This is an automatically translated article.
This article is expertly consulted by Master, Doctor Nguyen Le Duc Hoang - Emergency Medicine Doctor - Emergency Department - Vinmec Danang International Hospital. The doctor has a lot of experience in the treatment of Resuscitation - Emergency care for adults.Using industrial methanol can be toxic to internal organs, especially the nervous and visual systems. Therefore, it is necessary to detect and treat early when the patient shows signs of industrial Methanol poisoning.
1. What is Industrial Methanol Poisoning?
Alcohol or alcohol (alcohol) has many types including: Ethanol, Methanol, Ethylene glycol, isopropanol,... In which, ethanol (alcohol) can be used in alcoholic beverages. The rest are toxic.Methanol is fermented from cellulose-containing materials (wood) or synthesized using hydrogen and carbon dioxide. Methanol, also known as methyl alcohol, with the chemical formula CH3OH, is a clear, colorless liquid at room temperature. Methanol is currently widely used in many industries, used as a solvent to dissolve organic and inorganic substances or to extract oils,... On the market, Methanol is in cleaning solutions, antifreeze,... and used as an alternative energy source in engines. This substance is absolutely not used as a food alcohol like Ethanol.
Methanol itself is less toxic, but its metabolites are highly toxic. Methanol is readily absorbed from the skin, lungs and intestines, and is metabolized slowly by the liver. They can cause metabolic acidosis, blindness or even death. Methanol affects mainly the central nervous system with symptoms such as drunkenness, drowsiness, convulsions, coma,... The clinical course of industrial Methanol poisoning occurs many hours after ingestion. .
The fatal dose of pure Methanol is estimated at 1 - 2ml/kg. However, there have been cases of permanent blindness and death with doses of only 0.1ml/kg.
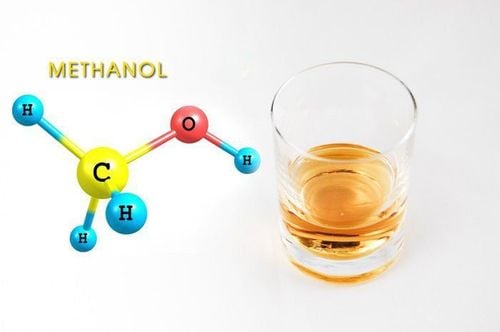
2. Causes of industrial Methanol poisoning
Drinking alcohol mixed from solutions containing methanol , use poor quality food alcohol.3. Symptoms of industrial Methanol poisoning
Symptoms of industrial methanol intoxication usually appear within 30 minutes of ingestion but can also appear later. Symptoms often depend on the stage: the insidious phase (first few hours - 30 hours) and the next obvious poisoning phase. Common symptoms in people with Methanol poisoning include:Nervous: The patient is usually awake but very headache, dizziness, then may forget, restlessness, confusion, lethargy, coma, convulsions,... When severely poisoned, the patient may have hemorrhage or infarction of duckweed, brain drop,...; Vision: Initially normal vision, after 12-24 hours, there are symptoms of blurred vision, double vision, photophobia, eye pain, impaired or lost vision, hallucinations. In severe poisoning, the patient's pupils may react poorly to light; Cardiovascular: Hypotension, vasodilation, heart failure; Respiratory: Weak breathing, stop breathing; rapid and deep breathing if metabolic acidosis is present;

4. Diagnostic tests for Methanol poisoning
Diagnostic tests, monitoring poisoning: Quantifying blood Methanol levels: Perform at least 2 times/day, test at the time of admission, before and after dialysis, at the end of treatment; Blood osmolality: Combined with blood glucose, urea and electrolyte tests, performed every 4 hours; Basic tests: Blood gas, blood count, glucose, urea, creatinine, electrolytes, ALT, AST, electrocardiogram, urinalysis,...; Other tests: Look for damage to other organs or complications: X-ray of the lungs, computed tomography of the brain, magnetic resonance imaging of the brain, ophthalmoscopy, abdominal ultrasound,... Note: Need to differentiate industrial Methanol poisoning from Ethanol poisoning, diabetic coma, coma due to sedative poisoning, retinal detachment,...
5. Treatment of industrial Methanol poisoning
5.1 Principles of treatment Ensure stabilization of the patient's emergency conditions: Airway, respiration and circulation; Prevent the conversion of Methanol into toxic substances; Use specific antidote, if there is clear evidence, early dialysis should be indicated; Increased elimination of Methanol and its metabolites; Treatment of symptoms, complications and supportive treatment. 5.2 Implementation of specific treatment Basic treatment measuresPatients with deep coma, tongue drop, convulsions, sputum stagnation, respiratory failure, weak breathing or apnea: Place the patient in the supine position. , put an oral cannula, aspirate sputum, breathe oxygen, intubate, put on mechanical ventilation with hyperventilation depending on the severity of symptoms; Patients with hypotension : Fluids and vasopressors if necessary;
Gastric catheterization and aspiration if the patient is hospitalized within 1 hour and has little vomiting. For patients who are hospitalized later but consume a lot of methanol, gastric aspiration can still be considered; Increase the elimination of toxins: Ensure urine flow, filter the body's blood as indicated (dialysis dialysis, continuous dialysis or peritoneal dialysis depending on the specific case); Using specific antidotes: Ethanol and Fomepizole (4-Methylpyrazole) have the effect of preventing Methanol from converting into toxic substances, eliminating free Methanol from the body through the kidneys or dialysis. If these drugs are stopped or used insufficiently, without dialysis, Methanol will continue to be converted into and toxic to the body. Ethanol is effective, low-cost treatment but has some side effects on the central nervous system, causing electrolyte disturbances, hypoglycemia. And Fomepizole is effective, easy to use, easy to monitor, but has high treatment costs; Use supportive medicine: Use Folic Acid or Leucovorin (promote the body's detoxification) and Sodium bicarbonate (when metabolic acidosis) with appropriate dosage.
Therefore, it is necessary to detect and bring patients to the hospital as soon as they have symptoms of industrial Methanol poisoning. In particular, should limit alcohol consumption, only drink food alcohol of clear origin to prevent the risk of Methanol poisoning.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Recommended video:Periodic health check at Vinmec: Protect yourself before it's too late!
MORE
Why can methanol alcohol cause poisoning? Treatment of acute ethanol poisoning Treatment of industrial methanol alcohol poisoning