This is an automatically translated article.
Currently, women are no longer strangers to the IUD method of contraception - the IUD. In addition to the contraceptive effect, the IUD also has a great effect in protecting the endometrium. Here's what you need to know about an IUD.
1. What is an IUD?
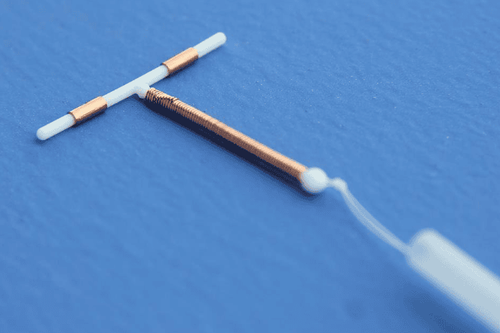
Intra Uterine Divice - The IUD, also known as the IUD, is a small birth control device made of flexible plastic. The IUD is inserted into the uterus, which provides safe, highly effective long-term contraception.
There are two types of IUDs available in the United States. One uses copper and the other uses the synthetic hormone levonorgestrel, a form of progestin. (The IUD does not contain estrogen.)
Copper T380A (ParaGard brand) is wrapped with fine copper wire and has a lifespan of 10 to 12 years. The hormonal IUDs are also called Mirena, which lasts for 5 years, and Liletta and Skyla, which lasts for three years. Both copper and hormonal IUDs are T-shaped and less than 1.5 inches long. They can be taken out at any time.
The IUD is a good choice for women who want a highly effective, long-lasting method of contraception and an easy return to its original state. It may also be an appropriate choice for women who cannot use certain hormonal methods such as birth control pills or who experience side effects from taking the pill. Remember, like the birth control pill, the IUD will not protect you from sexually transmitted infections (STDs).
Copper IUDs can also be used for emergency contraception. If it is inserted within 5 days after unprotected sex. This will be more effective than taking the emergency contraceptive pill. In addition, you use this method for the purpose of continuous contraception.
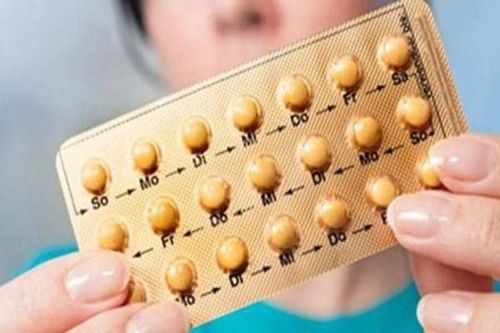
Phụ nữ không sử dụng được thuốc tránh thai nên chuyển sang vòng tránh thai
2. How does the IUD work?
Both types of IUD work primarily by preventing sperm from fertilizing an egg. The copper IUD releases copper into the uterus, which acts as a spermicide. The IUD contains a hormone that releases a form of the hormone progestin into the uterus. Progestin thickens cervical mucus so that sperm cannot meet an egg. In some women, progestin can also prevent ovulation.
In the unlikely event that the egg is fertilized and survives, both types of IUDs cause inflammation of the uterus making it harder for an egg to implant there. The hormonal IUD also causes the lining of the uterus to thin, making implantation more difficult.
3. Can I use an IUD if I'm breastfeeding?
It's correct. Neither type of IUD will affect the quality or quantity of breast milk.

Các mẹ có thể sử dụng vòng tránh thai nếu đang cho con bú
4. How effective is the IUD?
The IUD is one of the most reliable forms of contraception. The annual failure rate is less than 1%. This means that the IUD is as effective as non-surgical sterilization. However, unlike sterilization, you will be able to conceive again immediately after the IUD is removed.
Methods that can be easily returned to their original state, including the pill, patch, ring, or injection, can be very effective, but only in women who use them correctly and consistently. In fact, these methods have a much higher failure rate than the failure rate in women using the IUD.
That's because the IUD virtually eliminates the possibility of human error. All you have to do is check the device every month to make sure it stays in place.
5. Will it affect my ability to get pregnant after removing the IUD?
No. The IUD can be removed at any time during your cycle and you can start getting pregnant right away. Usually your fertility will be the same as it was before you put the device in.

Vòng tránh thai không gây ảnh hưởng đến khả năng sinh sản
6. When to place an IUD?
The medical staff who inserted your IUD will want to make sure you are not pregnant and may perform some sensitive pregnancy tests. They'll want to make sure you don't have an infection that can cause pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), so they'll ask you about your sexual history and examine you for signs of a problem. In addition, healthcare providers can test you for chlamydia and gonorrhea. And during the pelvic exam, they will also check the position of your uterus.
If you are deemed eligible for an IUD, you can usually get an IUD inserted right away. (If you are waiting for test results, you may have to schedule another visit to have the IUD inserted.)
You can also get an IUD inserted right after giving birth, whether you had a vaginal delivery or a cesarean section.

