This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Doctor Tran Thi Diem Trang - Respiratory Internal Medicine Doctor - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital. The doctor has more than 10 years of experience in the treatment of respiratory diseases.Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis is a lung disease that causes the tissues in the lungs to become stiff and fibrous. The fibrosis of the lungs makes it difficult for the patient to breathe. Let's learn about idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis through the article below.
1. What is idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis?
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis is a lung disease of unknown etiology, in which the thickening of the lung alveolar walls due to scarring makes it difficult for the patient to breathe, cough, and fatigue. blood is reduced.2. Causes of pulmonary fibrosis
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis is also known as primary pulmonary fibrosis, this term is used to distinguish it from pulmonary fibrosis secondary to lung lesions such as tuberculosis, pneumonia or pulmonary infarction,...Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis etiology means that the cause of pulmonary fibrosis is unknown, but there are many risk factors that trigger the process of damage to the cells lining the alveoli, such as:
Tobacco: Pulmonary fibrosis is common in people with smoke or have ever smoked; Viral infections: Certain strains of the virus including Epstein-Barr, hepatitis C; Gastroesophageal reflux disease: When gastric juices back up into the esophagus, if left untreated for a long time, the patient can inhale into the lungs unconsciously and cause pulmonary fibrosis; Genetics: In some cases, idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis can be hereditary; Some drugs like Methotrexate, Cyclophosphamide, Azathioprine... can cause side effects; Living environment, working environment is polluted, when exposed or exposed to wood dust, metal dust and some chemicals.
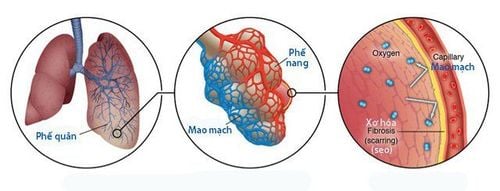
3. Signs of lung fibrosis
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis causes scarring and causes the lungs to harden. If not detected and treated, the scars in the lungs will become more severe and cause a number of symptoms such as:Difficulty breathing; Coughing profusely and persistently; Or tired; Unexplained weight loss; Feeling uncomfortable in the chest; When the lungs do not receive enough oxygen to supply the body, it leads to respiratory failure and heart failure, as well as a number of other health problems.
4. Who is prone to pulmonary fibrosis?
Most patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis with symptoms of cough and shortness of breath are usually between the ages of 50 and 70 years old, rarely in patients under 50 years of age; Men have the disease more often than women, but recently the incidence of pulmonary fibrosis has also increased in women; In some cases, idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis occurs in multiple members of the same family, so it is suspected that the disease is caused by a genetic predisposition.5. Stages of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis does not have a specific stage, but the disease still has stages with characteristic manifestations when it progresses:First time diagnosis: The patient may not need oxygen support. However, after that, patients may need oxygen during activity because they find it difficult to breathe during daily activities such as walking or cleaning the house. As the scarring of the lung gets worse, the person may need oxygen all the time even at rest, activity, and even sleep; Subsequent stages of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: The patient is constantly in need of oxygen. As the disease worsens, some patients experience flares or periods of more difficulty breathing. At this point, the damage to the lungs is irreversible and the lungs lose function.
6. Diagnosis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
Your doctor may suspect you have idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis based on symptoms of a dry cough or shortness of breath. Unusual breathing sounds, called crackles, may be heard by your doctor when you take a deep breath in. The crackling sound is like when you remove the Velcro tape. You or your doctor may also find that the tips of your fingers and/or toes are deformed (called clubheads). These signs are likely to lead to referral to a respiratory specialist. The respiratory doctor will do a physical exam and order some tests, like chest X-ray, respiratory function, or blood oxygen levels. Other tests that may be needed include blood tests, high-resolution chest CT, echocardiography, and in some cases, lung biopsy.In some cases, idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis can be diagnosed when high-resolution CT shows a particular pattern and other causes of pulmonary fibrosis are excluded. In some cases, when high-resolution CT does not show the “typical” form of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, a lung biopsy may be needed to confirm the diagnosis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. The most common way to do a lung biopsy is with video thoracoscopic surgery, under anesthesia. During this procedure, the surgeon makes two or three short incisions in the chest and uses a flexible camera that is able to look inside the chest and take a sample of lung tissue for evaluation.
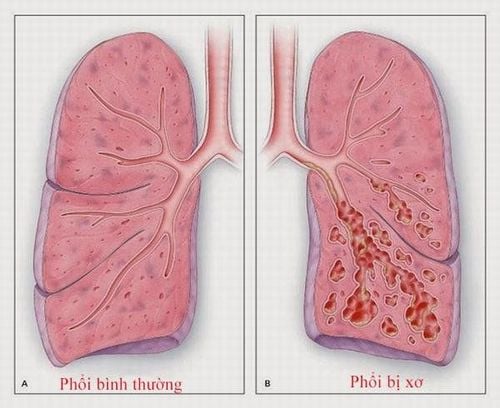
7. How is idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis treated?
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis does not have an optimal treatment, the main treatment is to control the symptoms:Use home oxygen therapy in case the symptoms get worse; Physical therapy/respiratory rehabilitation: This includes education about idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and some exercise; Quit smoking if you are smoking; Influenza and pneumococcal vaccines: Helps protect against infections that can become more serious if you have lung disease; Drug use: Two new drugs, nintedanib and pirfenidone, have been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Before these two new drugs were approved, corticosteroids and immunosuppressants were used to treat idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, but they often offered no benefit and could cause side effects such as high blood pressure. , diabetes, trouble sleeping, or osteoporosis... Other therapies may be recommended to treat symptoms or conditions arising from idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. These therapies include respiratory rehabilitation, oxygen therapy, and treatment of pulmonary hypertension. It's best to talk to your doctor about medications or other therapies that best suit your own needs. Lung transplant: is the only treatment to prolong life if you have idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Lung transplantation is a major surgery and requires lifelong treatment with immunosuppressive drugs to prevent rejection of the transplanted lung. Not all patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis are eligible for a lung transplant. Ask your doctor if you should be evaluated for a lung transplant. Evaluation for a lung transplant takes many months, so your doctor can start talking about a lung transplant with you before idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis becomes severe. No treatment: Treatment can cause side effects in some patients, so it should be considered. No treatment is usually advised for older patients with mild or not very severe symptoms. However, the patient's condition must be regularly monitored by a respiratory doctor.
8. Complications of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
Pulmonary fibrosis can get worse over time. Although you can get treatment to help control symptoms, scarring and damage to your lungs cannot be completely prevented. More dangerous, the disease can progress rapidly in some patients.When pulmonary fibrosis limits some functions of the lungs, the disease can cause serious complications such as heart failure, pneumonia, pulmonary embolism, pulmonary hypertension... In addition, it also causes symptoms get worse after a lung infection, heart failure, or pulmonary embolism.
To prevent pulmonary fibrosis, it is necessary to have a healthy lifestyle such as not smoking, losing weight, getting vaccinated, taking supplements, full vitamins.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.