This is an automatically translated article.
Posted by Doctor Ngo Van Dan - Neonatology Department - Vinmec Times City International Hospital
Pneumonia in newborns is now quite common, second only to gastrointestinal diseases, especially easy to occur in premature and low birth weight babies. The disease needs to be detected early and treated promptly, preventing dangerous complications to the health and life of children.
1. Why are babies prone to pneumonia?
Neonatal pneumonia is an infection (bacterial, viral, fungal) of the lower respiratory tract (alveoli, tissues surrounding the alveoli) occurring during the neonatal period (from 0 to 30 days of age). Newborns are very susceptible to pneumonia, which is a common disease, ranked second after gastrointestinal diseases. Especially if it occurs in premature, low birth weight babies.
Lungs are important organs of the respiratory system, where gas exchange between the external environment and the body. Normally, there are several different mechanisms that protect the lungs and body from environmental pathogens. Inhaled air is filtered and warmed, bactericidal in the nose, larynx, bronchi and gas exchange in the alveoli. When an agent enters the lower respiratory tract, it is expelled by the cough reflex. Smaller particles, able to penetrate deeper into the trachea, are adhered to the tracheobronchial wall by the mucous mat on the ciliated epithelium and then transferred upward to be expelled. Particles that reach the alveoli are processed by alveolar macrophages and local immune mechanisms. Particles phagocytized by alveolar macrophages are transported out of the alveoli by the lymphatic system.
Trẻ sơ sinh dễ bị viêm phổi
Newborns have different anatomical and physiological characteristics than older children and adults. The nose and pharynx are relatively short and small, the nostrils and nasal passages are narrow, so nasal breathing is limited. The nasal mucosa is thin, the barrier function of the nasal mucosa in children is still weak due to its poor ability to disinfect with mucus, so children are susceptible to nasopharyngeal infections, which easily leads to pneumonia.
Common characteristics of rods, gases and bronchi in children are relatively narrow lumen, less developed elastic organization, soft cartilage ring, easy to deform, mucosa with many blood vessels, so children are prone to inflammation Infections of the respiratory tract, mucous membranes of the larynx, gas, and bronchi are prone to edema, secretions and easily deformed in the pathological process. Children's ribcage is poorly mobile, so they are prone to atelectasis, emphysema, and alveolar dilation when pneumonia is present. The respiratory muscles are weak, so the child is prone to respiratory failure when the lungs are damaged, and at the same time, the child's need for oxygen is greater than that of an adult. The respiratory center of the child is not yet complete, so the newborn is prone to breathing disturbances and stops breathing.
2. Is neonatal pneumonia dangerous?
Pneumonia, if it occurs in children younger than 2 months old, is classified as severe pneumonia and is indicated for hospitalization. Neonatal pneumonia mortality rate is higher than other age groups. Moreover, the signs of pneumonia in children are often more difficult than other ages, so parents often take them to the doctor when the child's condition is severe.
Severe neonatal pneumonia prone to dangerous complications
Respiratory failure Blood infection Meningitis Effusion, pneumothorax Weakened immune system
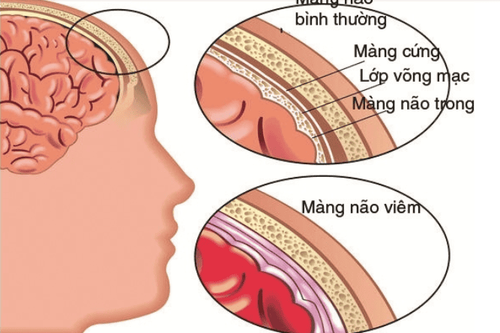
Viêm màng não là một trong các biến chứng viêm phổi trẻ sơ sinh
3. Warning signs?
Parents need to pay attention to some of the following warning signs
High fever High fever is just an initial sign based on it to monitor, not to diagnose pneumonia. Combine with subsequent symptoms before drawing final conclusions. In many cases, a child over 3 months of age with a fever of 39 degrees Celsius is still considered normal and can be caused by many other causes other than pneumonia. But if the infant has a high fever of over 38 degrees Celsius, parents need to take the baby to a medical facility immediately to find the cause and treat it promptly
Fast breathing Fast breathing is the sign with the highest diagnostic value for pneumonia . It is possible to count the child's breathing in one minute to assess the child's condition (children under 2 months of age > 60 breaths/minute). Pay attention to counting breaths when the child is lying still or when sleeping. For infants under 2 months of age, if the first count is 60 breaths per minute or more, the second count is required because at this age children often breathe irregularly. If it is still more than 60 times a minute, it is considered tachypnea. Cases like these should not be delayed but should take the child to see a doctor immediately

Một số dấu hiệu cảnh báo trẻ bị viêm phổi trẻ sơ sinh
Chest indrawing Thoracic indrawing is a sign of a child with severe pneumonia. To detect, parents can look at the lower part of the chest that is indented when the child inhales. For children under 2 months of age, only slight chest indrawing is not valid for classification because the baby's ribcage is still soft. In case the deep concave is clearly visible and easy to see, the child definitely has pneumonia.
Poor suckling, fatigue This is the first sign that the baby is sick. Poor suckling is when the amount of milk the baby sucks is less than 50% of the baby's normal needs. Parents may find that the child is not as agile and active as usual. Children may be irritable or lethargic, less responsive when communicating with parents. In some cases, the mother may find that the baby does not smell as good as usual.
Cough, runny nose Pneumonia usually starts with inflammation of the upper respiratory tract, then the causative agent will spread to the lungs. Therefore, in the early stages of pneumonia, children often have symptoms of upper respiratory tract infection such as cough, runny nose, and wheezing. If parents find these symptoms are more severe such as: Deep cough, heavy voice, runny nose, cough with thick sputum, they need to take the child to the doctor right away.

Dấu hiệu ho và chảy mũi ở trẻ
Cyanosis This is a sign of respiratory failure if the child has pneumonia. Parents can see the lips, toes and fingers are pale, purple.
Pediatrics Department at Vinmec International General Hospital is the address for receiving and examining diseases that infants and young children are susceptible to: viral fever, bacterial fever, otitis media, bronchitis , pneumonia in children, ... With modern equipment, sterile space, minimizing the impact as well as the risk of disease spread. Along with that is the dedication from the doctors with professional experience with pediatric patients, making the examination no longer a concern of the parents.
To register for child care at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide or register online HERE.
MORE
Treatment of pneumonia in children Signs of pneumonia in infants When does a child with pneumonia need to be hospitalized?














