This is an automatically translated article.
This article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor II Bui Thi Thu and Specialist Doctor II Tran Thi Mai Huong- Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.Uterine fibroids are benign gynecological diseases, common in women. About 1 in 5 women have uterine fibroids. Uterine fibroids often increase in size during pregnancy due to pregnancy hormones and often shrink after birth.
1. Can you get pregnant if you have uterine fibroids?
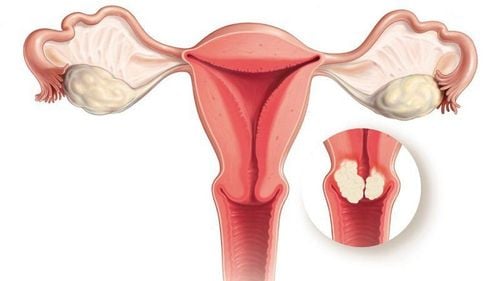
When having uterine fibroids, the patient needs an ultrasound to check the position and size of the fibroids. For uterine fibroids < 3cm in size, not submucosal fibroids or fibroids that have not invaded the uterine cavity, the patient can still have a normal pregnancy.
Uterine fibroids are small in size, located in the uterine muscle, often causing less menorrhagia symptoms as well as having little effect on pregnancy. For submucosal fibroids, they often cause menorrhagia, profuse blood clots, and often indicate surgery. On the other hand, submucosal fibroids often occupy the uterine cavity, making it difficult to get pregnant or easily cause miscarriage. Depending on the type and size of uterine fibroids, the doctor will specify specific treatment methods and pregnancy counseling for the patient.
Trắc nghiệm: Bạn có hiểu đúng về dấu hiệu mang thai sớm?
Các dấu hiệu mang thai sớm không phải chỉ mỗi trễ kinh mà còn có rất nhiều dấu hiệu khác như xuất huyết âm đạo, ngực căng tức,… Điểm xem bạn biết được bao nhiêu dấu hiệu mang thai sớm thông qua bài trắc nghiệm này nhé!
2. How long after fibroid removal can I get pregnant?
In case it is necessary to have a hysterectomy before pregnancy, the patient can have a normal pregnancy after 1 year from the date of cesarean section. Pregnancy should not be too early to avoid post-surgery, the uterus has not recovered, which will cause many risks of miscarriage, rupture of the fibroid incision during pregnancy.
3. Uterine fibroids form during pregnancy
Uterine fibroids often develop during pregnancy because pregnancy hormones make fibroids rapidly increase in size. Uterine fibroids formed during pregnancy, with no indication for dissection during pregnancy or during delivery, will be monitored in the postpartum period, counting from the date of birth to the end of 6 weeks postpartum, the patient should be re-examined according to the Schedule a doctor's appointment for specific assessment and monitoring of each case.
Only a small number of cases of uterine fibroids require surgery. After giving birth, uterine fibroids often decrease in size due to the decrease in pregnancy hormones. Fibroids usually shrink and do not grow during perimenopause and menopause.
4. Do uterine fibroids during pregnancy affect the fetus?
Effects of uterine fibroids during pregnancy :
Uterine fibroids can increase the risk of miscarriage , premature birth , premature rupture of membranes . Uterine fibroids can cause placenta previa, placenta tight, placenta abruption. When entering labor, women with uterine fibroids are at risk of having a difficult delivery due to an abnormal position of the fetus, fibroids obstructing the outflow of the fetus or causing disturbances in uterine contractions, and are prone to postpartum haemorrhage. In the postpartum period, women with uterine fibroids during pregnancy may have fluid retention and infection. Uterine fibroids pose a risk to the fetus: growth retardation in the uterus due to blood supply to both the fetus and the fibroid. However, depending on the location and size of fibroids, not all uterine fibroids during pregnancy cause these effects. Pregnant women should have regular antenatal check-ups to check for abnormalities during pregnancy.

5. When is indicated for fibroid removal right in pregnancy or during delivery?
As mentioned above, most uterine fibroids in pregnancy usually do not have an indication for dissection as well as do not perform dissection during delivery but only postpartum follow-up. In case there is an indication for surgery for uterine fibroids during pregnancy or during delivery:
Uterine fibroids with necrotic complications, infection Uterine fibroids located right at the uterine muscle incision in cesarean section Fibroids causing obstruction of the drainage canal. Fibroids are located under the mucosa (tumor encroaching on the uterine lumen, risk of bleeding).
6. Slow down the growth of uterine fibroids during pregnancy
Causes of uterine fibroids are being studied, a number of risk factors: genetics, environment, food, endocrine disorders, obesity... Some measures can help slow down the growth of fibroids. develop fiber such as:
Should use fiber-rich foods (green vegetables, fresh fruits) rich in vitamins, minerals, antioxidants to help lose weight and balance hormones. Drink green tea. Add foods rich in potassium such as: avocados, bananas, oranges, tangerines, red watermelon, lentils, oat bran powder, potatoes... Foods rich in vitamin D such as low-fat milk, sun exposure helps slow down uterine fibroid growth Light intensity exercise, weight control. Avoid foods high in estrogen such as red meat, animal organs. Avoid foods with high salt content (salt meat, canned foods...) Avoid caffeinated drinks, chocolate, soft drinks, tobacco (including secondhand smoke). Uterine fibroids are benign tumors that develop from the muscular layer of the uterus, this is the most common gynecological disease in women of reproductive age from 30 to 50, the rate from 20 to 40%. For treatment and pregnancy counseling for women with uterine cancer, it is necessary to consult a specialist doctor.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.