This is an automatically translated article.
Air pollution is a cause of premature death, worsens heart and lung disease, increases respiratory symptoms, contributes to health problems especially in children and the elderly. Therefore, each person needs to know how to protect their health when environmental pollution, fine dust emissions are appearing dense.
1. What is air pollution?
According to experts, air pollution is the process by which many chemical, physical or biological agents change the natural properties of the air that people are breathing indoors or outdoors. Pollutants proven to affect public health include:
Particulate matter, also known as fine dust (PM); Ozone (O3); Nitrogen dioxide (NO2); Sulfur dioxide (SO2). In particular, particulate matter with a diameter of less than 10 and 2.5 microns (PM10 and PM2.5) poses a risk to human health by penetrating deep into the lung tract and entering the bloodstream, lead to cardiovascular and respiratory diseases. In 2013, the WHO's Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) classified outdoor air pollution and fine particulate matter as carcinogens.
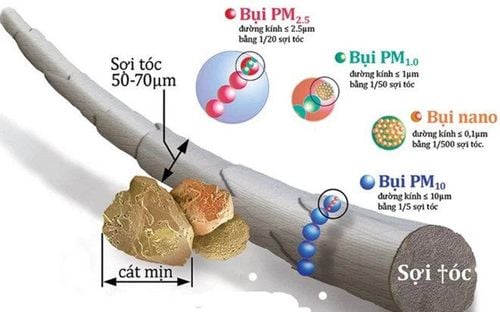
Các hạt PM10 và PM2.5 có thể gây nguy hiểm cho sức khỏe do có thể xâm nhập sâu vào hệ hô hấp và tuần hoàn
2. How does air pollution affect health?
Almost everyone is exposed to polluted air. Although a great deal is being taken to improve air quality, adverse health effects from air pollution persist in many parts of the world, including areas of the world. develope. Specifically, although European countries have reduced emissions of PM10 fine dust, most of the population living in urban areas in European countries are exposed to harmful chemicals in the air with concentrations higher than the average value. WHO annual average.
Air pollution affects everyone and is the second leading cause of death from non-communicable diseases, just behind smoking. According to WHO statistics in 2016, in Europe, there were more than 550,000 deaths due to the combined effects of air pollution from indoor and outdoor environments. Short or long-term exposure to ambient air pollution can affect the health of both children and adults.
In children, the effects of inhaling poor quality air can inhibit growth and reduce lung function, cause respiratory infections and worsen asthma. For adults, ischemic heart disease and stroke are the most common causes of premature death from outdoor air pollution. Some studies on other effects of air pollution have also shown a link to diabetes, brain problems in children (such as poor learning, developmental delays, autism, lack of exercise). central nervous system, or hyperactivity) and neurodegenerative conditions in adults (including Alzheimer's disease).
3. What should be done to improve air quality?
To improve air quality, the first thing to do is to address the sources of environmental pollution. Major sectors that contribute to air pollution include: agriculture, energy, transport, industry, commerce and waste disposal. There is also household solid fuel burning and cigarette smoke - another important source of indoor air pollution. Therefore, people need to approach a variety of different measures to tackle air pollution. Although a lot of changes are taking place in some countries to contribute to improving air quality, more efforts are still needed. Some good examples of steps taken in many countries and cities include:
Introduction of clean technology in industry to reduce smoke and emissions, as well as improve management waste; Ensure access to affordable clean energy for cooking, heating and lighting in households; Prioritize public transport in urban areas, including bus, pedestrian, cyclist and intercity rail travel; Improve the energy efficiency of buildings, contribute to greener cities, reduce pressure and thereby save more energy; Increase the use of renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind and hydroelectric power; Building schools, hospitals or houses away from major pollution sources such as highways, industrial zones; Invest in funding to install air purification systems in areas with high pollution levels, helping people reduce their exposure to toxic chemicals. Addressing emissions related to the transportation of goods; Join in support of organizations for the environment, speak up and act for air pollution, environmental pollution; Provide strategies for waste reduction, segregation, recycling, reuse and recycling.
4. Instructions on how to protect your health when air pollution
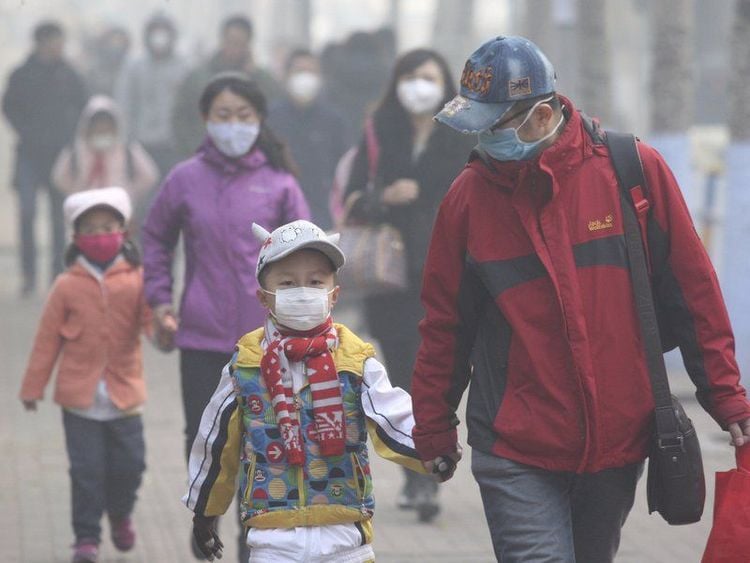

Đeo khẩu trang đạt tiêu chuẩn chất lượng cản bụi mịn để bảo vệ sức khỏe
To protect health when polluting the environment, specifically avoiding smoke from vehicles, dust from construction works or unpleasant odors, doctors recommend people:
Update information air quality from reliable sources to proactively prevent and protect health when polluting the environment; Give up and stay away from secondhand smoke; Wear a mask that meets the quality standards to prevent fine dust certified by the authorities, optimally covers the face, has a nose frame and a 1-way filter breathing valve when going out (not a regular medical mask); Regularly clean rooms and houses, clean and ventilate the living environment; Limit burning votive papers, burning incense too much on holidays; People in the suburbs should not burn straw, making the atmosphere more suffocating and polluted; Switch to using clean fuels (electric stoves, induction cookers) for cooking, replacing honeycomb charcoal stoves; Turn off the engine when stopping at a red light; Remind traffic vehicles or construction works that emit a lot of smoke and dust but are not properly covered; Planting more trees contributes to the protection of a healthy environment; In particular, patients with respiratory problems should not go out at a time when the air is heavily polluted unless absolutely necessary. Patients with asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease need to follow and maintain daily medication as prescribed by their doctor to protect their health when air pollution is present. If symptoms of discomfort are severe, ask your doctor to prescribe an increased dose of the bronchodilator. When detecting symptoms of an exacerbation, difficulty breathing, it is necessary to immediately contact medical staff for support, guidance on remedial and emergency solutions, to avoid endangering lives because of the effects of air pollution.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References: Euro.who.int and Ncbi.nlm.nih.gov