This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Doctor General Internal Medicine Doctor - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.
Infectious endocarditis is diagnosed based on specific criteria. Based on the diagnostic criteria, the patient will be assigned an appropriate and effective doctor.
1. Diagnosis of infective endocarditis
Suggestions for diagnosis of infective endocarditis in patients include:
Heart murmur; Vascular events of unknown origin; Sepsis of unknown origin; Fever in patients with prosthetic valves, valvular heart disease, congenital heart disease, heart failure, conduction disturbances. In addition to the above diagnostic suggestions, infective endocarditis was diagnosed based on Duke's criteria including major criteria and minor criteria: Specifically:
1.1 Main standards
Blood cultures are positive for common bacteria that cause infective endocarditis : The type of bacteria is typically matched to a strain of bacteria isolated from two separate blood cultures (Streptococci viridans, Streptococcus bovis, S. aureus). , enterococcus, group HACEK); Bacteria suitable for endocarditis isolates from consecutive positive blood cultures: at least 2 positive blood cultures from blood samples taken 12 h apart or all 3 times Blood cultures were either positive or more than four times, the vast majority of which were positive provided that the first and last blood samples were taken at least 1 hour apart. Evidence of damage to the endocardium:
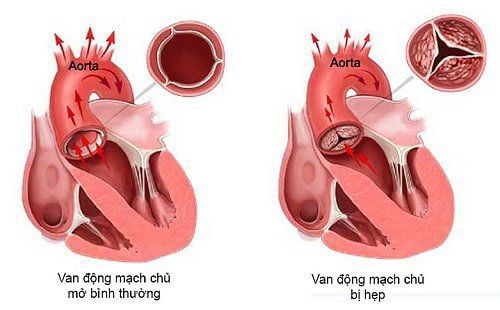
Echocardiography showed lesions of infective endocarditis such as warts, abscesses, and partial regurgitation of newly emerging prosthetic valves; New valve opening.
1.2 Sub-Criteria
Have heart disease common in endocarditis, have injected drugs; Fever higher than 38 degrees; Vascular signs: large artery occlusion, septic pulmonary infarction, fungal aneurysm, intracranial hemorrhage, conjunctival hemorrhage...; Immune markers such as: glomerulonephritis, Osler's nodule, Roth's spot, rheumatoid factor; Evidence of infection: positive blood cultures but not meeting major criteria or serological evidence of active infection consistent with the causative agent of infective endocarditis. A definitive diagnosis consists of two major criteria or one major criterion combined with three minor criteria or five minor criteria. A diagnosis of suspected endocarditis (with signs of endocarditis but not enough for a definitive diagnosis) but cannot be ruled out includes 1 major and 1 minor or 3 minor endpoints.
Diagnosis to exclude endocarditis includes confirming another diagnosis or resolving after 4 days of antibiotic therapy, biopsy or autopsy showing no evidence of disease or failing to meet the above diagnostic criteria.
>> See more: Learn about endocarditis - Article by Dr. Dao Thi Mai Lan - Vinmec Institute of Stem Cell and Gene Technology
2.Diagnosing the cause of infective endocarditis
Positive blood culture endocarditis: caused by streptococci and enterococci, staphylococci; Blood culture negative endocarditis: due to previous antibiotic use, strep throat; Endocarditis always has true negative blood cultures due to intracellular bacteria, hematology, cell culture or gene amplification; Endocarditis associated with negative blood cultures despite the use of antinutrients due to difficult-to-cultivate bacteria such as nutritional variants, HACEK, Brucella, and fungi gram-negative bacteria.
