This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by an Anesthesiologist - General Surgery Department - Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital.Anesthesia is an important factor contributing to the success of the surgery. Deep examination in anesthesia is a process that requires closeness and meticulousness from the anesthesiologist and the entire surgical team.
1. What is anesthesia?
Anesthesia is the process of using drugs or other measures to insulate or block the sensation of pain. Anesthesia helps the patient feel comfortable and safe during surgery. During surgery, the patient not only has to face pain, but also anxiety and fear. Therefore, anesthesia is an indispensable and important procedure that contributes to the success of every surgery. Deep examination under anesthesia is the necessary preparation and monitoring before, during and after surgery in order to bring safety and minimize complications during surgery.
Sử dụng thuốc trong gây mê
2. Procedure for pre-anesthesia examination
The purpose of the examination is to prepare and assess the patient's condition for the anesthetic process. The process of pre-anesthesia examination is to learn about family history, medical history, comorbidities, prognosis of difficulties and complications that may be encountered during anesthesia. In addition, doing the necessary clinical tests before anesthesia is very important in the preparation process. Building a doctor-patient relationship is the first necessary basic step, not only for the purpose of assessing the patient, but also for counseling, reassuring the patient, making the patient trust and feel. peace of mind during surgery.
The pre-anesthesia examination process includes: asking the patient, performing a clinical examination and doing paraclinical tests.
2.1. Asking the disease The process of asking the patient needs to extract information about
Medical history: see if the patient has any previous medical or chronic diseases that may affect the use of drugs and effectiveness of the drug no. For example, diseases of the heart, coronary, liver, stomach, cardiovascular, high blood pressure, diabetes, kidney, asthma, chronic respiratory diseases,... History of treatment of diseases Surgery: History of surgical surgery that the patient has previously undergone, have any complications, how long is the recovery time after surgery,... Allergic history: have a history of allergies to any medication, allergies to weather, food, pollen, fur, chemicals,... Family history: Need to ask about diseases that have a familial factor and are likely to affect effectiveness result of anesthesia. Drug treatment history: The patient should be asked if he is on any medication and has been taking any medication for a long time, and the half-life of the drug should be taken into consideration. . Instruct the patient if medication should be taken for the required period of time prior to surgery. Psychological assessment of the patient before surgery: Doctors and medical staff need to assess the patient's psychology and then give reasonable advice and encouragement so that the patient does not fall into a state of anxiety and stress. before surgery.

Quá trình hỏi bệnh, khai thác thông tin người bệnh
2.2. Clinical examination Includes procedures
Whole body examination Cardiovascular examination Respiratory examination Urological examination Gastrointestinal examination Pre-intubation examination in case of endotracheal anesthesia. In addition, it is necessary to anticipate and evaluate the factors that lead to difficult intubation.
After examining and evaluating the factors in the patient and the impact of the surgery on the patient's body, the anesthesiologist must make a plan for anesthesia resuscitation, care for the patient before, during and after the surgery. after surgery; detect, prevent and plan to manage risks related to comorbidities as well as risks of surgery that may occur during and after surgery, acute and chronic pain treatment for patients..
2.3. Some basic tests in the procedure of pre-anesthesia examination Patients will have the following tests done to prepare for the anesthesia process: hematology tests, blood biochemistry, chest x-ray, electrocardiogram. In addition to the above basic tests, the patient may be assigned to do other necessary tests depending on the comorbidities and condition of each patient.
Người bệnh sẽ được làm điện tim trước khi gây mê
3. Monitoring during anesthesia
Anesthesia is divided into 3 main stages:
3.1. Pre-anesthesia stage This stage patients may experience symptoms due to side effects of anesthetic drugs such as allergies, low blood pressure, nausea, vomiting, respiratory failure,... So in this stage it is necessary to Monitor the patient's general condition regularly and take care not to leave the patient alone without medical staff monitoring.
3.2. Induction phase Some complications during induction of anesthesia
Failed intubation Injury to the oropharynx due to aggressive intubation Bronchospasm: The patient presents with wheezing or stridor in case of incomplete contraction. If respiration is reversed, mask ventilation cannot be achieved. This is a condition that needs to be monitored and treated quickly because laryngospasm leads to hypoxia and cardiac arrest if not promptly and properly treated.
Trẻ được gây mê bằng phương pháp đặt nội khí quản
Laryngeal spasm: Vomiting, reflux: in case of gastroesophageal reflux, intestinal obstruction causing intestinal stasis, pyloric stenosis, coma, shock, pregnant women, obesity,... Vomiting and regurgitation reverse can cause bronchospasm and subsequent complications. Hypotension, cardiovascular collapse Cardiac arrhythmias Sinus bradycardia Sinus tachycardia Extrasystoles 3.3. Anesthesia maintenance phase It is necessary to closely monitor to prevent some common complications during the maintenance of anesthesia as follows:
Positional deviation of the endotracheal tube Hypoxemia Hypercoaemia Pneumothorax Co bronchospasm Some circulatory complications
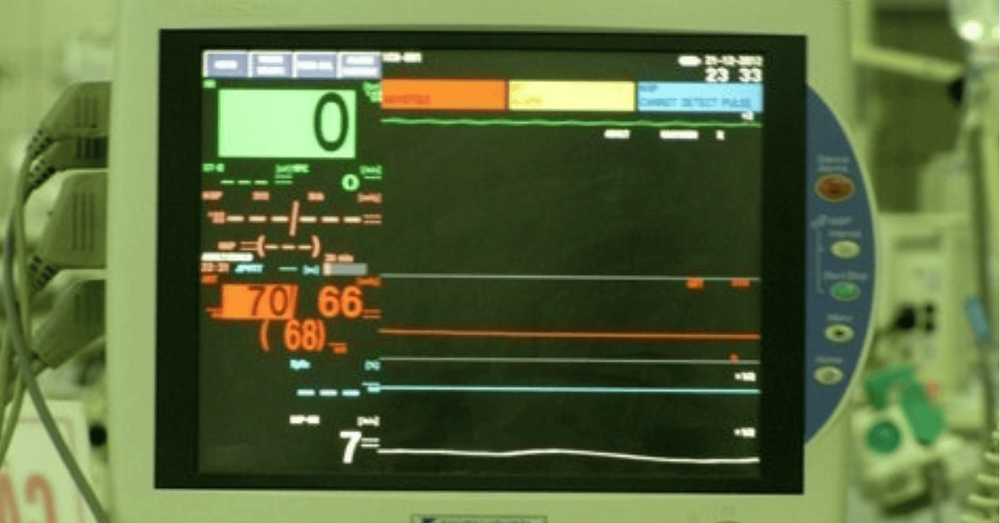
Màn hình monitor theo dõi chỉ số sinh tồn
4. Out of anesthesia stage
Respiratory failure Bronchospasm Increased blood pressure and tachycardia Pulmonary collapse Upper airway obstruction Acute glottis edema Deep examination or monitoring during anesthesia is a relatively complex process, requiring Anesthesiologists need to be highly trained and experienced. In addition, a coordinated surgical team and good preparation before surgery is one of the important factors leading to the success of the operation.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.