Vòng tránh thai được đặt ngay sau khi kì kinh kết thúc để đảm bảo bạn không mang thai
7. How is the IUD inserted?
When it's time to insert the ring, your doctor will insert a speculum into your vagina and clean your vagina and cervix with an antiseptic solution. The doctor then uses an instrument to grasp your cervix, which can cause a sharp pain. This instrument allows the doctor to straighten your cervical canal and draw the uterus closer to the vagina so that the depth of the uterine cavity can be measured. The IUD is then inserted, using a narrow applicator. You may feel some pain, but it's only temporary for now.
When the IUD is in place, the device is removed and the arm opens into a T. You might think it's weird to have a piece of plastic inside of you, but you won't be able to feel it when it's inserted. put into. The two wires attached to the end of the IUD will hang down the cervix and be clipped so that they only protrude slightly into the vagina. This whole process only takes a few minutes.
You may feel stomach or back pain for a few days after the procedure. Taking ibuprofen about an hour before the procedure and if needed afterward will help ease any discomfort. You can use tampons right after the IUD is inserted.
Your doctor may recommend that you come back for a checkup after your next period, a few weeks to a month after the IUD is inserted. Your doctor will check that the IUD is still in place and make sure you don't have any signs of infection. Your doctor will also check your IUD at your annual pelvic exam.
8. Do I need to use back-up birth control after the IUD is inserted?
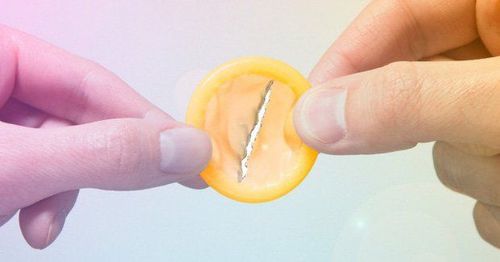
The copper IUD is effective as soon as it is placed. The progestin IUD is effective immediately if inserted within 7 days of the start of your period. Otherwise, you will need to use a backup form of birth control (such as a condom) for the first 7 days after the IUD is inserted.
Some experts recommend using a backup method for the first month after the IUD is inserted because that is when the device is most likely to be ejected.

Bạn có thể sử dụng bao cao su như một phương pháp tránh thai dự phòng
9. How do I make sure my IUD stays in place?
You will need regular check-ups because the IUD can be pushed through the cervix or even out completely without you even realizing it.
9.1. How to check?
Your doctor will show you how to check the IUD. Wash your hands first. Then squat on the floor, sit on the toilet, or rest one leg on a chair. Place a finger in the vagina and feel the cervix. You should be able to feel the two lines come out of it and it may feel a bit like fishing line. Feel the string only with your fingertips, do not pull hard.
If you cannot locate the IUD cord or if you feel the device pass through your cervix into your vagina, see your doctor for an examination. Be sure to use another method of birth control (such as a condom) in the meantime because the IUD won't work if it's not completely in your uterus.
If you can't feel the wires and your doctor can't find them either, you'll be ordered to do an ultrasound to see if the IUD is still in place. Less than 5% of women who use an IUD will have it removed within the first year. Teenagers, women who have never had children, women with irregular periods, and those with severe menstrual pain may be more susceptible to an IUD prolapse.
If your IUD is sticking out of your uterus or has been completely expelled, you can put another ring in, but there is a 30% chance it will come out again.
9.2. When to test?
Health professionals recommend testing once a week for the first month and at least monthly thereafter. Right after your period ends is the right time to get tested, as the IUD is more likely to come out during your period than at other times.
If you've had a progestin IUD and no longer have your monthly period, choose an easy-to-remember date like the first of every month. Also check after whatever time period you have.

