This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by - Master, Resident, Specialist I Trinh Le Hong Minh - Department of Diagnostic Imaging - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.Abdominal aortic aneurysms are often found during a physical exam or during medical tests such as an echocardiogram or abdominal ultrasound. To diagnose an abdominal aortic aneurysm, doctors will review your personal and family medical history and perform a physical exam. If your doctor suspects you have a disease, he or she may order some necessary imaging tests. What techniques are used to evaluate abdominal aortic aneurysms?
1. Characteristics of abdominal aortic aneurysm
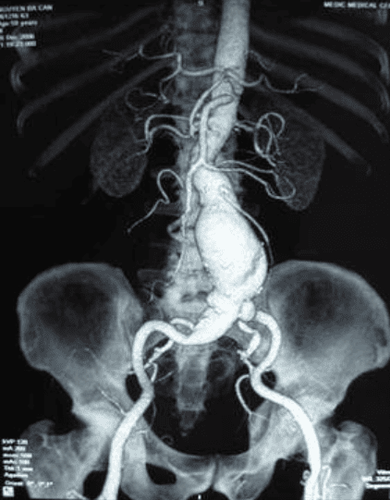
Abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAA) occur when atherosclerosis or plaque buildup causes the wall of the abdominal aorta to become weak and easily deformed, expanding like a balloon. Abdominal aortic aneurysms usually develop slowly over time with few notable characteristic symptoms. The larger the abdominal aorta, the higher the risk of rupture of the abdominal aorta. Once the abdominal aorta ruptures, they cause severe abdominal pain, back pain, dizziness, nausea, and shortness of breath.Doctors can identify abdominal aortic aneurysms with methods such as abdominal ultrasound, abdominal and pelvic computed tomography, or angiography. Treatment for an abdominal aortic aneurysm depends on the location and size of the aneurysm, as well as the patient's age, kidney function, and other medical conditions. Aneurysms less than 5cm in diameter are usually monitored with ultrasound or computed tomography every 6 to 12 months. Larger diameter abdominal aortic aneurysms or rapidly progressive disease may warrant open surgery or endovascular surgery.
2. Symptoms of abdominal aortic aneurysm
Most patients with an abdominal aortic aneurysm do not develop any symptoms until the aorta is maximally dilated and ruptures. If the abdominal aorta ruptures, the person may experience one or more symptoms, including:A sudden, severe pain in the abdomen or back. The pain can then spread from the abdomen or back to the pelvis, legs or buttocks of the patient. Pale skin, sweating, increased heart rate In many cases, shock or temporary loss of consciousness occurs. Abdominal aortic rupture is a dangerous condition, so if you detect any of the above symptoms, you need to take the patient to the nearest medical facility for timely emergency treatment. .

3. Causes and some factors that increase the risk of abdominal aortic aneurysm
The cause of abdominal aortic aneurysm is still a conundrum for scientists. However, several factors that have been studied and proven to potentially increase the risk of an abdominal aortic aneurysm can be listed as follows:Smoking : Cigarette smoke can be directly damage the lumen of the blood vessels, causing them to bulge, increasing the risk of abdominal aortic aneurysm. In addition, smoking also causes blood pressure to rise, thereby increasing pressure on the vessel walls leading to reduced elasticity of the vessel walls. High blood pressure: High blood pressure is a condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is increased. High blood pressure can weaken the walls of your arteries, including the abdominal aorta, increasing your risk of developing an abdominal aortic aneurysm. Vasculitis: Inflammation in certain blood vessels, especially the abdominal aorta and other arteries sometimes also leads to an abdominal aortic aneurysm, but this is rare. Aneurysms can occur in any blood vessel in the body. However, abdominal aortic aneurysms are considered the most serious because of the size of the abdominal aorta and the amount of blood flow through it. In addition, a number of other factors can also increase the risk of abdominal aortic aneurysm, which are:
Gender: The incidence of abdominal aortic aneurysm is much higher in men than women. Obesity Age: People over 60 have a higher risk of developing abdominal aortic aneurysms. Genetic factors: People with a family history of abdominal aortic aneurysms also have a higher risk of developing abdominal aortic aneurysms than other people. Hypertension, especially in the age group 35 to 60 years. High blood cholesterol or atherosclerosis Sedentary Have had a number of injuries that caused damage to the abdomen.

4. Imaging techniques used when evaluating abdominal aortic aneurysm
Most cases of abdominal aortic aneurysm are discovered accidentally through abdominal ultrasound techniques, computed tomography to determine the cause of other diseases. In other cases, the patient actively detects abnormalities and visits the doctor, the doctor through the physical examination can detect the status of the abdominal aorta pulsating or hearing abnormal sounds in the abdominal cavity. abdomen with a stethoscope.To be able to make an accurate diagnosis of this disease, doctors will order a number of imaging tests to diagnose abdominal aortic aneurysm, including:
Abdominal ultrasound: Abdominal ultrasound: Abdominal aorta is a highly accurate method of measuring the diameter of the abdominal aorta to determine if the abdominal aorta is excessively distended. A special ultrasound technique called a doppler ultrasound may be ordered to check blood flow through the abdominal aorta. Sometimes the images of the abdominal aorta are not clear on ultrasound because they are often located deep, obstruct vision or perform ultrasound in overweight and obese patients. Computed tomography of the abdomen and pelvis: This technique offers relatively high accuracy in determining the size and extent of abdominal aortic aneurysms. In addition, computed tomography can detect changes in the structure of the abdominal aorta. This can be very helpful in planning surgery for an abdominal aortic aneurysm. Abdominal aortic angiography: Considered the old “gold standard” in the diagnosis of abdominal aortic aneurysm, aortic angiography allows optimal assessment of the length of the aorto-iliac lesion or its anatomical variations. , location and severity of obstructive arterial disease and associated visceral or iliac artery aneurysms. The disadvantage of this method is that it is invasive, high radiation dose, and must use contrast agents. In addition, this method does not provide information on thrombus or aneurysms and may not accurately assess the diameter of the aorta. Magnetic resonance imaging: Recent advances in technology have allowed physicians to use magnetic resonance imaging in the diagnosis of abdominal aortic aneurysms. Therefore, this method emerges as the new "gold standard" in the evaluation of abdominal aortic aneurysms before and after surgery with its less invasive nature and much lower technical cost compared to other methods. other.
Vinmec International General Hospital is the leading medical address for diagnosis and treatment of aortic aneurysms. It has all the necessary medical equipment to perform simple to complex treatments such as medical treatment, stent-graft intervention, surgery... Highly qualified, trained and certified in technical skills, can handle quickly and effectively, especially in cases of urgent emergency. Therefore, patients with thoracic aortic aneurysms can rest assured with a strict, methodical and effective treatment process at Vinmec.
Before taking a job at Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital, the position of Doctor of Radiology since February 2018, Doctor Trinh Le Hong Minh used to work as a resident in the Radiology Department at Vinmec Central Park. hospitals: Cho Ray, University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Oncology, People's Gia Dinh, Trung Vuong... from 2012-2015. Working officially at Cho Ray Hospital from 2015-2016, City International Hospital since 2016.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: radiologyinfo.org