1mg prednisolone/kg) after exclusion of contraindications (diabetes, tuberculosis, peptic ulcer, mental disorders...) In addition, special antiviral drugs can be used. for cases of viral infection or pain behind the ear, sensory disturbances in the face. Surgical treatments such as physical therapy, acupuncture, and facial exercises will bring comprehensive results to the patient.
Central paralysis VII: it is necessary to determine the cause of central damage: tumor, infarction or hemorrhage in the brain stem (where the nerve nucleus originates) ... to have the right treatment. For safe and effective treatment of VII nerve palsy, you can contact the neurology department of Vinmec International General Hospital to be assigned specific treatment for each case by doctors. fit.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.