This is an automatically translated article.
Hypovolemic shock is a sudden decrease in body fluid volume that causes reduced blood flow to the body's organs and systems and affects the functions and metabolic activities of these systems. this agency. Besides adults, hypovolemic shock in children can also occur and it is necessary to have the most appropriate first aid methods for children with hypovolemic shock.
1. Hypovolemic shock in children
Hypovolemic shock in children is a state of shock caused by decreased tissue perfusion in the body due to decreased intravascular volume. This condition is caused by loss of fluid volume or by a disorder that results in an inability to supply enough fluid to maintain basic life activities in the body. For cases that can compensate for the loss of fluid, the patient often has specific manifestations such as tachycardia, increased myocardial contractility, and importantly, the patient's blood pressure in these conditions. is still within normal limits.
However, for patients with hypovolemic shock with reduced blood pressure, at this time, the amount of fluid in the patient's body can be lost up to > 30%, so this is the late stage of hypovolemic shock in patients with hypovolemic shock. children, it is necessary to have quick and timely treatment measures for pediatric patients.
Hypovolemic shock in children has many causes, which are divided into 3 large groups as follows:
Causes of loss of intravascular fluid include:
Massive blood loss due to trauma or hemorrhage in one area. number of organs in the body. Drainage into the interstitial tissues Drainage into the third compartment in some diseases such as pancreatitis, small bowel obstruction, nephrotic syndrome or intussusception.
Có nhiều nguyên nhân gây ra tình trạng sốc giảm thể tích tuần hoàn ở trẻ
Causes of extravascular fluid loss include:
Vomiting a lot due to some diseases Loose stools leading to dehydration Symptoms of polyuria in some diseases such as hyperglycemia or diabetes insipidus. The patient is taking too much diuretics. Causes of invisible dehydration include:
Rapid breathing, high fever. Burns The patient is unable to eat or drink due to certain conditions such as inflammation of the oral mucosa or sore throat. Children with hypovolemic shock at diagnosis are nearsighted based on clinical symptoms as well as laboratory findings with diagnostic value:
Clinical symptoms:
Shock Hypoperfusion: At the stage The infant is usually stimulated in the early stages but still awake, the late stage of shock is often jittery, lethargic and leads to coma. Peripheral hypoperfusion: In the early stages, children often have signs of rapid, clear pulse, normal or slightly increased blood pressure, capillary filling time usually < 2s. At the late stage, the child begins to have a small, fast pulse, which is difficult to catch or even can't catch the child's pulse at this stage, the child's heart rate is fast, the skin and extremities are cold, the body sweats, time Capillary re-filling time is slower (>2s), blood pressure often drops, children have signs of oliguria or anuria in some cases. Central venous decrease (<5cm H2O) Subclinical symptoms:
Peripheral blood cytology test shows that Hb and Hct increase is a sign of hemoconcentration. Blood glucose may decrease in children with hypovolemic shock caused by gastroenteritis. Blood glucose is elevated with hypovolemic shock in children with severe burns and trauma or may be due to polyuria due to increased osmotic pressure in the body.
Thực hiện các xét nghiệm để phát hiện và đánh giá tình trạng sốc giảm thể tích tuần hoàn ở trẻ em
Electrolyte and blood gas measurement are also very valuable in diagnosing hypovolemic shock in children. Blood lactate elevation > 5 mmol/L in infants at risk of death. Coagulation testing can find some causes of bleeding leading to hypovolemia, such as thrombocytopenia hemorrhagic disease, liver failure or pediatric patients on anticoagulant therapy. Blood group testing for hemorrhagic shock. Test 10 urine parameters in patients with diabetes or diabetes insipidus. Some other routine tests such as chest X-ray, abdominal ultrasound, computed tomography scan to find out some causes of the disease
2. First aid for children with hypovolemic shock
First aid for children with hypovolemic shock has some basic features including:
Maintain the child's shock function according to the ABCs principle Prioritize replacement of lost circulating fluid and monitor the condition continuously fluid loss in children, adjustment of homeostasis. Treatment of the cause of hypovolemic shock in children. First aid for children with hypovolemic shock should initially be performed and ensure certain goals from time to time as follows:
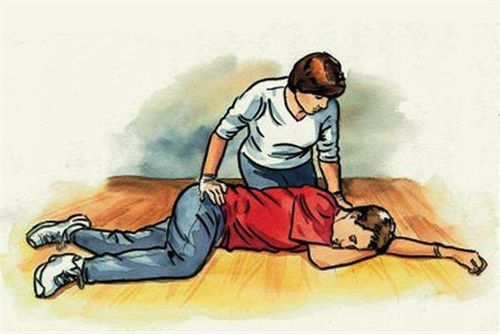
In the first hour, it is necessary to bring the child's pulse back to normal depending on the condition. According to the age of the disease, bring systolic blood pressure to >60 mmHg for infants younger than 1 month, and >70 mmHg + 2 x age for children aged 1 to 10, bring systolic blood pressure > 90 mmHg for children > 10 years old. Treatment in this phase should bring back capillary filling time < 2s, patient mental stability and urine output > 1ml/kg/h. In addition, the patient also needs to clear the airway, place a pillow under the shoulder and lie down with the head low. Pediatric patients need to be given oxygen at 5 – 10 l/min or intubated if necessary to support breathing, to avoid respiratory failure. Infusion of Ringerlactate or 0.9% sodium chloride solution reaches 20ml/kg over 5-15 minutes by peripheral intravenous route.
Cấp cứu trẻ bị sốc giảm thể tích tuần hoàn
After the initial phase, the next treatment for the pediatric patient is to continue infusion depending on the degree of hypovolemia as well as the amount of fluid being lost. To find some causes of shock for thorough treatment such as shock due to blood loss, it is necessary to transfuse red blood cells matching the blood group of the pediatric patient at a dose of 10ml/kg with adjustment of Hb > 10g% and Hct > 30%, Stop bleeding at the site of bleeding and possibly surgery in some specific cases. If shock is due to hypovolemic burns or increased vascular permeability, careful consideration should be given to the course of treatment because it is difficult to determine the exact amount of fluid lost. If arterial volume is reduced because of decreased oncotic pressure, then colloidal fluid should be infused in the pediatric patient. In summary, hypovolemic shock in children is an emergency due to a sudden decrease in body fluid volume, affecting the function and some vital activities of the body's organ systems. body. In the emergency of hypovolemic shock in children, in addition to the treatment and treatment of the cause, it is necessary to closely monitor the patient's signs to have a timely attitude to deal with complications due to the medical condition. caused by this. In case of emergency, parents should take the child to a reputable hospital for immediate examination and treatment. Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the leading prestigious hospitals in the country, trusted by a large number of patients for medical examination and treatment, not only equipped with modern and advanced equipment. nationally as well as in the region. The department has 6 ultrasound rooms, 4 DR X-ray rooms (1 full-axis machine, 1 brightener, 1 synthesizer and 1 mammography machine), 2 DR mobile X-ray machines, 2 cutting rooms. multi-row computer class with receiver (1 128-series and 1 16-series), 2 Magnetic Resonance imaging rooms (1 3 Tesla machine and 1 1.5 Tesla machine), 1 interventional angiography room with 2 planes and 1 room Measuring bone mineral density.... Vinmec is also the place to gather a team of experienced doctors and nurses who will greatly assist in the diagnosis and early detection of abnormal signs of the patient's body. The space is designed according to 5-star hotel standards, giving patients the most comfort, friendliness and peace of mind.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.