This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by an eye doctor - Department of Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Hai Phong International General HospitalEyelid ptosis is the prolapse of the upper eyelid lower than the normal position (normally, the upper eyelid margin covers the upper pole edge of the cornea by 1-2mm), causing loss of facial aesthetics and affecting visual function. Eyelid stenosis surgery is considered an effective method to solve drooping eyelids.
1. Indications and contraindications for surgery
1.1. Indications Blepharoplasty is indicated for the following cases:Acquired blepharospasm: The levator muscle is permanently or temporarily reduced in contractility in focal or diffuse myopathies (dysplasia). muscular dystrophy, oculopharyngeal muscular dystrophy, chronic progressive ophthalmoplegia, Guillain-Barré syndrome,...), after Botulinum toxin injection,... Mechanical slit stenosis: Upper eyelid is pinched pressure (upper eyelid tumor, orbital tumor, enlarged lacrimal gland,...) due to sagging eyelid skin, due to adhesions (perimuscular fibrosis, large scarring of eyelids, eyelid-bridge adhesions due to burns, drug allergies, trachoma, etc.) ...),... Neuro-muscular cleft stenosis in severe myasthenia gravis. Eyelid stenosis due to trauma, surgery, vascular intervention: Orbital surgery, craniocerebral surgery, vascular intervention can also directly damage the muscle and nerve fascia, causing eyelid collapse. Narrowing of the eyelids due to old age: The levator fascia muscle is stretched, the adhesion point slips, the upper eyelid is stretched, excess skin, excess fat, lacrimal gland prolapse,... 1.2 Contraindications Contraindicated in eyelid surgery with Case:
New lesions appear (scarred eyelids are less than 6 months stable, 7th nerve palsy is less than 3 months of follow-up). Systemic pathology does not allow surgery.

Các tổn thương mới xuất hiện có chống chỉ định phẫu thuật
2. Eyelid surgery
2.1 Treatment purposes Improve the function of releasing the pupil area, limiting complications (amblyopia, amblyopia ...) to improve aesthetics. Selection of eyelid surgery method: Based on the mechanism causing ptosis, the degree of ptosis, the function of the levator muscle and other influencing factors. 2.2 Timing of surgery With congenital ptosis: Usually when the child is 5-6 years old, if the ptosis is severe, there is a risk of amblyopia or deviated head, it is necessary to operate earlier, possibly from 1 year of age. With acquired cleft palate: When ptosis and cause are stable. Level of adjustment: Lifting the eyelids to the best level (both functional and aesthetic, with a preference for the upright position) but still ensuring the function of covering the eyeball of the eyelid (no corneal opening when eyes are closed). 2.3 Surgical procedure for cleft palate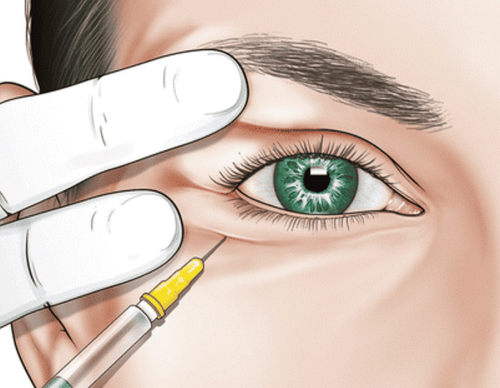
Trước khi bắt đầu phẫu thuật, bệnh nhân sẽ được gây tê tại chỗ
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.