3. Treatment of infective endocarditis
3.1 Medical treatment
Treatment when blood culture results are not available:
Early antibiotic treatment (right after 3 blood cultures) with the aim of killing bacteria in wart lesions. Use antibiotics with bactericidal effect, high dose, combination of two antibiotics. The intravenous route should be used. Duration 4-6 weeks. The best antibiotic choice should be based on the results of blood cultures and antibiograms. Treatment while waiting for blood culture results:
Spontaneous valvular bacterial endocarditis: one of 3 options:
Ampicillin-sulbactam: 12g/24h, divided into 4 times, IV injection x 4-6 weeks and gentamicin sulfate 3mg/kg/24h divided into 3 intravenous injections/TB x 5-14 days. Vancomycin 30mg/kg/24h in 2 divided doses with 200ml of 0.9% NaCl or 5% glucose intravenously for at least 60 minutes x 4-6 weeks and gentamicin sulfate 3mg/kg/24h in 3 divided IV doses/ TB x 5-14 days and ciprofloxacin 1000 mg/24 h orally x 4-6 weeks or 800 mg/24 h divided into 2 intravenous infusions x 4-6 weeks. Note: + Vancomycin is used for patients who are allergic to penicillin. + Children should not exceed the dosage of the drug for a normal adult.
Ampicillin-sulbactam 300mg/kg/24h divided into 4-6 intravenous injections and gentamicin sulfate 3mg/kg/24h divided into 3 intravenous injections/TB x 5-14 days. And vancomycin 40mg/kg/24h divided into 2-3 intravenous infusions as above. And ciprofloxacin 20-30mg/24h in 2 divided doses intravenously or orally. Infective endocarditis prosthetic valve occurring < 1 year after heart valve replacement surgery: - Adults: Combine the following 4 antibiotics: + Vancomycin 30mg/kg/24h divided into 2 intravenous infusions as above x 6 week. + Gentamicin sulfate 3mg/kg/24h divided into 3 intravenous injections/TB x 2 weeks. + Cefepim 6g/24h divided into 3 injections slow IV x 6 weeks. + Rifampin 900mg/24h divided into 3 times orally or mixed with 5% Glucose IV infusion x 6 weeks. - Children: Combination of the following 4 antibiotics: + Cefepim 150mg/kg/24h divided into 3 slow intravenous injections (TE> 2 months). + Rifampin 20mg/kg/24h divided into 3 doses orally or intravenously (mixed with 5% Glucose solution). + Vancomycin dosage and route of administration as above. + Gentamicin dosage and route of administration as above. Infective prosthetic endocarditis occurring > 1 year after valve replacement surgery: Treat as spontaneous valve endocarditis, duration 6 weeks. Treatment when blood culture results are available: a combination of specific antibiotics according to the antibiogram, the duration of treatment is 4-6 weeks, especially with aminosides, the treatment time should be as short as possible (5-14 days). no more than 14 days.
3.2. Surgical treatment
Indications for absolute surgical treatment for the following cases:
Moderate to severe heart failure due to heart valve dysfunction (acute valve regurgitation due to perforation or laceration, mitral valve obstruction by large warts). The artificial heart valve is unstable. Infections not controlled with antibiotics. Infectious endocarditis on prosthetic valve recurred after optimal antibiotic therapy In the following cases, surgical treatment is relatively indicated:
Invasive perivalvular infection. Infectious endocarditis recurs after optimal antibiotic therapy (on natural valves). Infective endocarditis with blood cultures (-) and persistent fever. Large papules > 10mm The ideal time of surgery is within 10 days of antibiotic use, surgical treatment should not be delayed to avoid severe disease, should give antibiotics with optimal effect 24-72 hours before surgery.
Depending on the condition of the disease, the treatment regimen will be different, in order to achieve the most effective treatment results, the patient needs to be detected as soon as possible. Cardiology Center - Vinmec International General Hospital has a team of experts including experienced professors, doctors, specialist doctors, and masters in the field of medical and surgical treatment. , interventional cardiac catheterization and application of advanced techniques in the diagnosis and treatment of cardiovascular diseases.
In particular, the Center has modern equipment, on par with the most prestigious hospitals in the world. The Center has a comprehensive cooperation program with the Heart Institute - Bach Mai Hospital, the Cardiology Department of Hanoi Medical University, Paris Descartes University - Georges Pompidou Hospital (France), the University of Pennsylvania (USA). .
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.