This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Bui Ngoc Phuong Hoa - Department of Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Danang International General HospitalPolyneuritis is a disease that sounds quite strange but is common in the community but is not well understood. Symptoms of polyneuritis are diverse, sometimes vague, but can lead to dangerous effects for patients if not detected and intervened early.
1. What is polyneuropathy?
Polyneuritis is the result of damage to the peripheral nerves. Common symptoms are weakness, numbness, and pain in the arms and legs. Symptoms can also occur in other areas of the body.The peripheral nervous system is responsible for receiving signals from the external environment and sending it to the processing center, which is the brain and spinal cord (central nervous system); then, the reflexes from the center are sent to the organ systems also need to be thanks to the peripheral nerves.
Peripheral polyneuropathy is generally caused by trauma, infection, metabolic disorders, genetic abnormalities or exposure to toxins. Among them, the most common cause in public life is diabetes.
2. Symptoms of polyneuritis

Sensory nerves: have the role of perceiving sensations, such as hot and cold temperature, pain, vibration or touch on the skin; Motor nerves: have the role of controlling muscle activities; Autonomic Nerves: Control the activities of the cardiovascular system such as blood pressure, heart rate, digestive system, bladder and beyond human will. Signs of peripheral polyneuritis may include:
Numbness, stinging or tingling sensation in the feet or hands, gradually spreading to the legs and arms; Sting; Increased sensitivity to external stimuli; Lack of coordination in movement and balance, so it is easy to fall; Muscle weakness; Reduced sensation of wearing gloves or socks; Weakness in limbs; If the autonomic nerves are affected, the manifestations are sometimes very vague, making it easy to mistake for other specialties, such as heart rate, blood pressure often fluctuate, easily cause dizziness, lightheadedness. ; inability to regulate body temperature, sweating excessively, or not being able to sweat; disorders of visceral motility, causing constipation, diarrhea, urinary incontinence or urinary retention.
3. Causes of polyneuritis
Autoimmune diseases: Sjogren's syndrome, systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, Guillain-Barre syndrome, chronic polyneuritis and vasculitis; Diabetes: More than half of people with long-standing diabetes will experience complications of peripheral neuropathy. Not only that, this complication also makes the feet susceptible to infections and takes a long time to heal, sometimes having to amputate; Infections: Due to viral or bacterial agents, including Lyme disease, shingles, Epstein-Barr virus, hepatitis B and hepatitis C, leprosy, diphtheria, and HIV; Genetic disorders: Congenital chromosomal disorders such as Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease; Tumors: Abnormal growths or cancer (malignant) can form and grow on the peripheral nerves. In addition, polyneuritis is also a consequence of some cancers in other organs metastasized to or due to the body's immune response in paraneoplastic syndromes; Bone marrow disorders: Due to the production and release of abnormal proteins in the blood (monoclonal gametes), a form of bone cancer, lymphoma, and amyloidosis. Other diseases: Kidney disease, liver disease, connective tissue disorders, hypothyroidism .... Besides, polyneuritis is caused by many other causes such as:
Alcoholism: Poor diet, malnutrition in alcoholics can lead to deficiencies in essential vitamins such as vitamin B; Toxic exposure: Toxic substances include industrial chemicals and heavy metals such as lead, mercury; Medications: Some drugs, especially those used to treat cancer, can cause peripheral neuropathy; Trauma or strong effects on nerves: Trauma, such as after a motor vehicle accident, fall or sports practice, can cut or injure a peripheral nerve; Vitamin deficiency: The B vitamins - including vitamin B1, vitamin B6 and vitamin B12, vitamin E are important for mental health. In some specific cases, if actively searched but no cause can be found, it can be concluded as idiopathic polyneuritis.
4. Complications of polyneuritis
Complications of peripheral polyneuritis can include:Burns and skin trauma: This condition occurs when the patient does not feel temperature changes or pain on the skin, so it accidentally leads to inflammation. to injury; Infection: Feet or other areas with sensory disturbances can be injured without being detected and cared for properly. Therefore, the infection when known has become severe. Therefore, it is necessary to observe the lesions on the skin every day, especially in difficult to check places such as the soles of the feet of diabetics; Fall: This is the result of a combination of limb weakness, decreased sense of position and decreased ability to control balance, sometimes affecting the patient's life. At the same time, the more the patient falls, the greater the risk of nerve damage.
5. How to treat peripheral polyneuritis?

5.1. Medication In addition to medications used to treat conditions associated with peripheral neuropathy, medications used primarily to relieve symptoms of peripheral neuropathy include:
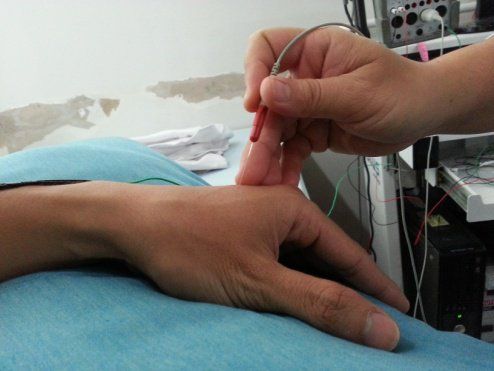
Medications Pain: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, work well when symptoms are mild. For more severe symptoms, your doctor may prescribe an opioid pain reliever, such as tramadol or oxycodone. However, these drugs carry the risk of dependence and addiction; Anti-epileptic drugs: Medicines such as gabapentin and pregabalin, which are used to treat epilepsy, can still reduce nerve pain. Side effects include drowsiness and dizziness; Antidepressants: Some tricyclic antidepressants such as amitriptyline, doxepin, serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors, duloxetine also help relieve pain in polyneuritis, by inhibiting chemical processes in the brain. The brain and spinal cord cause pain signals. Side effects of antidepressants are dry mouth, nausea, drowsiness, dizziness, decreased appetite, and constipation. 5.2. Therapeutic use When the patient is poorly responsive to medical therapy, consideration should be given to physical therapy or transcutaneous neurostimulation (TENS) therapies through which electrodes are used. placed on the skin, delivering a mild electric current at different frequencies. TENS is effective when applied for at least 30 minutes daily for about a month.
In addition, intervention with plasma exchange therapy and intravenous immunoglobulins to help suppress the activity of the immune system and neutralize autoantibodies will be effective in cases of polymyositis. neuropathy due to autoimmune disease.
For cases of compression polyneuritis, early surgery should be considered to release the nerve fibers from the pressure, which helps limit permanent damage.
6. Prevention of polyneuritis
The best way to prevent polyneuritis is to manage conditions that put you at high risk, such as diabetes, alcoholism, or rheumatoid arthritis.At the same time, it is necessary to build a healthy lifestyle from daily habits such as eating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains and a variety of vitamins; Exercise regularly, exercise flexibility for joints. At the same time, avoid factors that can cause nerve damage such as exposure to toxic chemicals, smoking, and excessive alcohol consumption.
In short, polyneuritis has a variety of symptoms, ranging from numbness and weakness to cardiovascular and digestive dysfunction. Therefore, it is necessary to detect and treat early to prevent further damage to the peripheral nerves.
Master. Doctor Bui Ngoc Phuong Hoa has more than 24 years of experience in the field of neuropsychology. Doctor Hoa was formerly the Deputy Head of the Department of Neurology - Quang Ngai Provincial General Hospital and participated in many continuous training courses on Epilepsy, Cerebrovascular Accident, Alzheimer's, Movement Disorders, Geriatrics. Endocrine Pathology.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: webmd.com; pmayoclinic.org