This is an automatically translated article.
Inflammation of the parotid salivary glands in children often causes painful swelling around the ears and under the jaw on 1 or 2 sides, fever, nausea, fatigue all over the body... Children with parotitis are not detected. Timely detection and treatment can cause adverse health effects.
1. Learn about salivary glands and parotid inflammation
Salivary glands are located around the oral cavity, performing the function of producing saliva, making an important contribution to the body's digestion of food. In each human body, there will be 3 pairs of main salivary glands distributed on 2 sides of the face. The parotid salivary glands are known as the newest glands that are concentrated on the cheeks and just behind the ears. This gland extends from the rim of the ear down to the jaw. The sublingual salivary gland is usually located deep in the mouth and is smaller in size than the other two glands.
Inflammation of the parotid gland in children often presents with a bacterial or viral infection of the saliva or an autoimmune allergic condition. This condition will affect the system as well as the duct. When ductal inflammation occurs, it can block or reduce the amount of saliva that enters the mouth.
Due to the function of saliva, it will support the body in the process of digesting food, washing away bacteria and food particles, making the mouth clean. Besides, saliva will help the body control the number of good and bad bacteria in the mouth, balance the microflora. If there is a disorder in the formation and movement of saliva, the bacteria have the conditions to enter, survive and grow, leading to inflammation of the parotid salivary glands.
Parotid salivary gland inflammation can appear at any age, even in infants. Parotid gland inflammation as well as submandibular salivary gland inflammation is often more susceptible to infection than the other inflammation. Most cases of salivary gland inflammation are acute and sudden due to inflammation caused by blockage or narrowing of the ducts.
2. Causes of parotid salivary gland inflammation and signs to recognize
Parotid gland inflammation in children and adults is typically caused by bacterial infection. One of the most common types of bacteria is Staphylococcus aureus. In addition, it may also be caused by the presence of other bacteria such as streptococcus viridans, Haemophilus influenzae, E. Coli... Infection occurs, causing a decrease in saliva production affecting the ducts, possibly narrowing or blocking the ducts. . Some diseases can affect the reduction of saliva production of the body, including: Mumps, HIV disease or influenza A virus or Herpes, blocked salivary ducts due to mucus...
Inflammation of the salivary glands Parotid foam in children can show some signs to help identify. If your child has this condition, it is important to see a doctor immediately for an accurate diagnosis. Because the manifestations of the salivary glands can also cause confusion for other diseases such as taste disturbances, prolonged bad breath, inability to open the mouth to the maximum...
Patient or child Children with parotid salivary gland inflammation, in case of high fever, difficulty breathing or worsening symptoms, need to see a doctor immediately for timely treatment.
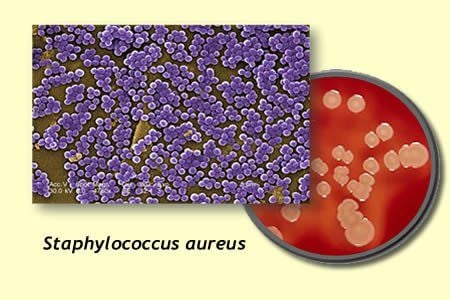
Staphylococcus aureus là một trong các vi khuẩn gây viêm tuyến nước bọt mang tai ở trẻ em
3. The degree of influence of parotid salivary gland inflammation
Inflammation of the salivary glands is less common with dangerous complications to the health of the patient. However, if parotitis in children is left untreated, pus can accumulate and form a salivary gland abscess. Furthermore, inflammation of the salivary glands can be caused by a benign tumor and cause the salivary glands to become larger than normal.
In the case of inflammation of the salivary glands can develop rapidly by malignant tumors that restrict movement inside the oral cavity. These tumors also affect the site where it is growing and spread to other areas.
Patients with recurrent parotid inflammation with symptoms of severe swelling can destroy the salivary glands. These complications can occur when bacteria from the salivary glands spread to surrounding and further areas of the body. For example, skin infections, cellulitis or in some cases can lead to Ludwig's angina syndrome, acute cellulitis in the mouth area and tongue thrusting, making it difficult for the patient to breathe and swallow.
4. Diagnosis and treatment of parotid salivary gland inflammation
Salivary gland inflammation can be detected through physical examination. Because the doctor can recognize the signs of painful salivary glands as well as pus formation. In cases where the doctor still has doubts about the symptoms of salivary gland inflammation, additional tests may be ordered to diagnose the effect and cause of the disease. When applying diagnostic imaging by ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) scan, it will help doctors see more closely the image of inflammation, abscesses or salivary stones, and tumors.
Treatment of parotid gland inflammation can apply different modalities depending on the extent or cause. Moreover, when treatment depends on the patient's current symptoms, such as swelling or pain...
The use of antibiotics can help kill bacteria, reduce pus as well as relieve pain. fever. If the patient has a severe infection that has formed an abscess, the doctor will need to perform a thorough aspiration of the pus from the site of inflammation.
If the inflammation of the salivary glands is mild, the patient should:
Drink about 8 to 10 cups of lemon juice a day to stimulate the salivary glands to work; Gently massage the inflamed salivary gland or apply a warm compress or towel to the inflamed gland; Gargle with salt water daily... Most people with salivary gland inflammation may not need surgical treatment. But where the inflammation is recurrent and has its own characteristics, surgery may be the treatment of choice.
Cha mẹ nên đưa trẻ đến gặp bác sĩ để được điều trị viêm tuyến nước bọt mang tai ở trẻ em
5. Ways to prevent inflammation of the parotid salivary glands
The majority of patients, including pediatric patients with parotitis, have no effective prevention. However, to reduce the risk of disease should use plenty of water and keep the oral hygiene clean. You can brush your teeth twice a day and floss.
Inflammation of the parotid salivary glands is quite common and very easy to get. However, the signs and symptoms can be easily confused with other conditions. In addition, the disease is usually not dangerous and has few complications. But if not treated early and definitively can affect the health of the patient. Therefore, when children have symptoms of parotid salivary gland inflammation, parents should take their children to a medical facility for timely examination and treatment.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.