This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted with Cardiologist - Cardiovascular Center - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.Inversion of the heart is a birth defect of the heart in which the two main arteries that carry blood away from the heart - the pulmonary artery and the aorta - are displaced. This is a rare but serious heart defect that changes the way blood flows through the body, leading to severe hypoxia. Without early artery bypass surgery, the body is not supplied with an adequate supply of oxygen-rich blood, so it cannot function properly and the child can face serious complications, including death.
1. What is angioplasty?
The aorta and pulmonary artery are the two main arteries that carry blood away from the heart into two important circulations of the body, bringing oxygen-rich blood to the organs and bringing oxygen-poor blood to exchange in the lungs. .Inversion of the arteries is when the positions of these arteries are opposite from the two ventricles. In other words, the aorta comes from the right ventricle, carrying oxygen-poor blood to the organs, while the pulmonary artery from the left ventricle carries oxygen-rich blood to the lungs.
In order to survive with this defect, the child must always have other heart defects associated with it. About 25% of children with inversion of the artery have a ventricular septal defect that allows the blood of the two circulations to be mixed. The site of blood mixing may also be located elsewhere, such as when an atrial septal defect or ductus arteriosus is present. In addition, in nearly one-third of cases, there is also an abnormality of the coronary arteries. In addition, the infant may also have a narrowing below the accompanying pulmonary valve, blocking the flow of blood from the left ventricle to the lungs.

Bệnh đảo gốc động mạch là một dị tật bẩm sinh của tim
2. What are the signs and symptoms of children with islets of the arteries?
Transposition of the great arteries can be diagnosed prenatally by fetal echocardiography. However, because this pathology is quite rare, the chances of being missed are high.After birth, transposition of the great arteries is almost always diagnosed within hours or within the first day due to the infant's cyanosis or low oxygen levels. All newborns have a ductus arteriosus at birth, so it is possible to allow enough blood to mix to prevent the initial severe cyanosis. Then, as the ductus arteriosus begins to close, which usually occurs in the first hours or days after birth, cyanosis worsens and this pathology is discovered.
Even with a ventricular septal defect, a heart murmur is often undetected during the first days or weeks of life. However, the existence of sites that allow the mixing of blood to provide a safe level of oxygen to the body's circulation will often lead to the development of signs and symptoms of congestive heart failure within a short period of time. the following weeks or months.
If left untreated, more than 50% of infants with islets of the artery will die within the first month of life, 90% within the first year.
3. How is the disease of the origin of the artery to be diagnosed?
When an infant has significant cyanosis after birth, congenital heart abnormalities should be checked. At this time, echocardiography will be a useful tool that can quickly and accurately demonstrate abnormal connections of the great arteries as well as important features of cardiac anatomy, such as presence and size. of atrial septal defect or ventricular septal defect, branching patterns of coronary arteries.At the same time, in order to accurately determine the anatomical features before surgery, the child may have cardiac catheterization or cardiac magnetic resonance imaging to clarify some details of the defect, helping surgery. members with appropriate regimens and preparations.
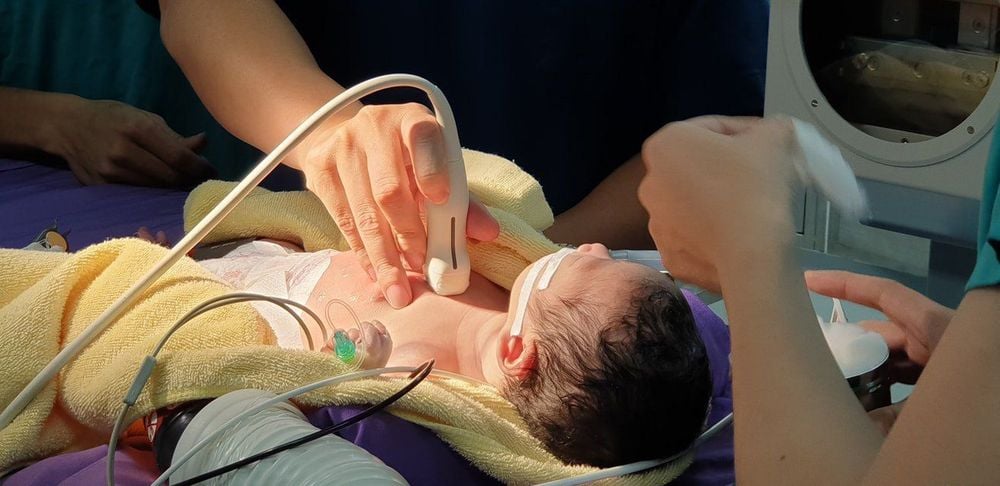
Siêu âm sẽ là công cụ hữu ích để phát hiện và chẩn đoán các vấn đề về tim ở trẻ sơ sinh
4. Surgical intervention to switch the origin of the artery
Indications for arterial bypass surgery are set forth immediately in order to establish a safe oxygen level for the life of the child.During the diagnosis and preparation for surgery, the child will receive continuous infusion of prostaglandins, a drug that helps keep the ductus arteriosus open. This will allow the mixing of oxygen-rich blood with oxygen-poor blood, improving the level of oxygen in the blood that enters the aorta to supply the body.
If for any reason the bypass surgery is delayed, such as the child's physical condition, cardiopulmonary function, and hemodynamics, a procedure called "balloon atrial septal resection is not possible. " is usually done to increase the site of blood mixing. Before birth, all newborns have an atrial septal defect between the right atrium and the left atrium. After birth, this orifice will either completely close up like a ductus arteriosus, or its partial existence may limit the ability to mix blood. Thus, transcatheter balloon septal resection helps to maintain the septum as well as enlarge the septum, so that the blood of the two circulations is better mixed. Compared with transarterial conversion, this supportive, interventional procedure is simpler, can be performed at the bedside, with echocardiographic guidance, or is sometimes performed in the operating room. combined with cardiac catheterization.
Although the newborn can still maintain a stable condition temporarily with the above-mentioned modalities, surgery to correct the radical defect is always an absolute indication.
In most cases, transposition is usually performed within the first week of life, when the infant has recovered from any instability that occurred during the appearance of cyanosis. head. In more complex cases, such as children with subpulmonary stenosis or pulmonary stenosis, the timing of surgery may vary.
The arteriovenous rooting surgery process has the principle that the aorta and pulmonary artery will be moved to its correct position: the aorta attaches to the left ventricle and the pulmonary artery attaches to the right ventricle. The coronary artery will be attached to the aorta.

Phẫu thuật chuyển gốc động mạch thường được thực hiện ngay trong tuần đầu tiên của cuộc đời
In summary, the indications for transarterial artery bypass surgery need to be established within the first few hours to weeks after birth. This is the mainstay of treatment for children with islets of the arteries. The repositioning of the great arteries will help the baby have a natural suitable circulation and have a chance to develop normally like any other newborn.
Vinmec International General Hospital currently has all the professional conditions and technical means to perform the artery bypass surgery. Vinmec gathers a team of highly qualified and experienced cardiologists; modern medical equipment, up to international standards; professional service quality, helping to improve the efficiency of disease diagnosis and treatment.
Customers wishing to be examined and treated at Vinmec International General Hospital, please register for an online examination on the Website for the best service.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.