This is an automatically translated article.
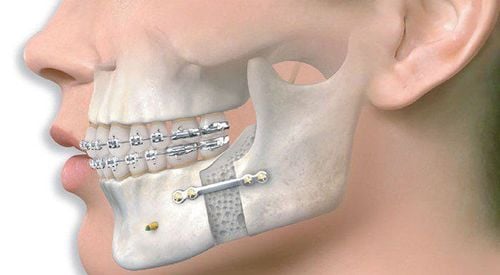
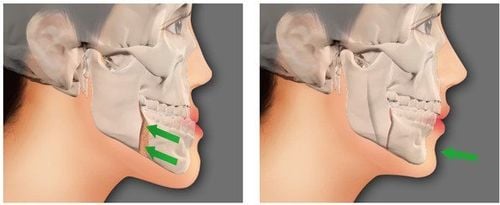
Root canal surgery to remove the pathological root along with the apical inflammatory tissue cannot be preserved after endodontic treatment in multi-rooted teeth. Root canal surgery is indicated to preserve the remains of the natural teeth that have been successfully endodontically treated.1. When is endodontic surgery to dissect the root of the tooth indicated?
Partition endodontic surgery (Apical apexectomy) is indicated when conventional endodontic surgery is not possible, endodontic treatment is unsuccessful, or re-endodontics cannot be performed.Patients often present with clinical signs including: Swelling, pain, appearance of fistula in the periapical or radiographic region (eg, radiographic lesions persist or continue to progress) despite treatment endodontic treatment. Specifically, the following cases need to be indicated for root canal surgery:
1.1. Due to abnormalities in anatomical structure The canal was calcified, pulp stones were observed. The root is bent at the bend, especially in the apical third. The root is not apex closed with the apical foramen open at a wide angle. The root canal system is complex, especially in the apical part. Signs of internal or external resorption in the apical third. The root is broken in the apical 1/3. 1.2. Due to reasons related to previous endodontic surgery, Fillings do not fit horizontally or vertically in the root canal system. Overfilling is too apex, if the residue is a sealant, it can be dissipated over time. On the other hand, materials such as cones are not digestible, leading to chronic irritation in the periapical region. Break the instrument in the canal. Performing root canal drilling in the wrong direction or perforating the canal. In terms of shortening endodontic treatment time: Mainly because patients do not have time to adhere to conventional endodontic treatment. 1.3. Due to the influence of fixed prosthetics In case the damaged tooth root has a good fixed prosthesis that cannot be removed due to the risk of root loss or economic reasons, endodontic surgery can be performed. root cutting without removal.
Therefore, root canal surgery combined with retrograde filling is necessary to prevent the growth and spread of bacteria from the canal to the periapical tissue.
2. In case of contraindications for root canal division
2.1. Systemic contraindications Root canal surgery should not be performed in patients who are elderly, have a history of cardiovascular disease, hypertension, myocardial infarction, are taking anticoagulants, or have coagulation disorders. , patients with diabetes or those undergoing radiation therapy,...2.2. Regional contraindications In case the tooth has a close relationship with neighboring nerve landmarks such as maxillary sinus, nasal cavity, chin hole, lower dental canal, palatal artery and alveolar septum.
Besides, this surgery is not indicated for difficult cases due to unfavorable surgical position; For example, the root of the molar is too deep, the patient cannot open the mouth wide, and the cheek muscle tone is too strong.
2.3. Local contraindications When conventional endodontic surgery is still possible, it is not possible to pinpoint the exact cause of failure when performing conventional endodontic treatment. There are indications for tooth extraction when bone loss exceeds 1/3 of the apex, leading to weak remaining roots. Patients with poor oral hygiene, chronic periodontal disease. The patient has a fractured tooth root.
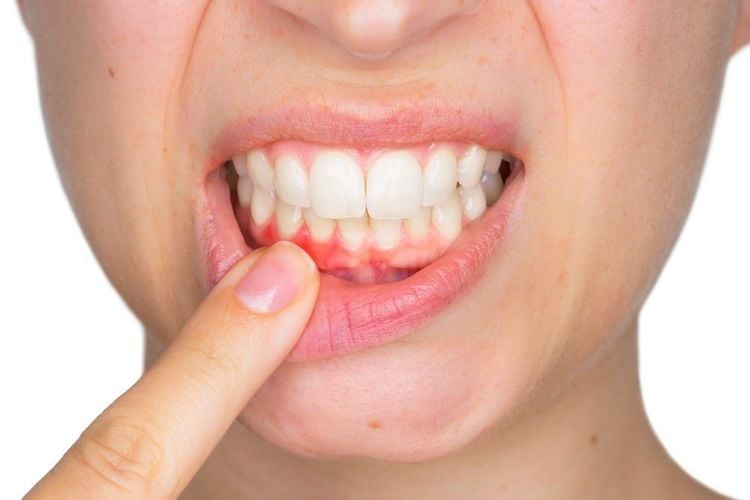
Bệnh nhân mắc bệnh nha chu mạn có chống chỉ định với phẫu thuật chia cắt chân răng
3. Steps to perform root canal surgery
The surgical sequence to dissect the root of the tooth includes the following steps:Create flap. Locate the apex, conduct an osteotomy to expose the periapical region and remove inflammatory tissue. Cut the tip. Backfill if necessary. Close flap. 3.1. The decision to choose a flap depends on many factors, mainly depending on the position of the tooth to be cut apical, the condition of the periodontal tissue, the restoration or not, the size of the peri-apical lesion. .