Sau đặt vòng, bạn cần thường xuyên đi kiểm tra phụ khoa
10. How is the IUD removed?
When it's time to remove the IUD, the doctor will insert a speculum into the vagina, clean the cervix, attach a small forceps to the cord, and use a cervical clamp to straighten the cervical canal. . Then, gently pull the cord and IUD out. This process takes less than 10 seconds.
IUDs are flexible and will fold as they pass through your cervix, but you may feel some pain in your abdomen. If you want to continue using your IUD, you can have a new IUD inserted at the same visit.
The IUD can be removed at any time during your menstrual cycle, if you are ready to conceive. However, if you are switching to another method of birth control, discuss when to start using it with your doctor. You may need to start using a new method before the IUD is removed to make sure you are fully protected.
11. How will the IUD affect menstruation?
With the progestin IUD, there will usually be irregular bleeding and spotting for the first three to six months. In the end, your period may become much lighter and shorter than it was before the IUD was inserted, and you may experience less abdominal pain. By the end of the first year, many women have irregular periods or stop menstruating altogether.
Copper IUDs can also cause irregular bleeding and spotting in the first few months. Your periods may become longer and heavier, especially during the first three to six months after the ring is inserted. They may lighten a bit over time but still be heavier than they were before the IUD was inserted. Some women also have more abdominal pain than before.
Women with heavy bleeding can be treated with medication and iron supplements if needed to prevent or treat anemia. If you continue to have heavy bleeding, you may have to remove the copper IUD. (You can replace it with a progestin IUD if you want.)
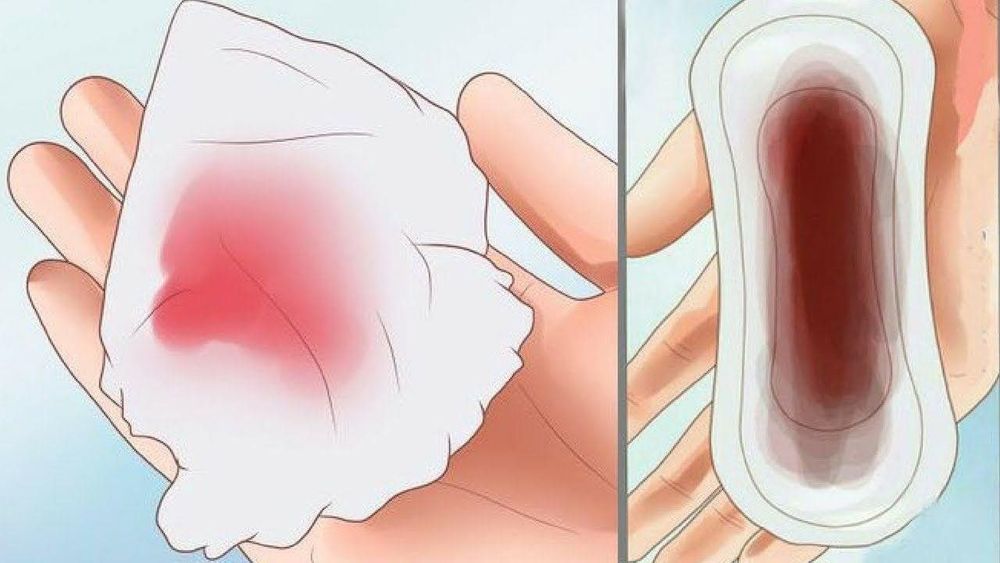
Vòng tránh thai có thể gây chảy máu âm đạo
12. Will the IUD cause any other side effects?
The IUD is not likely to cause any serious side effects. For a small number of women, the progestin IUD causes side effects such as acne, headaches, breast tenderness, and depression, which usually get better with time.
On the plus side, many health professionals recommend the progestin IUD for women who have heavy, prolonged, or painful periods because it tends to delay periods or even stop them altogether. And because they lose less blood, women using this IUD are less likely to develop iron-deficiency anemia, a condition that can cause fatigue and other symptoms.
Since the IUD is placed in your uterus, not your vagina, neither you nor your partner will be able to touch the device during sex, although your partner can feel the fibers.
13. What symptoms could signal a problem?
Warning signs may include sharp or severe pain in the pelvic area or lower abdomen, unexplained fever, unusual or foul-smelling vaginal discharge, genital sores, pain when having sex, bleeding or spotting after sex or between periods and severe or prolonged vaginal bleeding.
Call your doctor right away if you notice any of these symptoms or if you have any signs that you are pregnant, such as a missed period (with a copper IUD), chest pain or morning sickness. You should also call your doctor to rule out pregnancy the first time you miss a period after a progestin IUD is inserted.
Contact your doctor if you cannot feel the thread, if the thread is longer or shorter than usual, or if you or your partner feel the end of the IUD protruding from your cervix. Finally, call your doctor if you think you may have been exposed to an STI, even if you don't have any symptoms.

Đau rát khi quan hệ có thể là dấu hiệu cảnh báo tình trạng bất thường
14. What if I get pregnant while I have an IUD?
The first thing your doctor will do is check to make sure you don't have an ectopic pregnancy by giving you blood tests, a vaginal exam, and an ultrasound.
If your pregnancy is not ectopic, you can choose to continue the pregnancy. If you choose to continue, your doctor will remove the IUD, if possible. The device can be easily removed without invasive procedures as long as the wires are visible. There is a small risk that removing the IUD will cause you to lose a pregnancy, but you are more likely to get an infection that causes a miscarriage (and endangers your own health) if you keep the IUD.
In the event that the IUD cannot be easily removed and you choose to continue with the pregnancy, you will be carefully monitored. You are at risk of preterm birth if you become pregnant with an IUD
Currently, there are many methods of contraception that you can trust and have high safety such as using oral contraceptives daily, using condoms su. IUDs also have certain advantages and disadvantages. So you can consider and choose the right contraceptive method.
Vinmec International General Hospital is the address for examination, treatment and prevention of many diseases, including the specialty of Obstetrics and Gynecology. Therefore, if you are looking for a place to visit and want to have a suitable method of contraception, you can go to Vinmec for the best advice from experienced and qualified doctors. With the dedication and enthusiasm of the medical team, along with modern facilities will definitely make you satisfied.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: babycenter.com