This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted with General Internal Medicine Doctor - Department of Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital.Is hyperthyroidism in pregnant women dangerous? This is a question asked by many pregnant women. Hyperthyroidism during pregnancy affects both mother and baby. In addition, some treatment methods should be noted for pregnant women with hyperthyroidism.
1. What is hyperthyroidism?
Hyperthyroidism is an immune system disorder that leads to an overactive thyroid gland, leading to increased production of thyroid hormone into the bloodstream, causing metabolic disorders of the body.Hyperthyroidism is the second most common endocrine disease after diabetes with a prevalence of 1 in 1,500 in pregnant women. Because thyroid hormones affect a number of different body systems, signs and symptoms involve different organs. Pregnant women with hyperthyroidism often have symptoms such as irregular weight gain, heart palpitations, abnormal vomiting...
The main treatment goal is to inhibit the overproduction of thyroid hormone and reduce the level of thyroid hormone. severity of symptoms.
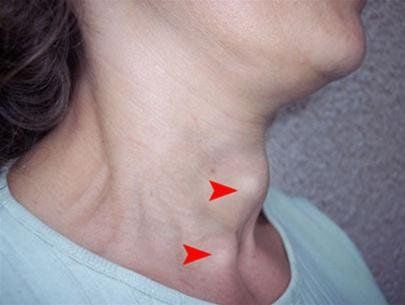
2. Causes of pregnancy hyperthyroidism
Basedow is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism (80-85%), occurring in 1/1500 pregnant women. In addition, some cases of HCG too high also cause symptoms of hyperthyroidism. Diagnosis of Graves during pregnancy is more difficult because emotional symptoms, fear of heat, hot and humid skin, and sweating are easily confused with symptoms of morning sickness. Iodine concentration test cannot do because it will affect the fetus. Therefore, the diagnosis is based on history, tachycardia above 100 beats/min, echocardiography of enlarged, diffuse thyroid gland, TSH, FT4, TRAb tests. The hormone HCG is produced during pregnancy, which peaks around 12 weeks into pregnancy. This causes mild irritation of the thyroid gland and causes some symptoms of hyperthyroidism. If you're carrying multiples, your HCG levels will rise even higher and symptoms will become more pronounced. About 10-20% of pregnant women develop these symptoms, but most do not need treatment. Women with severe morning sickness (hyperemesis gravidarum) may also have mild symptoms of hyperthyroidism. However, these symptoms usually go away after the first trimester.
Immune disorders, such as Graves' disease, can cause the thyroid gland to overproduce hormones. A family history of thyroid problems or autoimmune diseases can also increase your risk of developing hyperthyroidism during pregnancy. Certain medications, such as those that help the heart beat normally, can also cause hyperthyroidism during pregnancy. An infection near the thyroid gland can also be a cause. Other thyroid problems such as an enlarged thyroid, swelling from an infection, or thyroid cancer can also affect how the thyroid gland works. High iodine levels can also cause hyperthyroidism. The thyroid gland uses iodine to make hormones. Therefore, the thyroid gland will make more hormone if the iodine level in your body is high.
3. Symptoms of Hyperthyroidism in Pregnancy
Weight loss or not gaining weight as expected, frequent cravings, diarrhea or constipation Tachycardia and rapid breathing, even at rest Increased sweating and poor heat tolerance U, painful swelling in the neck or bulging eyes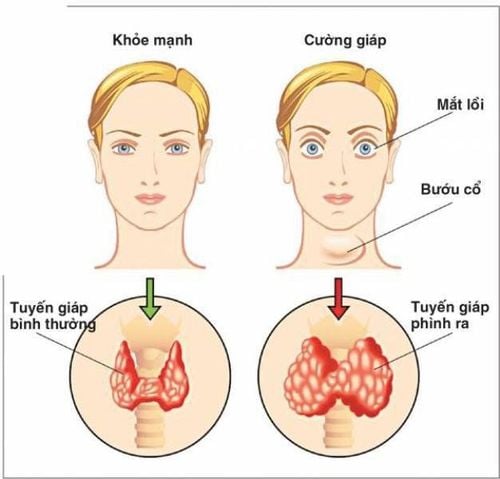
Trắc nghiệm: Bạn có hiểu đúng về dấu hiệu mang thai sớm?
Các dấu hiệu mang thai sớm không phải chỉ mỗi trễ kinh mà còn có rất nhiều dấu hiệu khác như xuất huyết âm đạo, ngực căng tức,… Điểm xem bạn biết được bao nhiêu dấu hiệu mang thai sớm thông qua bài trắc nghiệm này nhé!
4. How does hyperthyroidism affect pregnancy?
About 1% of babies born to women with Graves' disease will develop hyperthyroidism after birth. This is because thyroid-stimulating antibodies can be passed through the placenta and affect the baby. Before birth, if the fetal heart rate is high (greater than 160 beats/min), when ultrasound shows the presence of goiter in the fetus, poor fetal growth or abnormal bone growth, it may be a sign of pregnancy. found that the fetus has hyperthyroidism. If this is the case, your doctor may prescribe medication (PTU or MMI) to treat your unborn baby. After birth, hyperthyroidism can be detected by blood tests. Graves' disease can occur during the first trimester of pregnancy or in women who have had Graves before. In addition to the classic symptoms, the mother may also have preterm labor or preeclampsia. In addition, the mother will be at high risk of heart failure, acute thyrotoxicosis. Basedow's disease may improve in the third trimester of pregnancy or may also worsen in the postpartum period.
5. Treatment options for women with gestational hyperthyroidism?
Mild hyperthyroidism (poor symptoms, slightly elevated hormone levels) will usually be followed closely without any treatment for both mother and baby after birth. When severe hyperthyroidism requires treatment, a synthetic antithyroid drug should be selected as PTU and closely monitored (monthly TSH test, thyroid hormone) to avoid hypothyroidism for the mother and child. In women who cannot be treated with synthetic antithyroid drugs (drug allergies), surgery may also be an option. However, thyroidectomy should be considered very closely because of the high risk in anesthesia and surgery for both mother and fetus. Surgery may be done to remove all or part of the thyroid gland. Your doctor will perform surgery during pregnancy if they feel that it is safe for you and your baby.
In which, hyperthyroidism in pregnant women is closely coordinated between the two specialties, endocrinology and obstetrics, with modern equipment and machinery to bring efficiency in diagnosis and treatment. Closely monitor the unwanted effects, then find the appropriate treatment to limit the effects of hyperthyroidism for mother and baby.
Specializes in applying new techniques in disease treatment: Treating benign thyroid nodules with high-frequency ablation (avoiding thyroid surgery for patients). Especially, there is a team of well-trained and experienced medical doctors:
Associate Professor, Doctor, Doctor Nguyen Thi Hoan Associate Professor, Doctor, Doctor Chu Hoang Van Doctor, Doctor Pham Thi Hong Hoa Master, Doctor Pham Thi Thu Huong Master, Doctor Bui Minh Duc
Master, Doctor Nguyen Thi Cam Tu Doctor Nguyen Ngoc Son
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.