In apical surgery, three types of flaps are usually used: semicircular flap, triangular flap, trapezoidal flap. A semicircular flap is usually indicated in cases of small, individual tooth lesions and is usually indicated in the maxillary anterior teeth and most apical surgery is performed. To ensure the best healing, the incision must be a certain distance from the contour of the defect so that the flap is well nourished.
In the case of a large defect, especially when the defect is directed towards the alveolar crest, a triangular or trapezoidal flap is preferable. Note that pathological lesions that have penetrated or have adhered to the periosteum must be separated from the flap with a scalpel. Where a fistula is present, the fistula must be cut close to the bone, because if it is cut intramuscularly, a larger perforation of the bone may occur and will interfere with bone healing.
When apical surgery is performed in the anterior region (eg, in the maxillary lateral incisors) and there is a large bone defect near the alveolar crest, then a trapezoidal flap is used. Trapezoidal flap incision begins at the proximal surface of the central incisor, continues to make a continuous incision around the cervical line of the lateral incisors, canines, and ends at the distal side of the canines. Use a spatula to carefully separate the flap from the bone and flip the flap upwards.
3.2. Locate and expose the tooth apex: The next step after flap creation is to locate and expose the tooth apex. Once the periapical lesion was opened to the cheek, after removing the diseased tissue with a curette, it was relatively easy to locate and expose the root apex. If the outer alveolar bone covering the lesion has not been completely destroyed but is very thin, its surface can be found with a probe or curettage, then, thanks to the reduced bone density, the underlying bone will be easily removed and at this time the tooth apex will be located. When the outer alveolar bone is still completely intact, then the tooth apex will be identified by X-ray film.
More specifically, after taking the film, the root length is determined by a sterilized endodontic file or metal endodontic ruler. The measured length is transferred to the surgical field and the exact position of the apex is determined. Then, use a handpiece with a round drill with isotonic saline spray to clean all the outer alveolar bone surrounding the apex, creating a "bone window" until the apex is exposed. If the upper bone is thin, and the lower lesion is wide, then the "bone window" will be enlarged with a fine drill or with bone forceps. Widen the window until the entrance to the lesion is wide enough. At this time, use a scraper to remove the diseased tissue and foreign bodies, the obturator... before the apical resection begins.
3.3. Wash the wound and close the flap After the amalgam filling is complete, remove the gauze from the lesion, clean the wound with physiological saline solution, take a film to check if excess amalgam falls into the surrounding tissue or not. Close the flap with removable stitches. Evaluation of the healing process was performed every 6-12 months with radiographs until periapical healing was observed. To compare results, it is recommended to take preoperative films and then compare them with postoperative films.
Apical surgery when performed in the anterior tooth region (eg in the central incisor), the size of the lesion is small, and when the anterior tooth is crowned, the semicircular flap is preferred.
The procedure for performing an apical surgery using a semicircular flap is similar to that of using a trapezoidal flap described above.
4. Post-operative care

Sau khi thực hiện chia cắt chân răng, bạn có thể bị đau, phù,...
Pain: Usually not severe and responds to pain medication. Edema: Most common in prolonged intervention and extensive tissue trauma. The most edematous manifestations usually fall on the second and third day after surgery and will be reduced with cold and hot compresses after the intervention. Bruise: Caused by bleeding under the tissue, common in patients with less stable subcutaneous vascular structure, patients often have skin discoloration from dark to light, then disappear after about 10 day. Indications for endodontic surgery to remove the root of the tooth are not common. However, if indicated, you should do so as soon as possible.
To examine and treat dental problems, you can go to the Department of Odonto-Stomatology - Vinmec International General Hospital. Vinmec is a high-quality medical facility in Vietnam with a team of highly qualified medical professionals, well-trained, domestic and foreign, and experienced.
A system of modern and advanced medical equipment, possessing many of the best machines in the world, helping to detect many difficult and dangerous diseases in a short time, supporting the diagnosis and treatment of doctors the most effective. Hospital space designed according to 5-star hotel standards will bring patients comfort, friendliness and peace of mind.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference articles: ranghammat.com, kcb.vn, bvdkquangnam.vn